Virginia Tech BIOL 2614 Microbiology Lab Final - Spring 2024
1/248
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
249 Terms
germs
__________ can include bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses that are ubiquitous (found everywhere in nature, including water, food, the air, and on and in our bodies
pure culture
a culture that contains only 1 species of microorganism
sterilization
the destruction or removal of all forms of microorganisms (eukaryotes, prokaryotes, and viruses)
aseptic technique
the methods of obtaining and maintaining pure cultures
trypticase-soy
a type of media that contains glucose, enzymatically digested milk protein, enzymatically digested soybean meal, and a small amount of NaCl
SAB (sabouraud dextrose)
a microorganism like yeast and fungi that prefer an environment with a higher sugar concentration would like _________ media
stock
refrigerated slant cultures are examples of _________ cultures
slant cultures
cultures not used to characterize and identify microorganisms, but rather used for the growth and refrigerates storage of pure microbial cultures
agar deeps
type of stab culture made in either a solid (1.5-2% agar) or a semisolid (0.5-0.7% agar)
underlined
nomenclature
handwritten names should be _____________
italicized
nomenclature
typed named should be _____________
broth
any liquid medium used for growing microorganism is called a __________
turbidity
some microbes uniformly increase the _____________ (milkiness/cloudiness) of the broth as their numbers increase
pellicle
other species of microorganisms grow only at the surface of a static broth culture, forming a mat of cells called a _______________
sediment
other microbial species may settle to the bottom of the tube to form a _____________ or button of cells that stick together
mycelia
other microorganisms form intertwined ____________ during growth; these may form clumps of filamentous cells having the appearance of small cotton balls floating in clear broth
😁
know the parts of the microscope
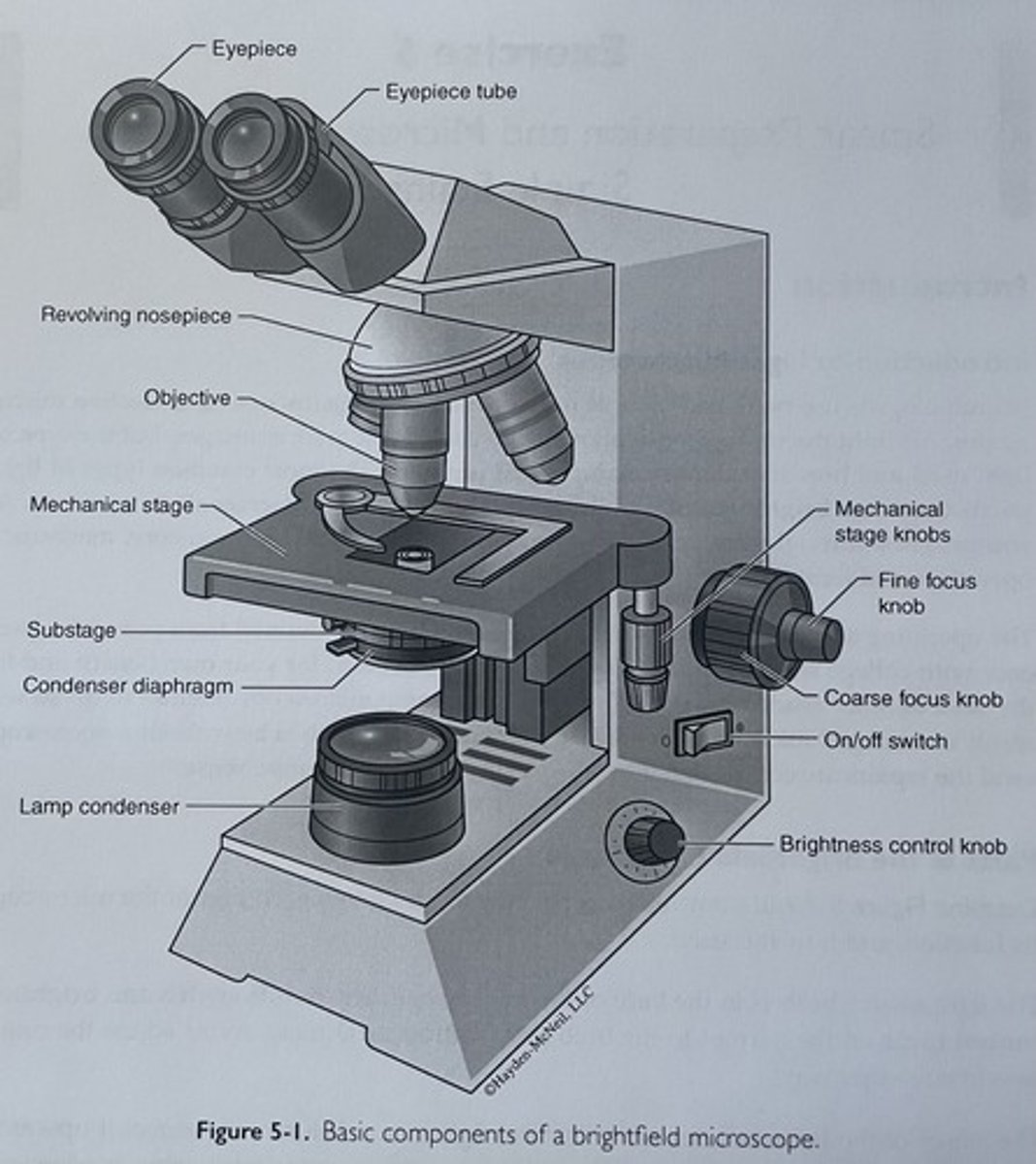
eyepiece
total magnification = objective x ____________
heat fixation
a common method for killing cells prior to staining
simple stain
stain technique that colors the cell or the background in a way that enables you to observe whether the cell is a straight or curved rod or cocci and whether the cells are arranged in pairs or clusters
differential stain
stain technique that uses a combination of dyes that take advantage of chemical differences among cells; dyes the entire cell of only certain types of bacteria
simple
basic dyes and acidic dyes are types of __________ stain
differential
gram stain and acid-fast stain are types of _________________ stain (stains whole cells but only those of a certain type)
morphology
the study of the size, shape, and arrangement of cells
yeasts
a single-celled fungi eukaryotic microorganism
molds
a filamentous fungi eukaryotic microorganism
algae
a photosynthetic plant eukaryotic microorganism
protozoa
a single-celled animal eukaryotic microorganism
prokaryotic
bacteria are (prokaryotic/eukaryotic)
mordant
Gram Stain
the ___________, Gram's iodine, increases the affinity between the primary stain and the reactive substances in the cell
counterstain
Gram Stain
the ________________ can be any dye as long as it is a color that contrasts with the deep blue-violet of the stained gram-positive cells; common examples are basic fuchsin and safranin
