Biology - Movement into and out of cells
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
1
New cards
Active transport
The movement of particles through a cell membrane from a region of their lower concentration to a region of higher concentration (i.e. against a concentration gradient), using energy from respiration
2
New cards
Diffusion
The net movement of particles from a region of their higher concentration to a region of lower concentration (i.e. down a concentration gradient), as a result of their random movementOsmosis
3
New cards
Osmosis
The net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential (dilute solution) to a region of lower water potential (concentrated solution) through a partially permeable membrane
4
New cards
Examples of diffusion in living organisms
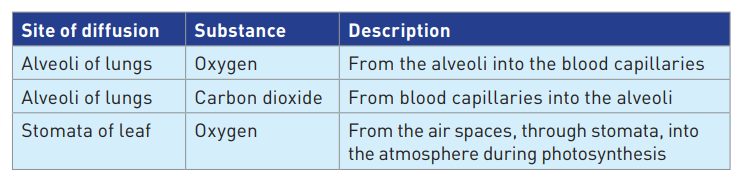
5
New cards
Rates of diffusion
* distance (the shorter the better), for example the thin walls of alveoli and capillaries
* concentration gradient (the bigger the better); this can be maintained by removing the substance as it passes across the diffusion surface (think about oxygenated blood being carried away from the surface of alveoli)
* surface area for diffusion (the larger the better), for example there are millions of alveoli in a lung, giving a huge surface area for the diffusion of oxygen
* temperature (molecules have more kinetic energy at higher temperatures)
(Do not confuse cell walls with capillary walls – animal cells do not have walls.)
* concentration gradient (the bigger the better); this can be maintained by removing the substance as it passes across the diffusion surface (think about oxygenated blood being carried away from the surface of alveoli)
* surface area for diffusion (the larger the better), for example there are millions of alveoli in a lung, giving a huge surface area for the diffusion of oxygen
* temperature (molecules have more kinetic energy at higher temperatures)
(Do not confuse cell walls with capillary walls – animal cells do not have walls.)
6
New cards
water is essential for the following processes:
Digestion – water helps to break down and dissolve food molecules in the process of digestion.
\
Transport – blood is made up of cells and a water-based liquid called plasma. The plasma is a way of transporting many dissolved substances, for example carbon dioxide, urea, glucose and hormones.
\
Excretion – water is important in the process of excretion in animals because some of the excretory materials, for example urea, are toxic. Water dilutes these to make them less poisonous. Urine is a solution containing dissolved mineral ions, urea, used hormones and drugs.
\
Transport – blood is made up of cells and a water-based liquid called plasma. The plasma is a way of transporting many dissolved substances, for example carbon dioxide, urea, glucose and hormones.
\
Excretion – water is important in the process of excretion in animals because some of the excretory materials, for example urea, are toxic. Water dilutes these to make them less poisonous. Urine is a solution containing dissolved mineral ions, urea, used hormones and drugs.
7
New cards
Effects of osmosis on plant and animal tissues
* When placed in water, plant cells will take in the water through their cell membranes because there is a higher water potential outside the cells than inside.
* Plant cells become turgid (swollen), but do not burst because of their tough cell wall. A turgor pressure is created, which will restrict any further entry of water into the cell.
* Animal cells will burst because they have no cell wall.
* Plant cells become turgid (swollen), but do not burst because of their tough cell wall. A turgor pressure is created, which will restrict any further entry of water into the cell.
* The reverse happens when plant cells are placed in concentrated sugar or salt solutions. This is because there is a higher water potential inside the cell than outside it.
* Plant cells become flaccid (limp) and the cytoplasm is no longer pressed against the cell wall. The process of water loss from a cell when it is placed in a solution with a lower water potential is called plasmolysis.
* Plant cells become turgid (swollen), but do not burst because of their tough cell wall. A turgor pressure is created, which will restrict any further entry of water into the cell.
* Animal cells will burst because they have no cell wall.
* Plant cells become turgid (swollen), but do not burst because of their tough cell wall. A turgor pressure is created, which will restrict any further entry of water into the cell.
* The reverse happens when plant cells are placed in concentrated sugar or salt solutions. This is because there is a higher water potential inside the cell than outside it.
* Plant cells become flaccid (limp) and the cytoplasm is no longer pressed against the cell wall. The process of water loss from a cell when it is placed in a solution with a lower water potential is called plasmolysis.
8
New cards
Water potential
The term water potential means the potential for water to move. Water always moves from a higher water potential to a lower water potential.
A weak (dilute) solution (or pure water) has a high water potential; a strong (concentrated) solution has a low water potential.
A weak (dilute) solution (or pure water) has a high water potential; a strong (concentrated) solution has a low water potential.
9
New cards
Active transport
However, cells need to provide energy to achieve movement by active transport. This energy is supplied through respiration. Mitochondria (cell organelles in the cytoplasm) control energy release. Respiratory poisons block energy release, so they can prevent active transport.
\
Protein molecules, called carriers, in the cell membrane play an important part in moving particles across the membrane. The protein uses energy to move the particles against their concentration gradient.
\
Protein molecules, called carriers, in the cell membrane play an important part in moving particles across the membrane. The protein uses energy to move the particles against their concentration gradient.
10
New cards
Examples of active transport in living organism
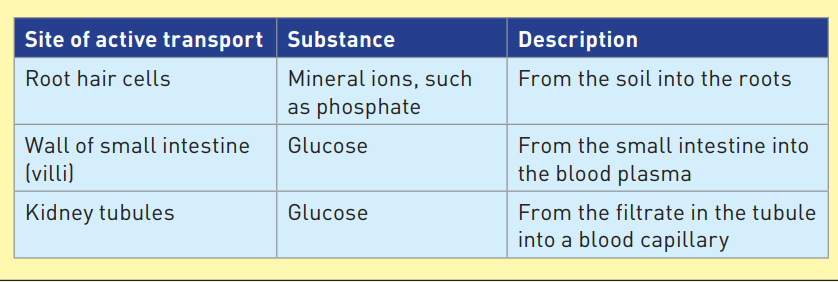
11
New cards

