Lecture 2: Intro to Eukaryotes
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Domain of Life - Eukarya
Branched off from Archaea, uni and multicellular organisms, and less than prokaryotes but have larger size
Eukaryotes Characteristics
Highly diverse: Structurally & functionally complex, larger size and genome, nucleus w. membrane, and membrane bound organelles
Endosymbiosis
How eukaryotes evolved from archaea from engulfing bacteria
Endosymbiosis evidence
Similar size, 70s ribosomes, small circular dna genome, phospholipid bilayer, and ability to replicate by binary fission
Mitochondria origin
an engulfed nonphotosynthetic bacteria
Chloroplast origin
an engulfed photosynthetic bacteria
Eukaryote Kingdoms: 4 branches
Fungi, plant, protists, and animals
Phylogenetic tree
Non-membrane Enclosed Structures
Ribosomes and cytoskeleton
80S ribosomes found
cytoplasm and rough ER
70S ribosomes found
mitochondria and chloroplasts
Membrane-bound Organelles
Nucleus, endomembrane system (ER, golgi apparatus, vesicles and vacuoles), and mitochrondria
Nucleus
Houses DNA genome within nucleoplasm with multiple linear chromosomes and chromatin (histone)
Nucleolus
dense region of rRNA biosynthesis; ribosome assembly begins that’s enclosed in nuclear envelope that contains nuclear pores to control traffic of materials
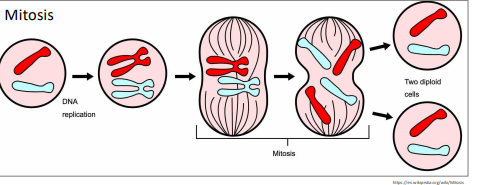
Mitosis – Asexual replication
1 parent cell divides into 2 genetically identical daughter cell clones → 1 division

Meiosis - Sexual reproduction
2 cell division stages, 1 parent cell produces 4 genetically distinct haploid gametes (homologous)
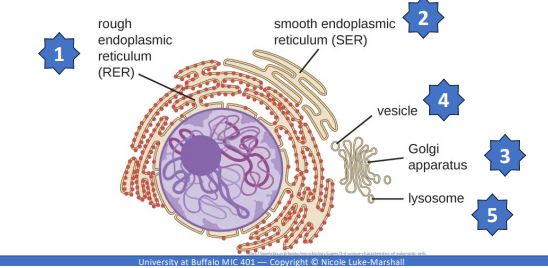
Endomembrane System - EMS
Cell size is big so it needs a cellular transport system of membranous tubules, sacs, and flattened disks (cisternae), and organelles and connections b/t them
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Interconnected array of cisternae and tubules originated from nuclear envelope, and can be rough or smooth ER
Cisternae
flattened, membrane-bound sacs that are used in golgi apparatus and rough ER
Rough ER - Cisternae
Contains ribosomes that buds off in vesicles transported to golgi apparatus for further processing to membrane, another organelle, or out of cell
Smooth ER - Tubules
No ribosomes and involved in biosynthesis of lipids, carbohydrates metabolism, and detoxification of toxic compounds
Golgi apparatus
Arrays of cisternae that contains modified lipids and proteins of transported from the ER
Golgi apparatus: enzymes
Produces glycolipids, glycoproteins, or proteoglycans
Golgi apparatus: Sorts and distributes
Transport vesicles containing products pinch off and move to and fuse with cell/organelle membranes
Golgi apparatus: Cell surface significance
Distinguishes types of cell types, role in cell recognition, and serves as cell surface receptors

Vesicles
Small fluid filled lipid bilayer enclosed sacs needed for cell survival for transport, secretion, digest, and sequester materials
Vesicles functions
Transports materials within cells ‘shipping containers’
Secretory- stores and traffic to cell surface for exocytosis
Vacuoles
Larger than vesicles and are often used for storage
Degradative Vesicles
cellular compartments that break down waste and damaged components
Lysosomes and Peroxisomes
Lysosomes
Cellular garbage disposals b/c its a digestive enzymes that breaks down particles and is compartmentalized
Peroxisomes
Oxidative degradation by enzymatically degrading fats, amino acids, toxins by metabolizing oxygen containing waste
Protects cells from toxic oxygen intermediates
Mitochondria Charcteristics
Double membrane, 70s ribosomes, circular chromosomes from endosymbiosis
Mitochondria Function
Generates energy for cell by producing ATP, amino acids, vitamins and carrying out apoptosis
External Eukaryotic Cell Structures
Plasma membrane, glycocalyx, cell wall, ECM, flagella, and cilia
Plasma membrane
Phospholipids bilayer cell membrane, peripheral and integral proteins, fluid mosaic, selective, and contains sterols
Membrane Transport Mechanisms
Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport
