LGN
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
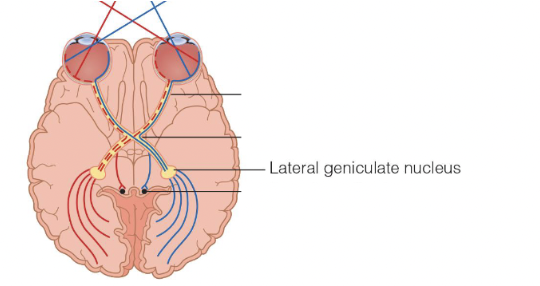
What does LGN stand for
Lateral Geniculate nucleus
there are two! (yellow dots)
LGN visual field
The LGN on the left is responsible for processing from the right visual field and LGN on the right is responsible for processing the left visual field.
primary function of the LGN in visual processing
LGN regulates neural information from the retina before sending it to the visual cortex (V1)
How do LGN cells process visual information
LGN cells have center-surround receptive fields, similar to the retina, which help filter and refine incoming signals.
Does the LGN pass all incoming signals to the cortex?
No, the LGN reduces incoming information, often sending fewer signals to the cortex than it receives from the retina.
Where does the LGN receive information from?
The LGN receives input from the retina, cortex, brainstem, and thalamus, with most input coming from the cortex (top down input)
Is processing in the LGN unidirectional?
No, signals can loop back to the LGN after being processed in higher brain areas, allowing for feedback.
Does each LGN receive input from one or both eyes?
Each LGN receives input from both eyes, but processes them in separate layers.
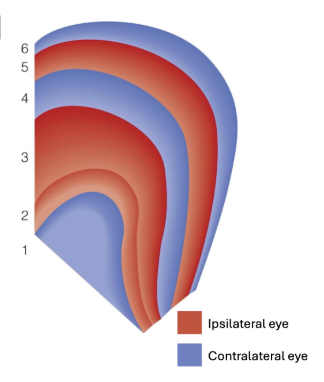
Which LGN layers receive input from the contralateral eye?
Layers 1, 4, and 6

Which LGN layers receive input from the ipsilateral eye?
Layers 2, 3, and 5 receive input from the ipsilateral eye
What is a helpful mnemonic to remember the layer organization in the LGN?
"See I? I see, I see." → C I I C I C
(Layers: 1 = C, 2 = I, 3 = I, 4 = C, 5 = I, 6 = C)
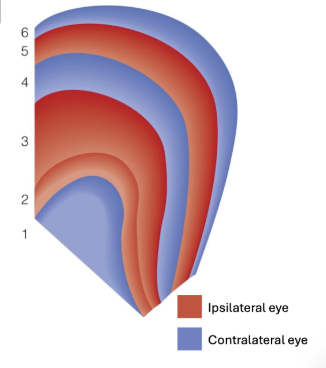
Does each LGN get information from both eyes or just one?
Each LGN gets input from both eyes, but it only processes information for the contralateral visual field.
The right LGN processes the left visual field.
The left LGN processes the right visual field.
Since both eyes see part of both visual fields, each LGN must receive input from both eyes to fully represent its contralateral visual field.
What are the two main types of cells in the LGN?
Magnocellular cells (M-cells) and Parvocellular cells (P-cells).
Which LGN layers contain magnocellular cells?
Layers 1 and 2.
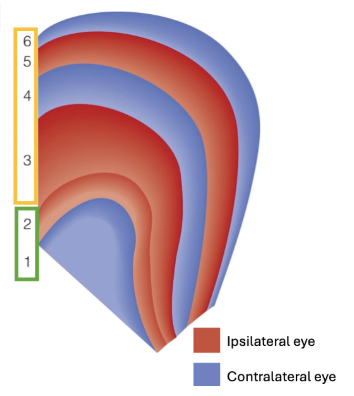
Which LGN layers contain parvocellular cells?
Layers 3 to 6.

What type of ganglion cells provide input to magnocellular cells?
M-type ganglion cells.
What type of ganglion cells provide input to parvocellular cells?
P-type ganglion cells.
How do magnocellular cells process visual information?
Larger receptive fields
Fast processing
Detects form, movement, depth, and brightness differences
Input mostly from peripheral vision
How do parvocellular cells process visual information?
Smaller receptive fields
Slow processing
Detects color and fine details
Input mostly from central vision (fovea)
Summary of organzation in LGN
What is a retinotopic map in the LGN?
A mapping where each location on the retina corresponds to a specific location on the LGN.
How is a retinotopic map determined?
By recording from LGN neurons while stimulating their receptive fields on the retina.
What happens when two objects are near each other on the retina?
Their signals are processed near each other in the LGN.
How does the receptive field organization change as we go side to side vs. deeper into the LGN?
Side to side: Different locations are processed.
Deeper: Overlapping receptive fields appear across different LGN layers.
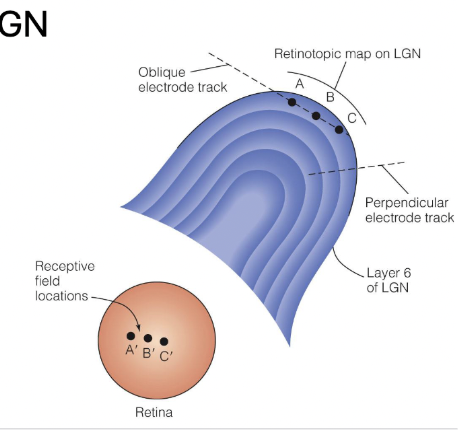
What does it mean that receptive fields overlap in deeper LGN layers?
The same retinal location is represented multiple times across different LGN layers.