Biology Chapter 5
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
how many valence electrons does carbon have?
four
how many valence electrons does oxygen have?
six
how many valence electrons does nitrogen have?
five
how many covalent bonds does carbon form?
four
how many covalent bonds does oxygen form?
two
What are the four macromolecules?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Protein, Nucleic Acids
how many covalent bonds does nitrogen form?
three
water is a _____________ molecule
polar
carbohydrates are _____________ molecules
polar
lipids are _________________ molecules
nonpolar
thing being dissolved
solute
thing doing the dissolving
solvent
polar solutes are dissolved by ______________ solvents
polar
nonpolar solutes are dissolved by ________________ solvents
nonpolar
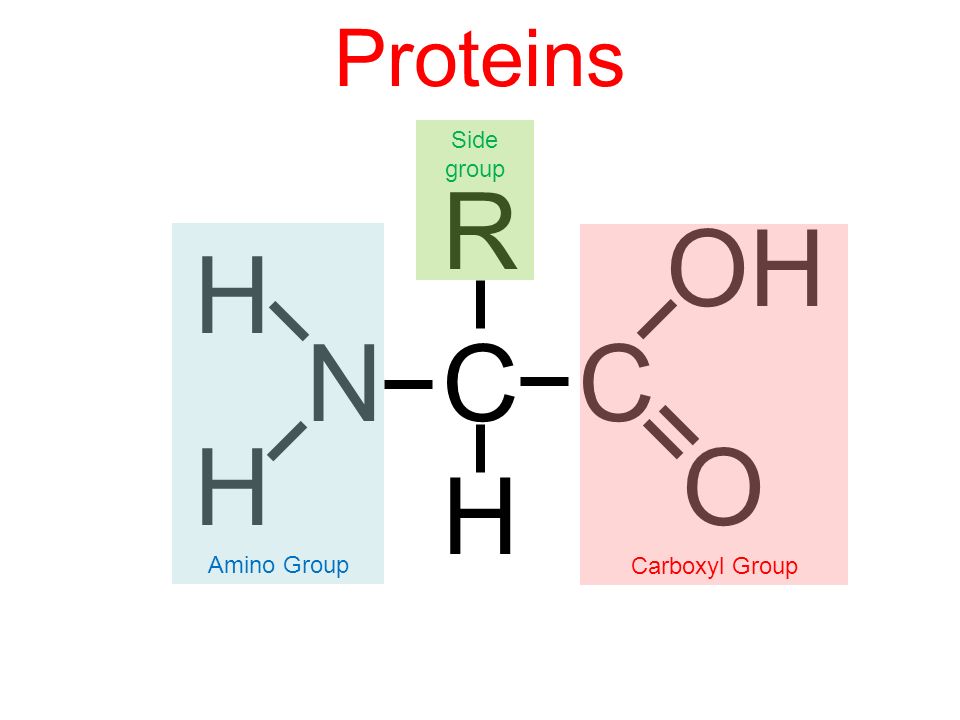
R group bonded to a C with OH and H (amino acid)
carboxyl
carboxyl groups are ________________
acidic
acids are proton ______________
donors
bases are proton ________________
acceptors
NH2
amino group
Amino groups are ____________.
basic
monomer (protein)
amino acid
monomer (carbohydrate)
monosaccharide
monomer (nucleic acid)
nucleotide
A strand of amino acids is called a _____________.
polypeptide
type of bond between two amino acids
peptide bond
monomer (triglyceride)
fatty acids
polymer (protein)
protein
polymer (carbohydrate)
polysaccharide and disaccharide
polymer (nucleic acid)
DNA and RNA
Types of Lipids
Tryglycerides, Phospholipids, Steroids
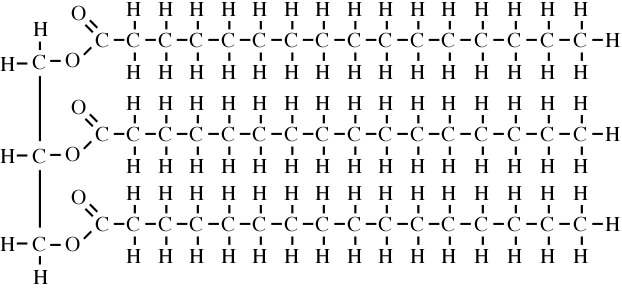
Fat for energy storage.
Triglycerides
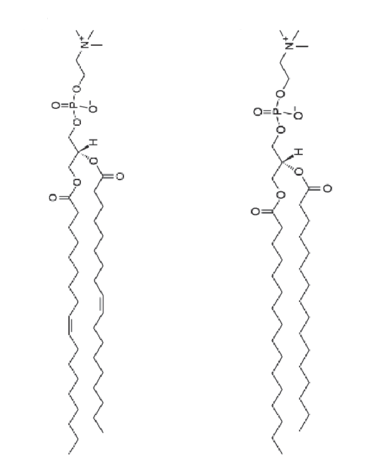
Type of lipid that forms cell membranes.
