Oxidation, reducing and redox reactions
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
define oxidation in terms of electrons
loss of electrons
define oxidation in terms of oxygen
gain of oxygen
define oxidation in terms of hydrogen
loss of hydrogen
define reduction in terms of electrons
gain of electrons
define reduction in terms of oxygen
loss of oxygen
define reduction in terms of hydrogen
gain of hydrogen
what is an oxidising agent?
an electron acceptor, gets reduces
what is a reducing agent?
electron donor, is oxidised
what is a redox reaction?
reaction where oxidation and reduction occurs, oxidation states change
what is a disproportionation reaction?
A redox reaction in which the same element is both oxidised and reduced
how are all disproportionation reactions redox reactions?
they all involve changes in oxidation states
if an element is oxidised, how does the oxidation state change?
increases;
e.g. 0 to +2
if an element is reduced, how does the oxidation state change?
decreases
rules for oxidation states?
Any element/diatomic by itself = 0
Monoatomic ions = 0
compounds: sum of oxidation states = charge
group 1 atoms = +1
group 2 atoms = +2
fluorine = -1
hydrogen = +1
oxygen = -2
chlorine = -1
rule 8 is overruled by 7, rules 7-9 are overruled by earlier ones; e.g. oxygen in H2O2 has an O state of -1
how to balance simple half equations?
1 balance atoms
2 balance charge with electrons
how to balance complex half equations?
1 balance atoms
2 to balance oxygen, add water
3 to balance hydrogen, add protons (H+)
4 balance electrons and charges
(protons and electrons are always on the same side)
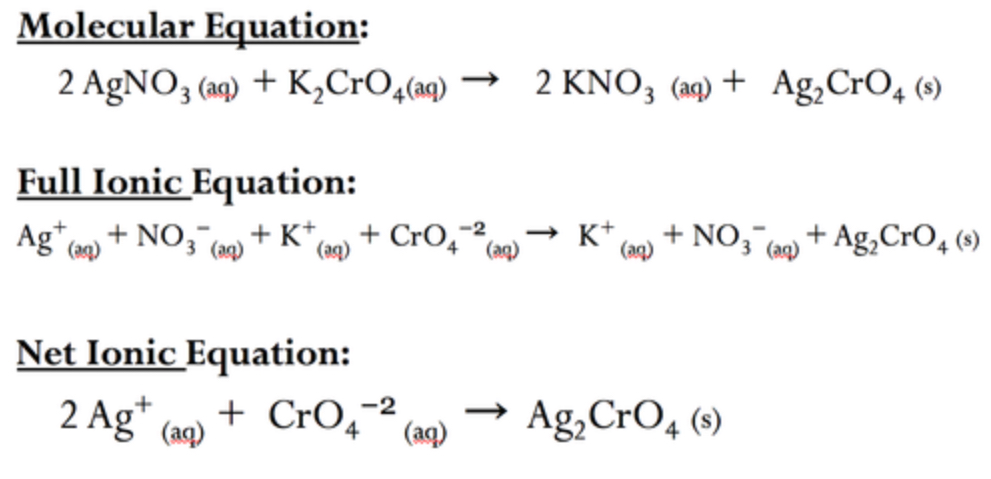
steps to writing a net ionic equation?
1) Write the balanced molecular equation.
2) Write the balanced complete ionic equation (dissociation).
3) Cross out the spectator ions that are present.
4) Write the "leftovers" as the net ionic equation.
state symbols!!!
what is dissociation?
when an ionic compound dissolves in water, the ions separate and move around independentley
what are spectator ions?
ions in solution that are present but are unchanged by the reaction, charges stay the same
what is the net ionic equation?
an ionic equation where the spectator ions are removed
what is a complete ionic equation?
an equation that shows dissolved ionic compounds as dissociated free ions, they need balanced charges on each side