FIU Bio 1 Test
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
positive control
known response is expected
negative control
no response is expected
theory
an accepted general principle or body of knowledge
inductive reasoning
logic flows in the opposite direction from the specific to the general
analogous/homoplasy vs homology
homologous: same evolutionary origin, difference in structure and function
analogous: similar function but different evolutionary origin
what did darwin use as his evidence of natural selection
his observation that although every organism has the potential to produce more offspring than can survive, only a limited number actually do survive and produce further offspring. Also his observations of the finches on the galapagos islands: they differed in their beaks and feeding habits, so he concluded that the different shapes of their bills represented evolutionary adaptations that improved their ability to eat the foods available in their specific habitat. He also observed that the traits of offspring could be changed by artificial selection.
what do we use as proof of natural selection
the discovery of other fossils provide comparative anatomy and molecular evidence
know all cell parts + what they look like + functions
peroxisome: contains enzymes involved in the oxidation of fatty acids. contain digestive and detoxifying enzymes that produce hydrogen peroxide as a by product
plasma membrane: regulates what comes in and out of the cell
nucleus: instructions for protein synthesis and cell reproduction; contains genetic information
chromosomes: contain hereditary information used to direct synthesis of proteins
nucleolis: synthesis of rRNA and ribosome assembly
ribosomes: site of protein synthesis
endoplasmic reticulum: forms transport vesicles, participates in lipid synthesis and synthesis of membrane or secreted proteins
golgi apparatus: packages proteins for export from cells
lysosomes: digest worn out organelles and cell debris
microbodies: isolate particular chemical activities from rest of cell
mitochondria: power plants of the cell; site of oxidative metabolism
chloroplasts: site of photosynthesis
cytoskeleton: structural support; cell movement and movement of vesicles
flagella: motility or moving fluids over surfaces
