CDAP - Basic Dental Instruments
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Non-cutting instruments
mirrors, explorers, probes, condensers
cutting instruments
scalers, excavators, chisels, other
Excavators (types)
spoon excavator, black spoon
Chisels (types)
enamal hatchet, bin-angle chisel, gingival margin trimmer
Other (types)
Discoid-cleoid, hollenback carver
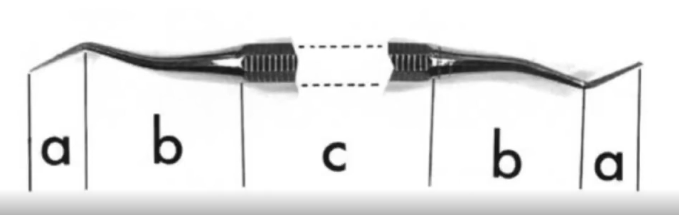
Three main regions of dental instruments
handle, shank, working end (blade and cutting edge or nib and face)
Dental mirror
Non-cutting instrument - An instrument used to reflect light and provide a view of areas in the mouth that are difficult to see, often used for indirect vision and to keep the mouth open.
Indirect vision
To look at oral structures using a dental mirror
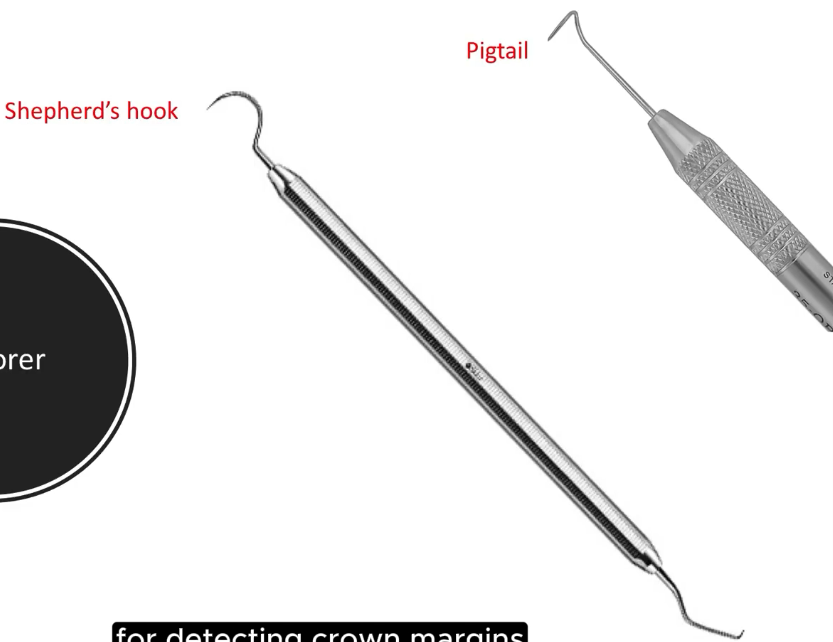
Explorer
Non-cutting instrument - A dental instrument used to detect cavities and tooth surfaces by using tacticle sensitivity.
Shepherds hook : curved end of explore (No.23)
No. 17 Explorer - flatter, shorter hook on the other end for interproximal areas between the teeth
UH3CH : curves under and around the teeth to detect crown margins
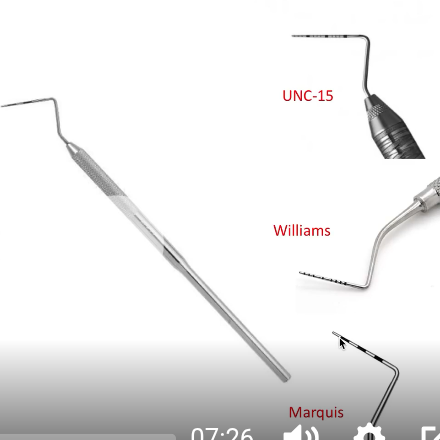

Periodontal probe
Non-cutting instrument - used to measure the pocket depth between gum and tooth to detect the presence of gum disease, width of teeth, amount of overbite
UNC-15 Probe: each line represents each mm to 15 mm
Williams Probe : 1 mm increments but leaves out 4 and 6 mm
Marquise Probe (3 mm increment)
Amalgam Condenser
Non-cutting instrument - Used to squish amalgam material into the depths of cavity preparation and composite material
The nib is the portion that comes into contact with the restorative material being condensed
The end of the nib is called the face which is smooth

Ball Burnisher
Non-cutting instrument - Used for burnishing or carving the surface of an amalgam filling, smooth out occlusal surface of a composite restoration
Two spherical ends or one spherical end with a football shape
Scalers —>
Responsible for removing calculus (hardened dental plaque)
Excavators —>
Responsible for cutting dentin
Chisels
Used for cutting enamel
Other —>
Used for restoration
Cutting instrument formula
This formula is used to classify dental cutting instruments based on their dimensions and design.
