2011 lec wk 3
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms

Chronic Conditions
Physical or mental condition / functional limitation that has lasted, or expected to last 6 months or more
Self-management
An individuals engagement in activities and role in promoting and managing their health and wellbeing
Prevent / control disease progression
Monitoring self
Components of Self-management
Medical =
Compliance/adherence to medical treatment
Medications, appointments etc.
Coping and understanding symptoms
Social =
Behaviour adjustments
Acting according and being able to deal with situations (eg. roles in life, work etc.)
Prevent negative outcomes and exacerbation of illness
Emotional =
Emotional responses
Mental wellbeing
Management of feelings
Eg. depression, anxiety, stress etc.
What does self-management involve?
The individual completing tasks and skills in order to sustain and maintain health
Eg. HF patients doing daily weights, fluids restrictions, adhering to their care plans
Prerequisites to Self-management
People need:
Self-efficacy
Health literacy
Awareness and capability of maintaining their health
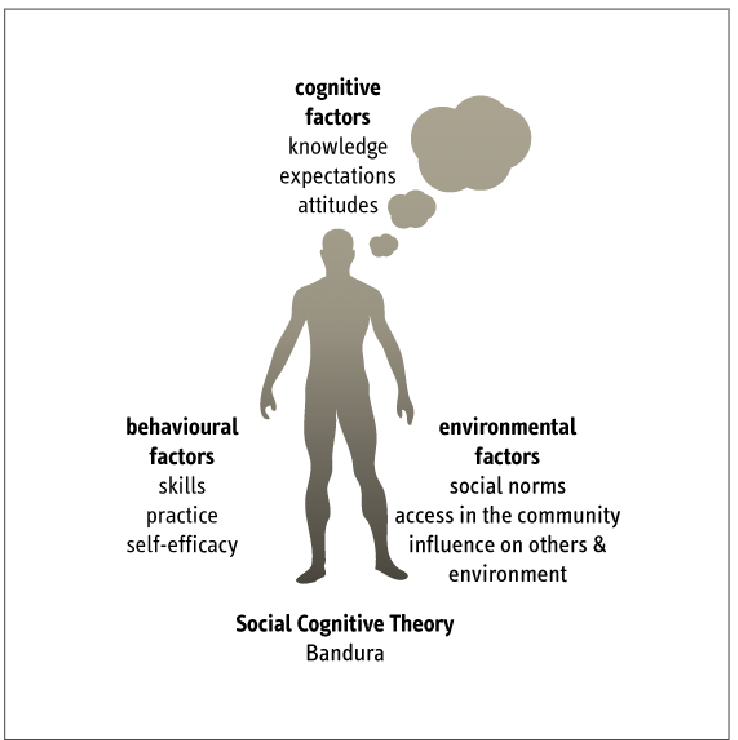
Social Cognitive Theory
Psychological framework explaining how people learn and change their behaviour by observing others and learning from them + interactions with their environment
Not just from direct experience (trial and error)
Learning through observation, understanding, imitating and modelling their behaviours based on their interpretations
Self-efficacy
Person’s belief in themselves
Motivation to manage themselves
Determination
Willingness
Personal judgement of their capabilities and efforts in being able to succeed in their tasks
if someone believes in themself to be able to do it ~ They are more likely to succeed.
Social Cognitive theory in self-efficacy
Self-efficacy beliefs operate with:
Goals
eg. Aim to lose 10kg
Expectations
eg. After losing 10kg, they expect better health and feeling better, improved appearance etc.
Environmental support and barriers
eg. Support (facilitator) = friends and family | barrier (impediments) = lack of access to gym, low SES etc.
in order to regulate motivations, behaviour and wellbeing
Self-regulation theory
An individual is motivated to self-regulate when they have a desired goal (something perceived as ideal for them - and upholds value to them)
Medical treatment adherence and self-management is significantly influenced by both internal and external factors
Person must believe and portray that they want to achieve it.
Social Learning Theory
That new behaviours are developed through observation, instructions and copying others
Behavioural Theory
Learning is attained through conditioning behaviours
Eg.