cell wall: protection, support
what is an isotope
atoms of a single element that possess different numbers of neutrons
atomic number
number of protons
know the functional groups
just be able to recognize alcohol, carbonyl, carboxyl, amine, sulfide, phosphate and methyl
uniport, symport, antiport
uniport: carrier proteins that transport a single type of molecule
symport: carrier proteins that transport two molecules in the same direction
antiport: transport two molecules in opposite direction
coupled transport
molecules are transported across a membrane against their concentration gradient by the cotransport of sodium ions or protons down their concentration gradient
inter, intra, between, among
inter: between
intra: within
between: two
among: more
five prime three prime
the terminal 5' Carbon of the growing strand adds to the 3' carbon of the new molecule
hydrolysis + dehydration synthesis
dehydration synthesis: formation of large molecules by the removal of water (monomers are joined to form polymers)
hydrolysis: breakdown of large molecules by the addition of water (polymers are broken down to monomers)
ligand
signaling molecule
receptor
molecule to which the receptor binds
monomer of a carbohydrate
monosaccharides
monomer of DNA
nucleotides
monomer of a fat (lipid)
fatty acids and glycerol
monomer of a protein
amino acids
amino attaches to
carboxyl
triglyceride is composed of
three fatty acids attached to one glycerol
endosymbiosis theory
proposal that eukaryotic organelles evolved through a symbiotic relationship; one cell engulfed a second cell and a symbiotic relationship was developed; mitochondria and chloroplasts are thought to have evolved this way
cis and trans
receives material for processing in transport vehicles on the cis face and sends material packaged in transport or secretory vesicles off the trans face
which organelles have their own dna besides the nucleus
mitochondria and chloroplasts
hyper vs hypo vs iso
isotonic: two solutions have the same osmotic concentration
hypertonic: solution outside of cell has a lower water concentration so water moves outside the cell
hypotonic: solution outside of cell has a higher water concentration so water moves into the cell
what is needed for natural selection to occur