endospore
a structure that is formed inside certain types of bacteria
vegetative
a cell that lacks an endospore is called a _______________ cell
capsule
term that is used to refer collectively to all extracellular polymers that are produced by the cell and accumulate (at least in part) around its outer surface
motility
the movement caused by the action of the flagella is called
positive chemotaxis
motility toward a favorable environment
flagella
long, narrow strands that are coiled into rigid helices (spirals) that revolve around their points of attachment and push against the surrounding medium for motility
polar flagellation
cells with flagella inserted only at the ends of a cell
peritrichous flagellation
cells with flagella inserted all over the surface
flagellin
all bacterial flagella are composed of a protein called _____________
streak plate
the most practical method for obtaining pure culture; start with a mixed culture and spread it over the surface of a solid medium until each cell is separated from all others; the colony that develops from one cell is a pure culture by definition because all cells in that colony were derived from that first single cell
😁
T-Streak Method
know how to T-streak

turbidity
the effect of light scattering by a colloidal suspension
optical density (OD)
it is traditional to record growth as the change in __________ ____________ with time, as it is directly proportional to cell concentration
cell number
growth = increase in ______ __________
serological pipettes
glass or plastic pipettes that are calibrated to deliver any amount within the graduated scale
Pasteur pipette
small, tapered glass pipette that is not graduated and is used to transfer liquid where the volume is not critical
micropipette
pipette used to dispense very small volumes of liquid usually between 1 µl and 1000 µl
500
0.5 ml is _______ µl
1
1000 µl is _______ ml
.50 ml, 500 µl
when the micropipette reads "050", that is _______ ml = ______ µl
1 ml, 1000 µl
when the micropipette reads "100", that is _______ ml = ______ µl
dilution factor
the denominator of the final dilution (100 or 10^2)
# of colonies • dilution factor
CFU/ml =
viable number
the number of cells capable of division on a solid medium
serial dilution and spread plating
the best method available for determining viable numbers
sampling error
error that occurs because of an unequal distribution of cells in the culture or dilution fluid
technical error
error that is most often due to some inaccuracy in preparing dilution blanks or in pipetting
spread-plate method
method that involves spreading a small, known volume (usually 0.1 ml) of a cell suspension onto the surface of a pre-poured agar plate followed by evenly spreading the cell suspension across the agar surface
spread-plate
preferred method for determining viable numbers of strict aerobes, to study the proportions of cell types in a mixed culture, or to check for culture purity; uses a "hockey stick" that is sterilized with burning ethanol
pour-plate
method where a known volume of cell suspension is inoculated into a tempered agar deep; satisfactory for growing either the facultative or the microaerophilic bacteria
300
plates with more than ______ colonies are considered TNTC
TFTC (too few to count)
plates with less than 30 colonies are considered
2 (example: 2.2 • 10^6)
your answer for CFU/ml should be how many sig figs?
