Understanding Price Elasticity of Demand and Supply
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Price Elasticity of Demand
A measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price.
ED = %^QD/%^P
Formula of Price Elasticity Demand
ED = ^QD/QDaverage =^P/Paverage
price elasticity of demand can lead to conflicting results depending on whether price rises or falls. Therefor, economists use what formula
Absolute Value
The distance a number is from zero on a number line. ALWAYS POSITIVE
Elastic Demand
Occurs when the percentage change in quantity demanded is greater than the percentage change in price (Ed > 1).
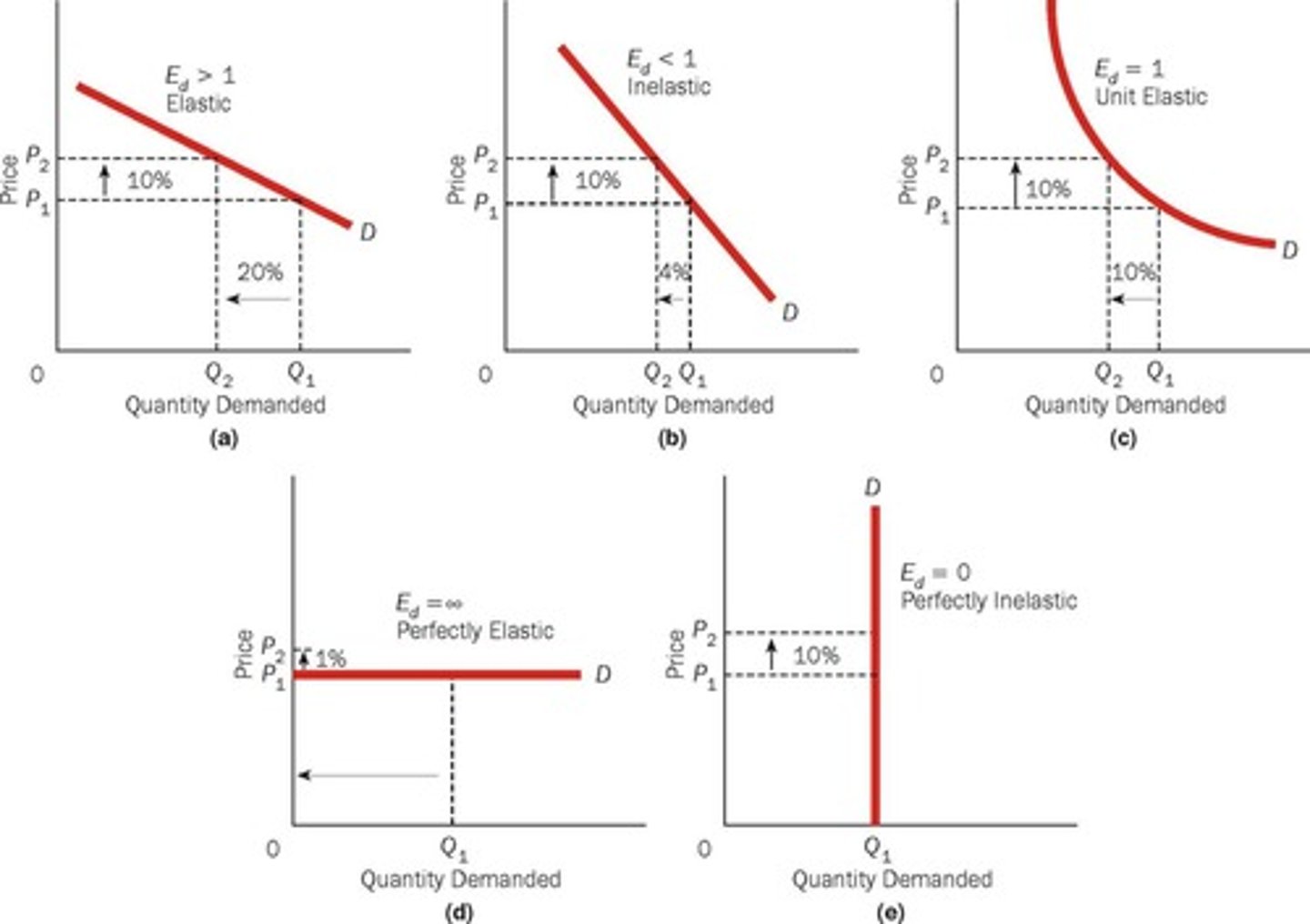
Inelastic demand
the demand when the percentage change in quantity demanded is less than the percentage change in price.
Unit elastic demand
the demand when the percentage change in quantity demanded is equal to the percentage change in price.
Perfectly Elastic demand
the demand when a small percentage change in price causes an extremely large percentage change in the quantity demanded.
Perfectly inelastic demand
the demand when the quantity demanded does not change as price changes.
Total revenue
the price of a good times the quantity of the good sold.