Blade width (10=1mm)
Cutting edge angle (omitted if perpendicular to blade)
Blade length (7=7mm)
Blade angle (14=14% of 360)
Scaler
Cutting instrument - Two sided instruments each with its own working end with two cutting edges that adapt closely to the tooth and remove plaque and debris (calculus)
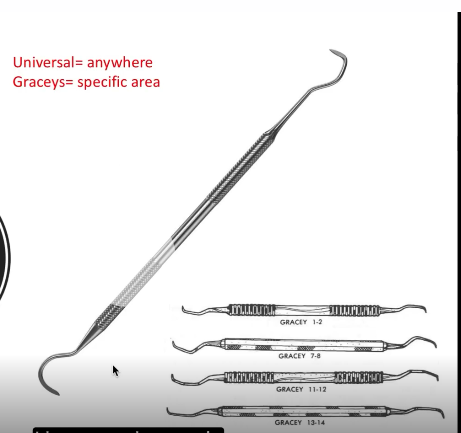
Universal
Anywhere
Graceys
specific area
Sickle scalers
Sharp points are used for surpagingival calculus
Curette
Rounded ends used for subgingival calculus
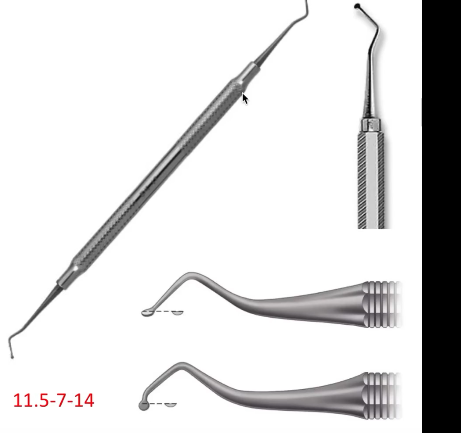
Spoon excavator
Cutting instrument - (11.5-7-14) Used for gentle and controlled carries removal to scrape dentin
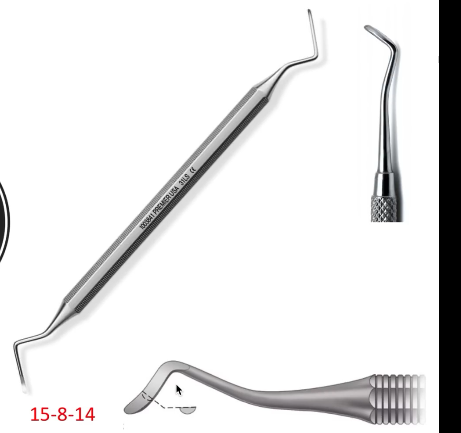

Black spoon
Cutting instrument - Larger more robust type of spoon excavator. Used to burnish metal with the rounded end or back side of the spoon
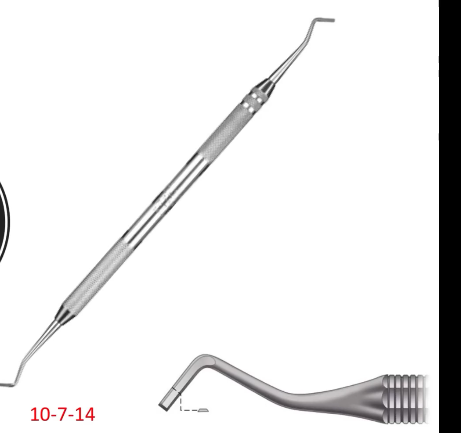
Enamal Hatchet
Cutting instrument - 10-7-14 Double ended cutting instrument used for planing walls of enamel. The bevel on one end planes the facial wall and the other planes the lingual wall
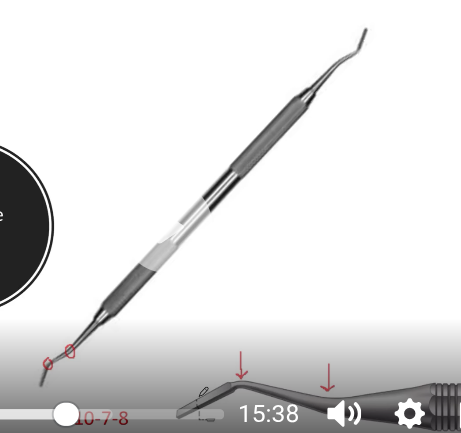
Bin-Angle Chisel
Cutting instrument - Double ended for planing walls of enamel. Bin angle because there are two angles in the shank of the instrumentused primarily for shaping and finishing enamel surfaces. Provide proper orientation and balance.The cutting edge is perpendicular to the blade.

Gingival Margin Trimmer
Cutting instrument - Designed for planning enamel for the gingivall floor of the prep. Tjhe cutting edge is not perpendicular to the blade.