all-purpose media
media used for maintaining pure stock cultures of many types of microorganisms and for growing these microbes for laboratory experiments
selective medium
media that contains at least one ingredient (selective agent) that can inhibit the growth of unwanted (more numerous) microorganisms without preventing the growth of the desired type
coliform bacteria
residents of the human intestine that, in their presence in water, indicate that the water is contaminated with fecal material
differential media
media that is designed to distinguish one type of microorganism from all others in a mixed culture; can be selective or nonselective
nutrient agar
name an example of an all-purpose medium
high-salt agar
name an example of a selective medium
mannitol-salt agar
name an example of a selective and differential medium
phenol red
dye used for mannitol medium
optimum growth temperature
the temperature at which the growth rate of a microbial species is closely correlated to the temperature of that organism's habitat
37°C
what is the optimum growth temperature for pathogenic microorganisms that infect humans?
mesophilic
most known microorganisms have optimum growth rates between 28°C and 38°C; these organisms are called _______________
psychrophilic
organisms that have optimum growth rates at temperatures lower than 16°C
thermophilic
organisms that have optimum growth rates around 60°C
tonicity
the normal osmotic pressure exerted by body fluids, which amounts to about the same as physiological saline (0.9% NaCl solution)
plasmoptysis
the result of placing a cell in a hypotonic solution (low osmotic pressure); exploding of the cell due to water rushing into the cell
plasmolysis
the result of placing a cell in a hypertonic solution (high osmotic pressure); shrinking of the cell due to water rushing out of the cell
osmophilic
osmotic-pressure loving
saccharophilic
sugar loving
halophilic
salt loving
obligate (strict) aerobes
organisms that grow only when oxygen IS present
microaerophiles
organisms that require only minimal amounts of oxygen to grow
obligate (strict) anaerobes
organisms that require NO oxygen for growth and oxygen is toxic; metabolism is fermentative
aerotolerant anaerobes
strict fermenters that do not find oxygen toxic but cannot use it in their metabolism
facultative aerobes/anaerobes
organisms that can grow either in the presence or the absence of oxygen, but grow faster in aerobic conditions; most microorganisms fall into this class
zone of hydrolysis
area that results from the enzymatic breakdown of the insoluble starch into smaller oligosaccharides and the disaccharide maltose
casein
insoluble protein found in milk secreted 3-5 weeks postpartum that can be readily attacked and solubilized by microbially produced extracellular proteinases
gelatin
as enzymes hydrolyze __________, it changes from a solid to a liquid, thus destroying its use as a solidifying agent
respiration
Fermentation Features
(1) can occur without oxygen
(2) energy-producing electron transport is absent
(3) much less energy efficient than ______________
(4) metabolic intermediates, often called fermentation end products, are excreted from the cell
lactic
Fermentation End Products
(1) acids: _________ or acetic
(2) neutral products: ethyl alcohol and butanediol
(3) gases: CO2 and H2
substrate-level phosphorylation
the way that fermentative microorganisms make all their ATP
Durham tubes
tubes used to detect gas production from fermentation
yellow
a positive reaction for sugar fermentation test is if the phenol red indicator turns _____________ in the ENTIRE medium and/or there is a bubble in the Durham tube
enteric bacteria
bacteria that grow aerobically on glucose (in broth cultures) and rapidly use all of the oxygen via respiratory metabolism; then they commonly shift to one of two types of glucose fermentation (mixed acid or butylene glycol)
methyl-red test
the test for mixed acid fermentation of glucose by enteric bacteria
Simmons' citrate agar
media used during the biochemical test used to determine utilization of citrate by enteric bacteria
green
Citrate Test
positive: growth and an alkaline reaction, turning the pH indicator (bromothymol blue) from _________ to blue