variation, increased reproductive success
saturated vs unsaturated
saturated fats make the membrane less fluid (they pack together well); unsaturated fats make the membrane more fluid (the kinks from double bonds keep them from packing together)
osmosis
water diffuses through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of high concentration of water to an area of low concentration of water
diffusion
a net movement of substances from regions of high concentrations to regions of low concentrations (move with concentration gradient)
facilitated diffusion
diffusion mediated by a membrane protein
active transport
requires energy and the use of highly selective carrier proteins (move against concentration gradient)
phagocytosis
process in which the material the cell takes in is made up of discrete particles; particle is engulfed by membrane which folds around it and forms a vesicle
sodium potassium pump
Direct use of ATP for active transport; uses an antiporter to move three sodiums out of the cell and two potassiums into the cell against their concentration gradient; ATP energy is used to change the conformation of the carrier protein; affinity of the carrier protein for either Na+ or K+ changes so the ions can be carried across the membrane
RTK
RTK (receptor tyrosine kinases) activation bring about changes in gene transcription (insulin)
chemically gated
molecular gates triggered chemically to open or close (ex. neurons)
binds signal extracellularly; catalyzes response intracellularly
what makes something living
evolutionary adaptation, homeostasis, energy utilization, growth, development, and reproduction, sensitivity, ordered complexity, cellular organization
hypothesis
a suggested explanation that accounts for observations. A proposition that might be true.
pinocytosis
process in which the material the cell takes in is liquid; fluid droplets are engulfed by membrane which folds around it and forms a vesicle
g proteins
binding of signal to receptor causes GTP to bind with attached GTP detaches to deliver signal messages inside cell
ensymatically gated
binds signal extracellularly; catalyzes response intracellularly
fluid mosaic model
model that explains the structure and function of cell membranes
