Exam 2 animal physiology
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Element
Matter that cannot be divided by ordinary chemical processes into another substance
Chemical Symbol
A letter that represents the element.
Subatomic Particles
Protons, electrons, and neutrons are the three types of subatomic particles.
Electrical Charge of Protons
Positive charge.
Electrical Charge of Electrons
Negative charge.
Electrical Charge of Neutrons
No charge; it is neutral.
Nucleus of an Atom
Contains protons and neutrons.
Mixture
Matter combined into a mixture of two or more substances.
Solution
A type of mixture where components can be gas, liquid, or solid, typically a clear liquid.
Colloid
A heterogeneous mixture that contains much larger solutes than those found in solutions.
Suspension
A heterogeneous mixture containing large solutes that settle down at the bottom of the liquid portion.
Compounds vs. Mixtures
Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements join together, while mixtures combine two or more substances.
Molecule
Forms when atoms are joined together by chemical bonds.
Ionic Bond
A bond where electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
Covalent Bond
A bond where atoms share one, two, or three electrons.
Hydrogen Bond
Occurs when a hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to a high electronegative atom.
Function of Hydrogen Bonds
Functions in molecular stability, structure, and interactions.
Organic vs. Inorganic Compounds
Organic compounds contain carbon-carbon or carbon-hydrogen covalent bonds, while inorganic compounds rarely contain carbon.
Essential Compounds for Life
Both organic and inorganic compounds are necessary for life.
Inorganic Molecules Important for Life
Water, salt, oxygen, and carbon dioxide.
Organic Molecules Important for Life
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Carbon's Feature for Life Chemistry
Carbon can form four covalent bonds with other atoms.
Functional Group
A specific group of atoms within a molecule that gives the molecule its characteristic chemical properties.
Polar Molecule
Water is called a polar molecule due to the unequal distribution of its electron density.
Four Properties of Water
High specific heat capacity, polarity, adhesion, and cohesion.
Ion vs. Atom
An ion is a positively or negatively charged particle; an atom is a single neutral particle.
Electrolyte
Salts in their ionic form.
Examples of Electrolytes
Potassium, chloride, sodium, magnesium, calcium.
Proton Donor
An acid is known as a proton donor.
pH Measurement
Measures acidity and alkalinity.
pH of 8.5
Basic.
Weak Acid as Buffer
Does not completely ionize in water and stabilizes the solution.
Elements in Carbohydrates
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Simple Sugar
Glucose.
Process Joining Simple Sugars
Dehydration synthesis.
Complex Carbohydrate
Polysaccharide.
Atoms in Lipids
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Lipid Backbone
Carbon makes up the backbone of all lipid molecules.
Polar Lipids
Phospholipids are polar lipids.
Function of Lipids
Used for energy, stored for future energy needs, and act as chemical messengers.
Element in Proteins but not Carbohydrates or Lipids
Nitrogen.
Building Block of Proteins
Amino acids.
Bond Holding Amino Acids Together
Peptide bond.
Peptide Definition
Formed when the carboxyl group of one amino acid links with the amino group of another amino acid via a peptide bond.
Enzyme Function
An enzyme speeds up a chemical reaction.