Behaviour is strengthened by rewards or punishments from behaviours
Punishment = less likely to perform behaviour again
Rewarded (eg. praised, given gifts) = more likely to perform behaviour again
Miro and “WALK??” which triggers a response of excitement because he has been conditioned to behaviours because he conditions his senses to his past experiences
Principles of Self-management
1) Problem solving
2) Decision Making
3) Effective resource utilisation
Access to resources and services (eg. consider low SES and social situations)
4) Forming a relationship with a provider
supportive environments, a resource that will guide them and support them through their journey
Healthcare provider and their involvements
5) Taking action
6) Self-tailoring
Being able to self-adjust and understand their treatment regimes and medications, and be able to act accordingly
Self-confidence and belief in themselves
Transtheoretical model of change
Self-management benefits
Builds confidence
Disease management
Social/role management
Emotional management
Why is Chronic Disease Self-Management important?
Significantly improves health outcomes
Traditional medical model is expensive and ineffective in cases of chronic conditions
Focuses on PCC - managing the individual rather than the condition itself (empowering the patient)
Models of Self-management
Chronic Disease Self-management (CDSM)
Support the individual
Tailor towards their goals
Actively manage their chronic condition through collaborative and active participation
Education
Behaviour management / Emotional management
CDSM programs
Collaboration
Personalised care plans
Self-management education
Adherence to treatment
Follow-up appointments, consistent monitoring and support
Self-management education interventions
From individual to population:
Face-to-face consultation
Telephone coaching
Internet individual courses
Internet group courses
Group cycles (rehab programs)
Structured and formal group programs
Written information
TV, Media, campaigns
Health Change Australia (CDSM approach)
Health Coaching
Applies:
Questioning
Conversation
Goal setting
Based on:
Readiness to change
Information
Confidence
Knowledge
(RICK)
Get Healthy Service (CDSM Approach)
Referred from health professional
Patients receive 10 free health coaching phone calls over 6 months
Eating habits, diet advice, physical activity, goal setting etc.
Chronic Care for Aboriginal People (Model of Care)
Main difference and the mainstream model of care = TRUST + cultural safety ?
Stemming from historical oppression and history of colonisation
Effective communication
Building rapport
Developing a relationship with the patient
Measures of self-management
Not based on statistics and numerical values
involves Patient Reported Outcome Measures (PROMS)
Patient Reported Experience Measures (PREMS)
Micro =
Patient engagement in risk factor modification and improvement
Meso =
Successful self-management
Eg. less use of hospital services (such as decreased length of stay)
Macro =
Policies and guidelines
In support of health clinicians to be able to provide effective and quality care
Eg. Staffing
Telemonitoring in Self-management
Allow patient to self manage by:
Measuring self BGLs
Taking their own vitals
Nurses can be shared this information - being able to provide early intervention and management
Telemonitoring Examples
Nepean Diabetes Service
CGM (Continuous Glucose Monitoring) - subsidised by GOV
Taking BGLs is uploaded to cloud
Allows for health clinicians to be able to adjust insulin accordingly (eg. in T1DM patients) over the phone to achieve glycemic control
Reduced pressure on endocrinologist
+ Allows for patient to develop self-management skills and allow them to be more proactive (as opposed to staying in hosptial)

Cultural Considerations in self-management
Culturally-safe
Understand and accept their values and beliefs - aiming not to contradict and oppose
Consider Ethnic diversity
PCC
Examples:
Food/diet
Culture & Tradition
Religion
Beliefs / values
Nurses’ role in self-management
Nurses’ consider new approaches that require collaborative interactions in care
CDSM Programs
Collaboration and active participation in management with multidisciplinary team + the patient, their family etc.
Motivational Interviewing
Motivational Interviewing
Develop empathy
Reflective listening
Understand any discrepancies between client’s goals and their behaviours
Are behaviours supportive or limiting their goals?
Don’t argue or oppose the patient - work around it
Optimism
Self-efficacy!!!!
Comprehensive Care Management
Assessment of:
Medical needs
Psychosocial needs
Functional needs
Review medication adherence
Appointments and scheduled services for the patient
Overview of the patients’ self management skills and engagement
Nurses’ role in self-management
Patient and health professional work together
Building a therapeutic relationship
Involves parents, carers, families etc.
HOLISTIC APPROACH
Proactive, adaptive strategies
Empower Individual and support throughout their journey