amphipathic
both hydrophobic and hydrophilic
osmoregulation
the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids, maintain homeostasis
4 basic types of signaling
paracrine, autocrine, endocrine and direct
golgi apparatus
process and packeges the proteins and lipids tells them where to go (what their function is in that cell)
forms of signaling
intracellular and intercellular
intracellular signaling
communication within the cell in response to external environmental cues (goes in)
intercellural signaling
communication between cells (doesnt go in)
protein kinase
an enzyme that adds a phosphate to a protein
protein phosphatase
an enzyme that removes a phosphate from a protein
exoxytosis
materials in vesicles are secreted from the cell when the vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane
endocytosis
transports macromolecules, large particles and small cells into eukartotic cells by means of engulfment
receptor mediated endocytosis
a cellular process that allows cells to absorb molecules from outside of the cell by binding to receptors on the cell surface
bulk transport
endocytosis and exocytosis
how many sodium pumps are pumped out for every potassium pumps
3 sodium for every 2 potassium
septate/tight junctions
link adjacent epithelial cells
restrict migration of proteins/phospholipids from one region of the cell to another
prevent substances from moving into intercellular space
anchoring/adhesive junction
spot welds on adjacent cells holding them together
use desmosomes and hemidesomosomes as points of adhesion tied together with cadherins, intermediate filaments, actin filaments and others
communicating junctions
has 2 types
connections that faciliatet communication between cells
2 types of communicating junctions
gap junctions and plasmodesmata
gap junctions
ONLY IN ANIMALS
made up of specialized proteins channels called connexons
Plasmodesmata
ONLY PLANTS
microscopic channels that connect plant cells and some algal cells but more structurally complex
fluidity depends on
degree of saturation
temperature (heat)
cholesterol
what can be found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
ribosomes, genetic material, a cytoplasm, and plasma membranes
9+2 relates to what
cilia and flagella
