Properties and Reactions of Alkenes
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts and reactions related to alkenes, including their properties, stereoisomerism, addition reactions, and environmental considerations.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What are alkenes and cycloalkenes?
Unsaturated hydrocarbons with at least one carbon-carbon double bond.
What is the general formula for alkenes?
CnH2n.
Why are alkenes susceptible to electrophiles?
The carbon-carbon double bond has high electron density.
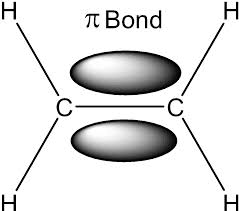
What types of bonds are present in a carbon-carbon double bond in alkenes?
A normal covalent σ bond and a π bond.
What is the bond angle around carbon in an alkene? and the shape of it
120° and tetrahedral
What color change occurs in bromine water when alkenes are present?
From orange-brown to colorless.
What is E-Z isomerism?
A type of stereoisomerism due to limited rotation around a double carbon bond due to the pie bonds.
In E-Z isomerism, what does the E isomer signify?
Higher priority groups are on opposite sides.
In E-Z isomerism, what does the Z isomer signify?
Higher priority groups are on the same side.
What are addition reactions in alkenes?
Reactions where the double bond opens to form single bonds with other atoms.
What is required for the hydrogenation of alkenes?
A nickel catalyst.
What forms when alkenes react with halogens?
Haloalkanes (di-substituted or mono-substituted depending on the halogen reaction).
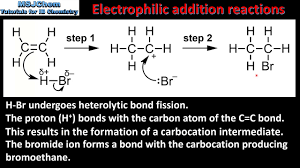
What is the mechanism for electrophilic addition?
Electrophiles attack the double bond, forming a carbocation intermediate.
What is the most stable type of carbocation?
Tertiary carbocation.
What are addition polymers? and how would you draw an additional polymer? ( repeating units)
Polymers produced from short-chain alkenes that join together to form long chains.
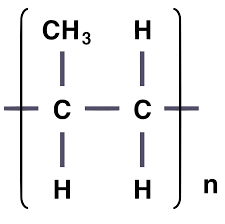
What is a major environmental concern regarding addition polymers?
They are non-biodegradable.
What toxic byproducts can be released from the combustion of haloalkanes? And why is this bad?
Hydrochloric acid (HCl).
Toxic gas released during the disposal by combustion.
What are some alternatives to handling waste polymers?
Recycling, organic feedstock use, or combustion for energy.
What effort is being made to address plastic waste?
Development of biodegradable and photodegradable polymers.
When adding Bromine to the Alkenes?
Bromine forms bonds to the Carbon bonds, removing the c=c bond, causing it to be saturated.
What does the pie bonds do around the Carbon bonds?
It restricted rotation.
Why does Stereoisomer occur?
due to the limited rotation around the double bond.
What is Electrophiles
They are electron par acceptors and are attracted to areas of high electron density.
Name all of the common Electrophiles?
HBr
Br2
H2SO4
What is Electrophillic addition?
Electrophilic addition is the reaction mechanism that shows how electrophiles attack the double bond in alkene.
show an electrophillic addition of c2h4 with H-Br?
last product is major
How are polymers made and where is it obtained?
Polymers are made from alkenes which are obtained from Crude oil, non-renewable resource.
One negative when it comes to the disposal of Polymers?
non-biodegradable.