Elastic Demand and Total Revenue
If demand is elastic, △Qd is greater than △P. Price and total revenue are inversely related.
Inelastic Demand and Total Revenue
If demand is inelastic, △Qd is less than △P. Price and total revenue are directly related.
Unit Elastic Demand and Total Revenue
If demand is unit elastic, △Qd is equal to △P. A rise or fall in price will leave total revenue unchanged.
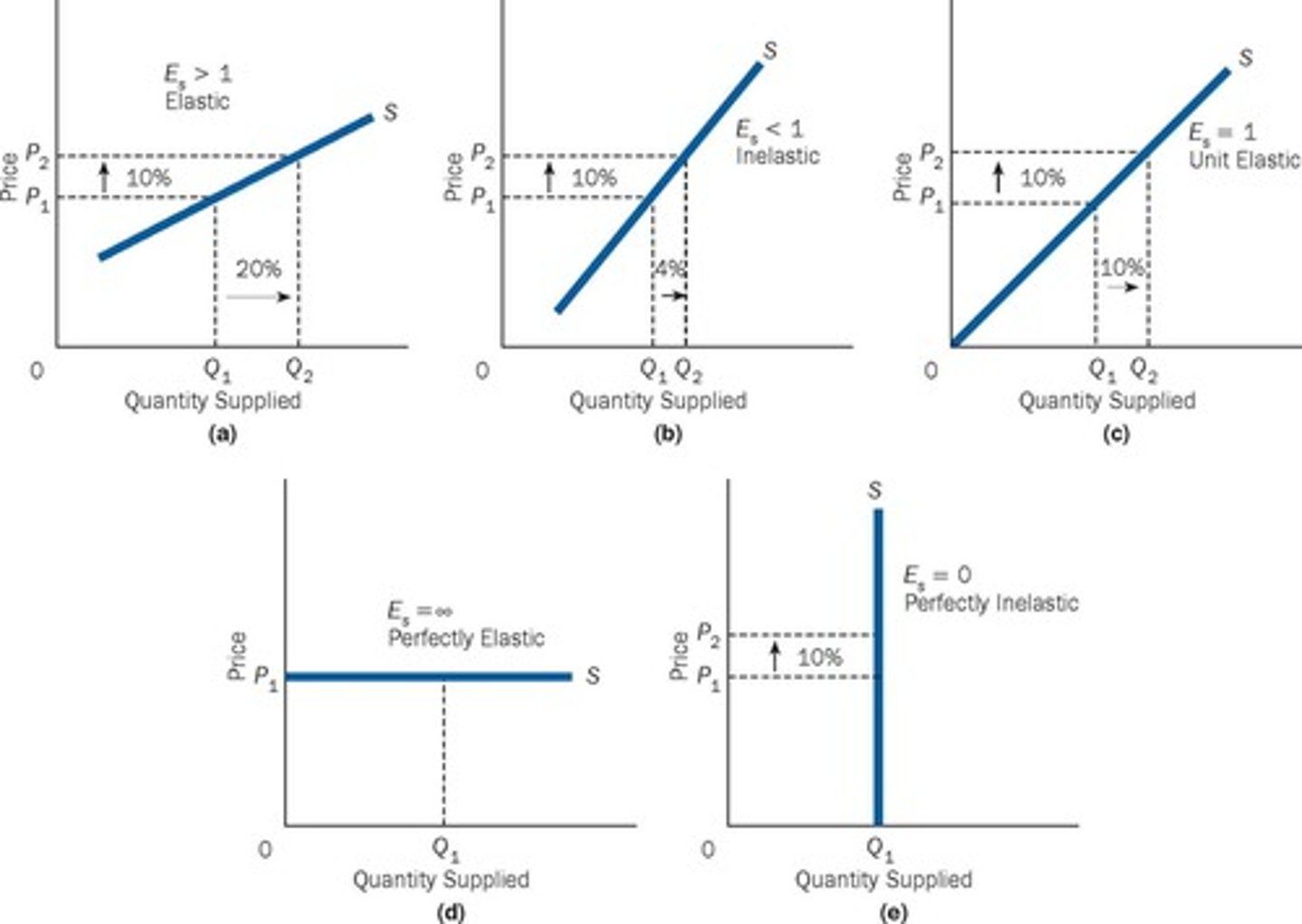
Price Elasticity of Supply
a measure of the responsiveness of quantity supplied to changes in price.
Formula for coefficient of price elasticity of supply
Es = %△Qs / %△P
Elastic supply
refers to a percentage change in quantity supplied that is greater than the percentage change in price.
Inelastic supply
refers to a percentage change in quantity supplied that is less than the percentage change in price.
Unit Elastic supply
refers to a percentage change in quantity supplied that is equal to the percentage change in price.
Perfectly Elastic supply
a small change in price changes the quantity supplied by an infinitely large amount.
Perfectly inelastic supply
a change in price brings no change in quantity supplied.