9 pairs of microtubules surrounded by 2 central mircotubules
3 main components of the cytoskeleton
microtubules, intermediate filaments, microfilaments
intermediate filaments
provide structural stability
microtubules
act as highways, organization of the cell division, and cilia/flagella movement
actin filaments
help with cell shape, support, cells to migrate, engulf and divide
Motor proteins (movers)
Kinesin, Dynein,Myosin
3 major intracellular organells that digest proteins
lysosome, proteasome, peroxisomes
lysosomes
gets rid of extracellular proteins, endocytosis and phagocytosis
proteasomes
endogenous proteins, improperly folded proteins
peroxisomes
break down only toxic materials in cells
order of endomembrane system
nuclear membrane
plasa membrane
er (rough/smooth)
golgi
lysosomes/proteasomes
peroxisomes
vesicles
vacuoles
Vesicles
small sacs that move in and out of the cells
2 types of prokaryotes
archaea, bacteria
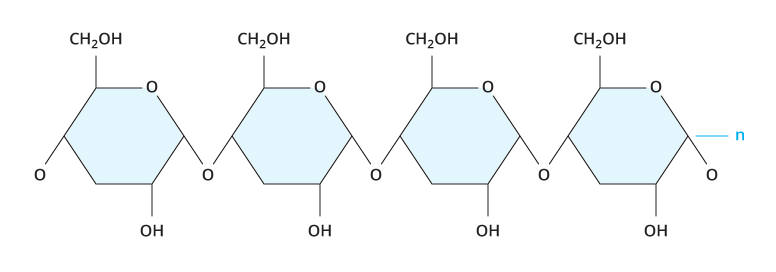
what is this
carbohydrates
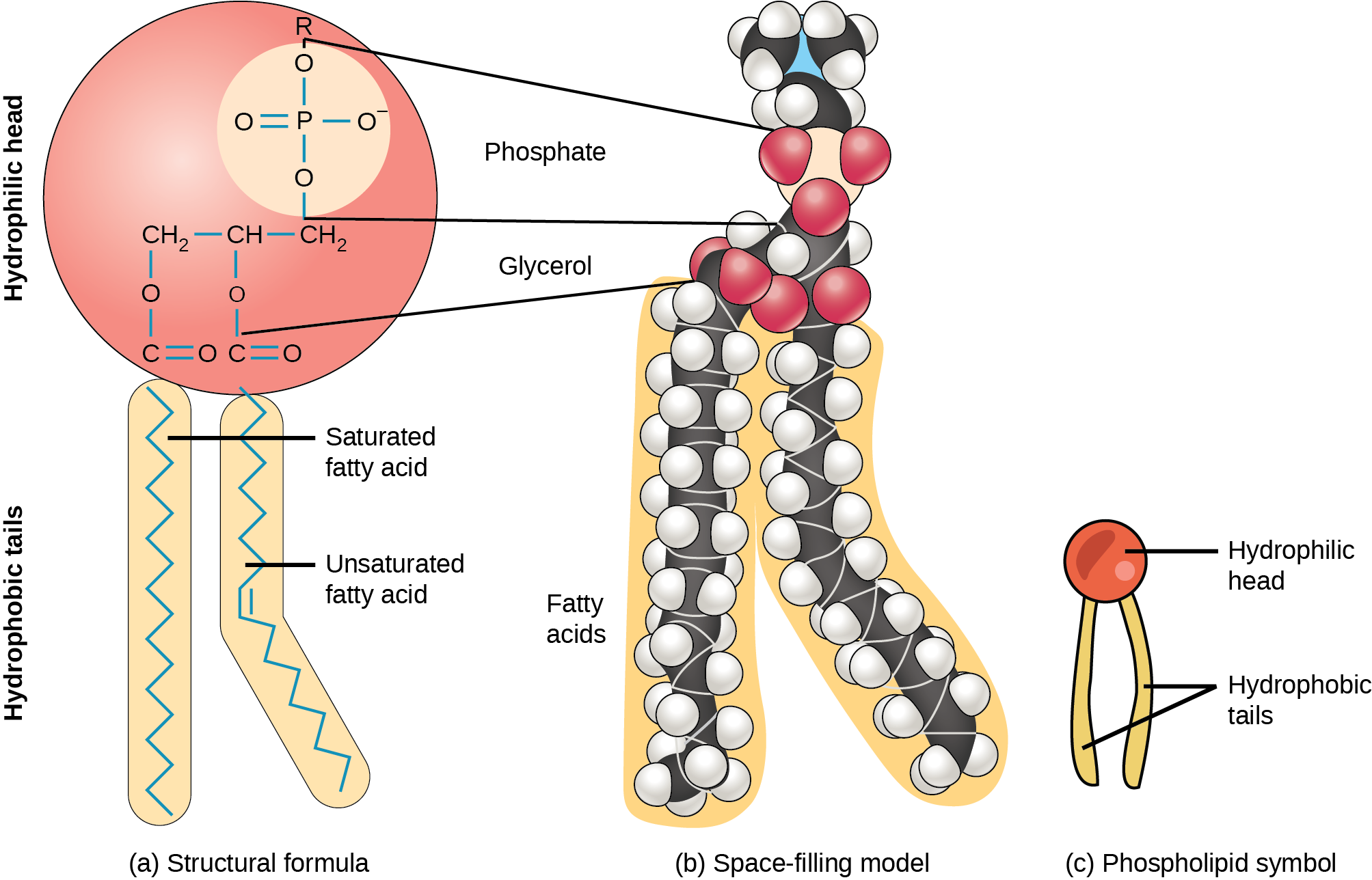
what is this
phospholipid
what are phospholipids composed of
1 glycerol
2 fatty acid
one phosphate group
triglycerides
1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids
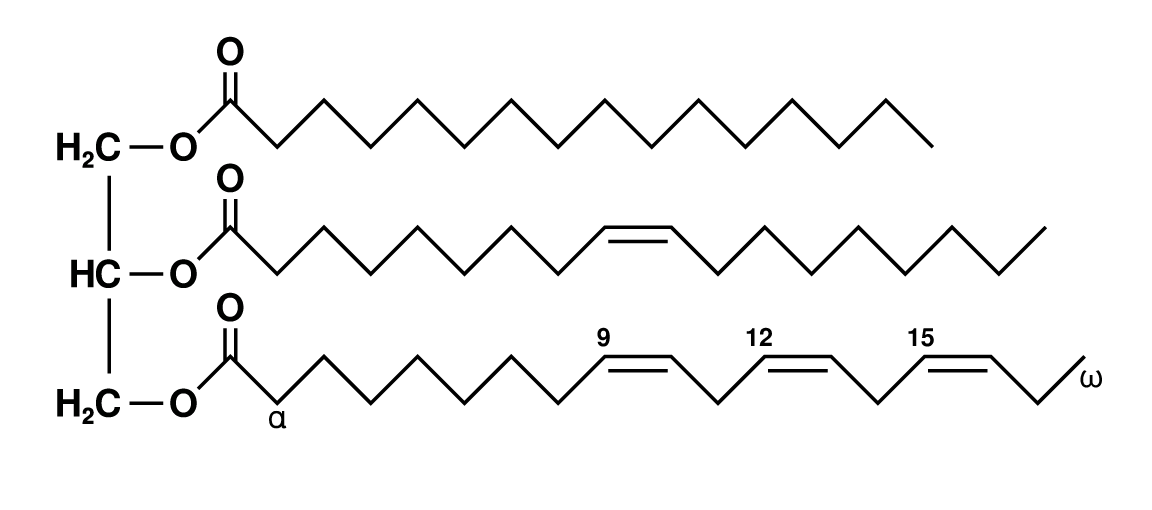
what is this
triglyceride
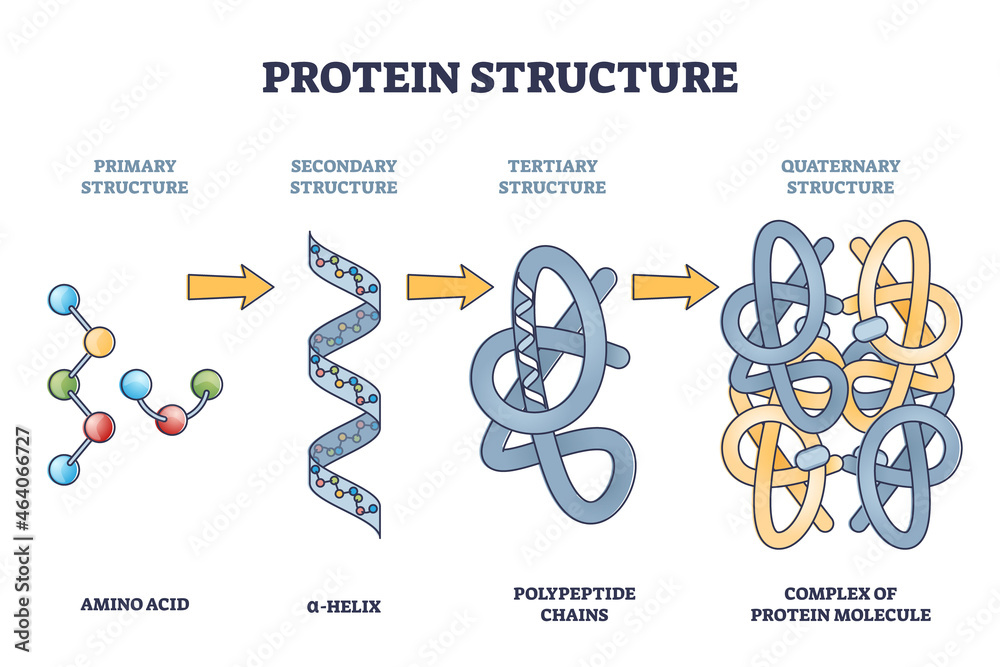
what is this
proteins
polypeptide
chains of amino acids linked together to make protein
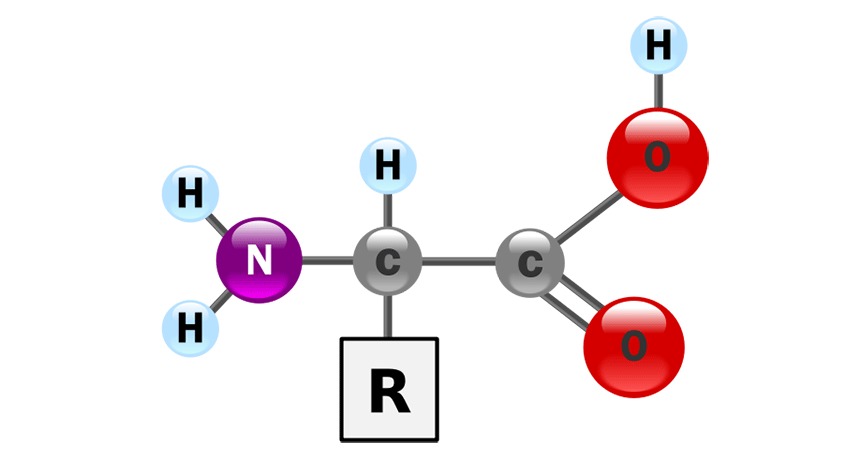
what is this
amino acid
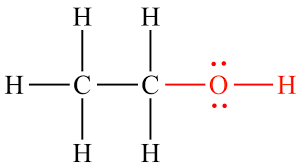
name this functional group (only the red)
hydroxyl
what is this functional group
carboxyl
what is this functional group
amino
what is this functional group
—- S — H
sulfhydryl
what functional group is this
phosphate
what functional group is this
methyl
properties of water
polar, high heat capacity, heat of vaporization, solvent, cohesive and adhesive
ionic bond
the complete transfer of valence electron(s) between atoms.
covalent bond
the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms
hydrogen bond
attraction that occurs between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom
Potential energy
stored energy based on positon and forces acting on it
kinetic energy
energy and object has because of its motion
Molecule
a group of atoms bonded together