Unique to eukarya – endocytosis and exocytosis
Glycocalyx
Sticky, polysaccharide gel coating extracellular surface of the PM
Role in protections, interactions, adhesion, and association with other macromolecules
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
Helps maintain shape, provide structural stability, transmits signals and produced animal and some protist cells (cells lacking cell walls)
Extracellular Matrix (ECM): Secretions
Secretes mass of carbohydrates and proteins
Proteoglycans form bulky mass of ECM, collages, and fibronectin
Cell wall found
only in eukaryotes that lack ECM which is fungi and some protists
Cell wall function
Rigid, structural layer that helps maintain cell shape and protects against desiccation, mechanical and osmotic stress
Cell wall compositions
Fungi – chitin, glucans, &/or proteins
Protists – cellulose or glycoproteins
Motile structures: Cilia and Flagella
Membrane covered hairlike structures projecting out from cell surface composed of microtubules and connected to body
Flagella
Less numerous and longer tail-like
Cilia
Numerous, shorter and coordinated movement
Parasites
organism that lives on or in a host organism and obtains food from or at the expense of its host
3 Main classes associated with human disease
3 Main classes of parasites
Protozoa (unicellular), helminths, and ectoparasites
Protozoa and helminths are endoparasites
Protista
Highly diverse group of eukaryotes
Pathogenic protists → Parasitic protozoans “first animals” (no cell wall)
Parasitic protozoans
Many have 2-phase life cycles, alternating between proliferative stages (e.g., trophozoites) and resting cysts (survive harsh conditions)
-Portion of life cycle occurs w/in host
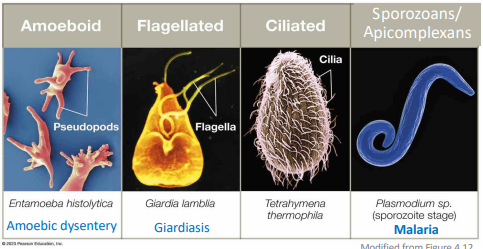
Parasitic protozoans Categorized
based on motility and morphology into 4 types:
Amoeboid, flagellated, ciliated, and sporozoans/apicomplexans
Animalia Endoparasites: Helminths
Microscopic aspects of life cycle → identified by microscopic eggs and larvae
287 species of multicellular parasites can infect and live within human body
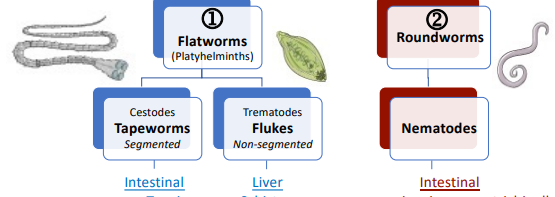
Helminths 2 main categories
Flatworms and roundworms
Animals ectoparasites
Some pathogenic microbes require arthropod vectors for part of life cycle, biting insects are important vectors as most feed on blood
Animals ectoparasites: Mosquitos
Causes malaria
Animals ectoparasites: Ticks
Causes lyme disease and Rocky Mt Spotted fever
Animals ectoparasites: Fleas
Causes plague and typhus
Mycology
the study of fungi
Fungi: Cell wall
Contains chitin and cell membrane contains ergosterols
Fungi: Growth
Typically grow slower than bacteria and at lower temperature & pH
Fungi: Reproduction
Unique and complex lifecycles involving asexual and sexual reproduction
Fungi: Life forms
Grow as yeast (microscopic) or mold (macroscopic) or both (dimorphic)
Multicellular Fungal characteristics: Mold
Multicellular form with tubular filaments termed hyphae
Septate hyphae, nonseptate hyphae, and mycelia
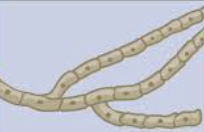
Septate hyphae
walls between the cells
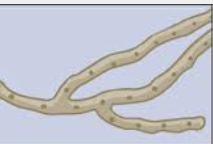
Nonseptate hyphae
lack separation between the cells
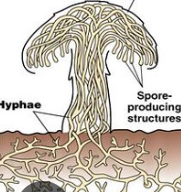
Mycelia
macroscopically visible intertwined mass of hyphae (fuzzy appearance)
Fungal characteristics: Reproduction
Reproduce by producing large numbers of spores, it is asexual (by mitosis) or sexual (by meiosis); many species can produce both types
Unicellular Fungal characteristics: Yeast
5-10x larger than bacteria and daughter cells that remain attached to parent for pseudohyphae
Yeast Reproduction
Reproduce asexually by budding off daughter cells; sexually by meiosis
Yeast: Dimorphic
change between yeast and mold forms in response to environmental changes (nutrient availability or fluctuations in temperature
Mold = cold, yeast =heat
Mycoses
Diseases caused by fungal infection
Few are serious pathogens – human body temperature a major deterrent
Superficial mycoses
infect skin & nails (tinea), mouth & vagina (candida)
Invasive, systemic mycoses
Widespread, involve internal organs, lethal
True pathogens and Opportunistic pathogens