If the number is less than 90 degrees, it’s used for the mesial side of the tooth
If it’s greater than 90 degrees, it’s used for the distal side of the tooth
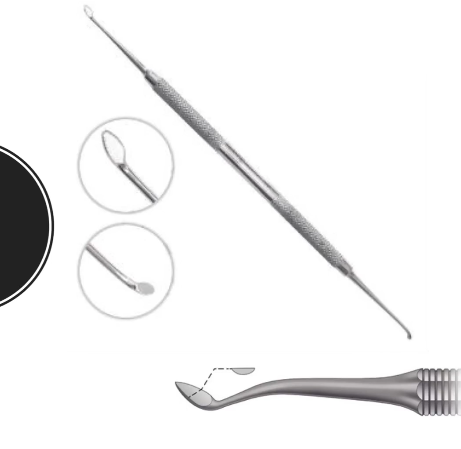
Discoid Cleoid Carver
Other - Double ended round handled instrument used for carving and contouring amalgam. The cleoid end is clawlike for carving grouves into the amalgam. The discoid is used for caving pits and fasa into the amalgam
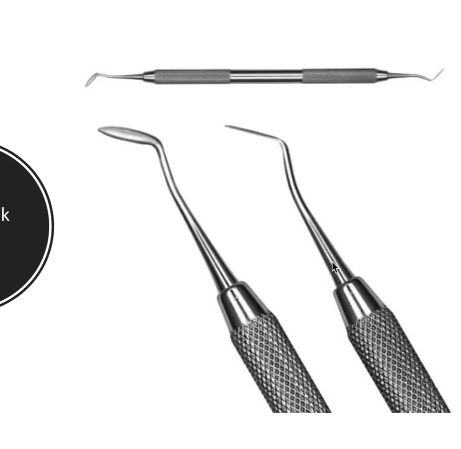
Hollenback Carver
Other- double ended round handled instruments used for placing, carving, and contouring amalgam. The two ends are oriented 90 degrees to one another
Instrument Grasp
Modified pen grasp - add the middle finger to grabbing the instrument and rests on your ring finger adding control, accuracy, and protection. Often used on the adjacent teeth, maxillary, and mandible if the patient is biting on a bite block
Low speed handpiece
A dental tool used for precision work, typically operates at less than 12,000 rpm, and is often employed for procedures like polishing, removing decay and refining tooth structure. Runs on air
Medium Speed handpiece
A dental instrument designed to operate between 12,000 and 200,000 rpm, used for various restorative procedures and cutting tasks.
High speed handpiece
A dental tool that operates above 200,000 rpm, used with a bur to cut a cavity/crown prep. Runs on air pressure
RPM
Revolutions per minute
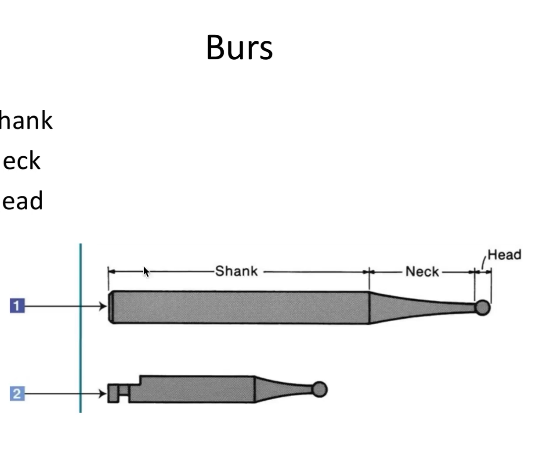
Burs
Small rotating instruments used with handpieces for cutting, shaping, or finishing dental tissue. It’s inserted in high speed or low speed handpiece to cut, polish, or fin
Shank
Neck
Head
Carbide Bur
A type of bur made from tungsten carbide, known for better end-cutting and producing lower heat for amalgam removal
Diamond bur
A dental bur made with diamond particles, better for side cutting, produce higher heat, greater hardness, and used for crown preparations, beral, and enamalplasty
Cotton Pliers
Used to remove cotton holders during procedures
Forceps
A dental instrument used for grasping, holding, and extracting teeth or tissue during oral procedures.
Cotton rolls
To isolate teeth and absorb saliva, act as a protective tissue barrier
Sickle Scaler
Remove large amounts of deposit from supragingival surfaces
Maxillary Universal Forceps
A type of bird beak forceps used to extract maxillary, central, laterals, cuspids, premolars, and roots. Usually has straight handles or one curved
Maxillary right forceps
Extract trifurcated maxillary first or second molars. Usually has right split beak to engage in lingual root
Trifurcated maxillary teeth
Upper molars with three roots instead of one or two that provide stability and support during extraction.
Maxillary left forceps
Extract trifurcated maxillary left first or second molars. Has left split beak to lingual root
Mandibular universal forceps
To extract mandibular central, laterals, cuspids, premolars, roots. Usually is straight handled or one curved
Mandibular molars (cowhorn) forceps
Used to extract mandibular first and second molars. Referred to cowhorn forceps, usually straight or one curved (2)
Air water syringe
to rinse and dry specific teeth or entire oral cavity. Three way: air, water, or spray with water and air. Syringe tip: disposable plastic or autoclavable metal which attaches to air water syring eon dental unit
Used for fillings
chisels, hoes, dental drills, and hatchets while scalers and curettes remove decay
Used for Extractions
elevators, forceps, and surgical curettes
Restorative instruments
excavator, rotary instruments, burnishers, carvers, dental burst
Elevators
used in tooth extractions to loosen the tooth from its socket by enlarging it