Phospholipids
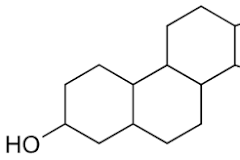
Involve hormones and structural functions.
Steroids
Which Lipid does this describe?
2 Fatty Acids + Phosphate + R group
Phospholipid
Which Lipid does this describe?
4-Carbon Ring
Steroid
Which Lipid does this describe?
Glycerol + Fatty Acids
Triglyceride
______________________ reaction (also called dehydration synthesis): joining monomers by pulling out water.
condensation
condensation reactions are ______________________
endothermic
______________________ reaction: separating monomers by putting water in
hydrolysis
hydrolysis reactions are ____________________________
exothermic
list the groups in an amino acid.
amino group, carboxyl group, R side chain group
the protein structure where a single chain of amino acids are bonded to each other (carboxyl to amine group) with covalent bonds.
primary
the protein structure where carboxyl and amino groups from the opposite sides of a chain interact and form α helices and β pleated sheets.
secondary
the protein structure where r groups forming hydrogen, disulfide, hydrophobic, and ionic bonds causes the amino acid chain to bend and fold.
tertiary
in tertiary structure, polar r groups interact with polar r groups, non polar r groups with nonpolar r groups. What is this an example of?
like interacts with like
the protein structure where multiple proteins in tertiary structure join via hydrogen bonding.
quaternary
Formula for Carbohydrates
(CH2O) n
This monomer is the primary metabolic fuel (glucose, galactose, fructose).
monosaccharide
polymer consisting of two monosaccharides, not stored. (ie: sucrose = 1 glucose + 1 fructose)
disaccharide
glucose + galactose =
lactose
glucose + fructose =
sucrose
glucose + glucose =
maltose
polymer consisting of more than two monosaccharides, stored. (starch, cellulose, glycogen)
polysaccharide
A condensation reaction between two monosaccharides molecules creates a ___________ _____________?
glycosidic linkage
Storage carbohydrates typically found in plant cells.
starch, cellulose
In which plastid in a plant cell is starch stored?
Amyloplasts
membrane-bound organelles that perform various functions essential to the cell's metabolism and health. (chloroplasts, chromoplasts, amyloplasts)
plastid
Where in a plant’s cell wall is cellulose stored?
microfibril
Storage carbohydrate found in the liver and muscles.
Glycogen
_________________ fatty acids have more hydrogen and no double bonds.
saturated
___________________ fatty acids have less hydrogen and therefore more double bonds.
unsaturated
3 fatty acids attached to a glycerol
triglyceride
lipid that looks like a carbohydrate
steroid
lipids are ____________________ because they are _________________.
hydrophobic, nonpolar
orientation of nucleotide base sequence
5' to 3'
Adenine pairs with
thymine
Guanine pairs with
cytosine
base pairs bond to each other via ______________ bonds
hydrogen
structure determines ___________
function
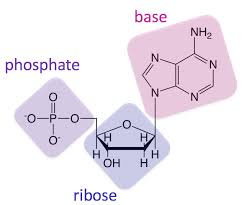
Components of a nucleic acid.
ribose sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
List the 4 nitrogenous bases in DNA
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
Which bases are considered purines?
Adenine, Guanine
Which nitrogenous base is unique to RNA
Uracil
Which bases are considered pryimidines?
Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil
Which base pairing is stronger because it’s formed with a triple bond.
Guanine and Cytosine
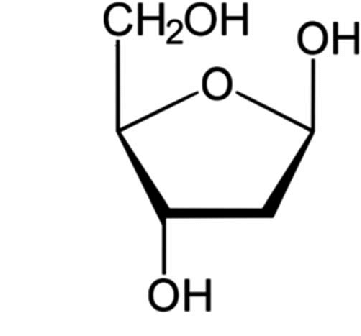
Which sugar is this?
Deoxyribose
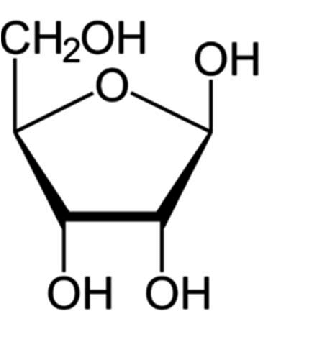
Which sugar is this?
Ribose
DNA: _________ stranded, contains deoxyribose sugar, bases A, T, C, G
RNA: ________ stranded, contains ribose sugar, bases A, U, C, G
Double, Single
orientation of phosphodiester bonds in a nucleotide.
3’ to 5’
What macromolecule is being described?
Antiparallel strands held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases (A-T, C-G)
DNA
A single chromosome typically contains how many strands of DNA that are wound together to form a double helix?
Two
The basic function of which macromolecule is to store genetic information for direct synthesis of proteins?
Nucleic Acid