Chromatin
Thread like granules dispersed throughout the nucleus
Cytosol
Gelatinous fluid that contains organelles
Endoplasmic reticulum
Found in the cytoplasm and is a transport system within the cell can be smooth or rough
Golgi apparatus
Processes and packages protein molecules for export
Haploid
1/2 the chromosome number
Inclusions
Nonliving structures within the cytoplasm
Integral proteins
Protein channels within the plasma membrane that allows certain substances to enter the cell
Lysosomes
Membrane structures that contains potent digestive enzymes
Meiosis
Cellular reproductive process that results an offspring with half as many chromosomes as the cell they originated from
Microfilaments
Contractile protein with the ability to shorten; found within cytosol
Microvilli
Finger like folds in the plasma membrane that act increased the surface area for absorption
Mitochondria
Manufacturers energy for cellular use
Mitosis
Cellular reproductive process that result in two daughter cells that are exactly like the cell they originated from
Nucleoli
Assembly site for ribosomal particles found within the nucleus
Nucleus
Control center for cell chromosomes are found within the structure
Organelles
Highly organized subcellular living system
Peroxisomes
Membranous sacs found within the cytoplasm containing oxidase enzymes
Phospholipids
Arranged in two layers in the plasma membrane
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis
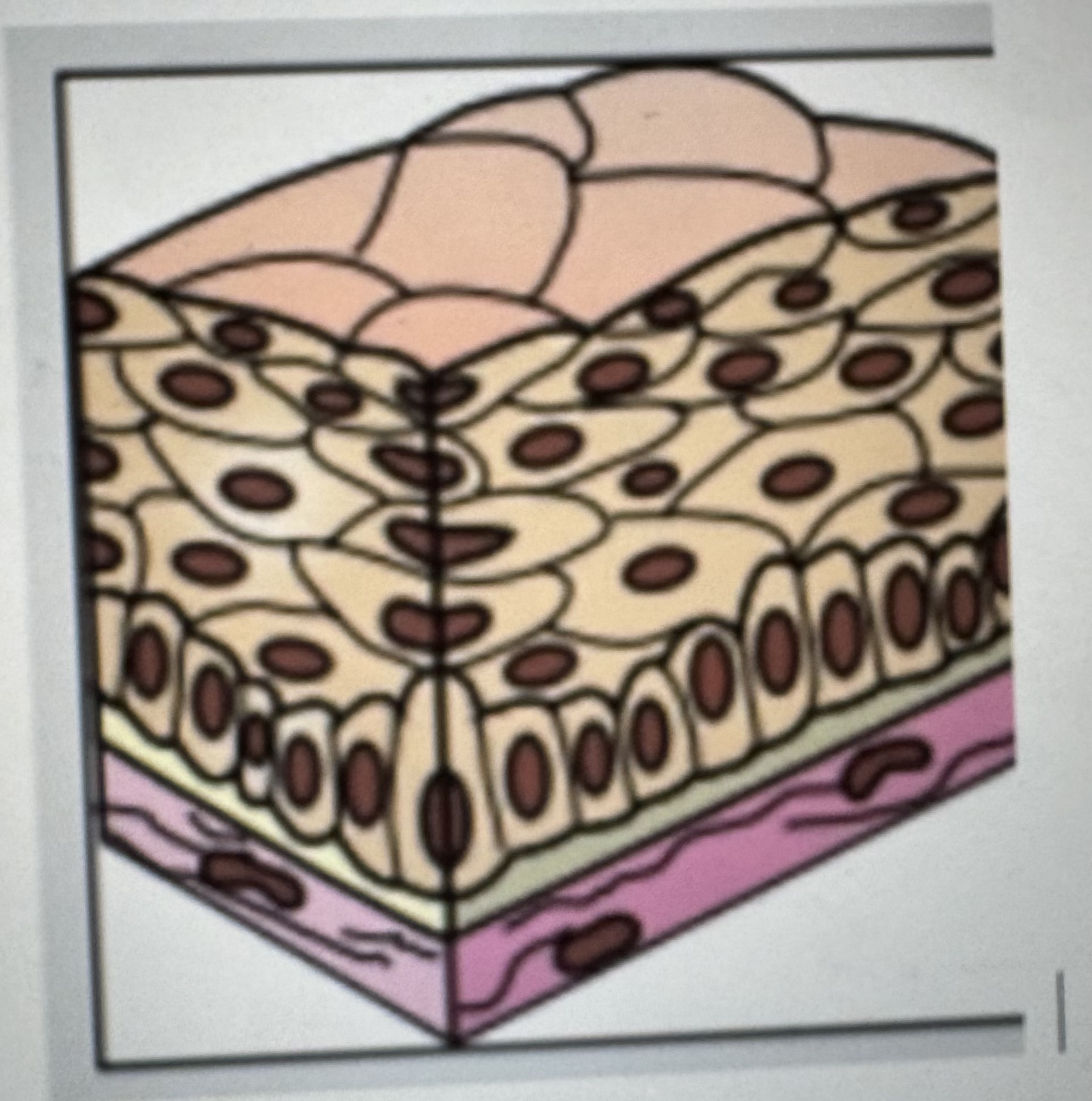
Label identify and classify epithelial tissue
Stratified squamous epithelium
Where it’s found: areas that are prone to abrasion
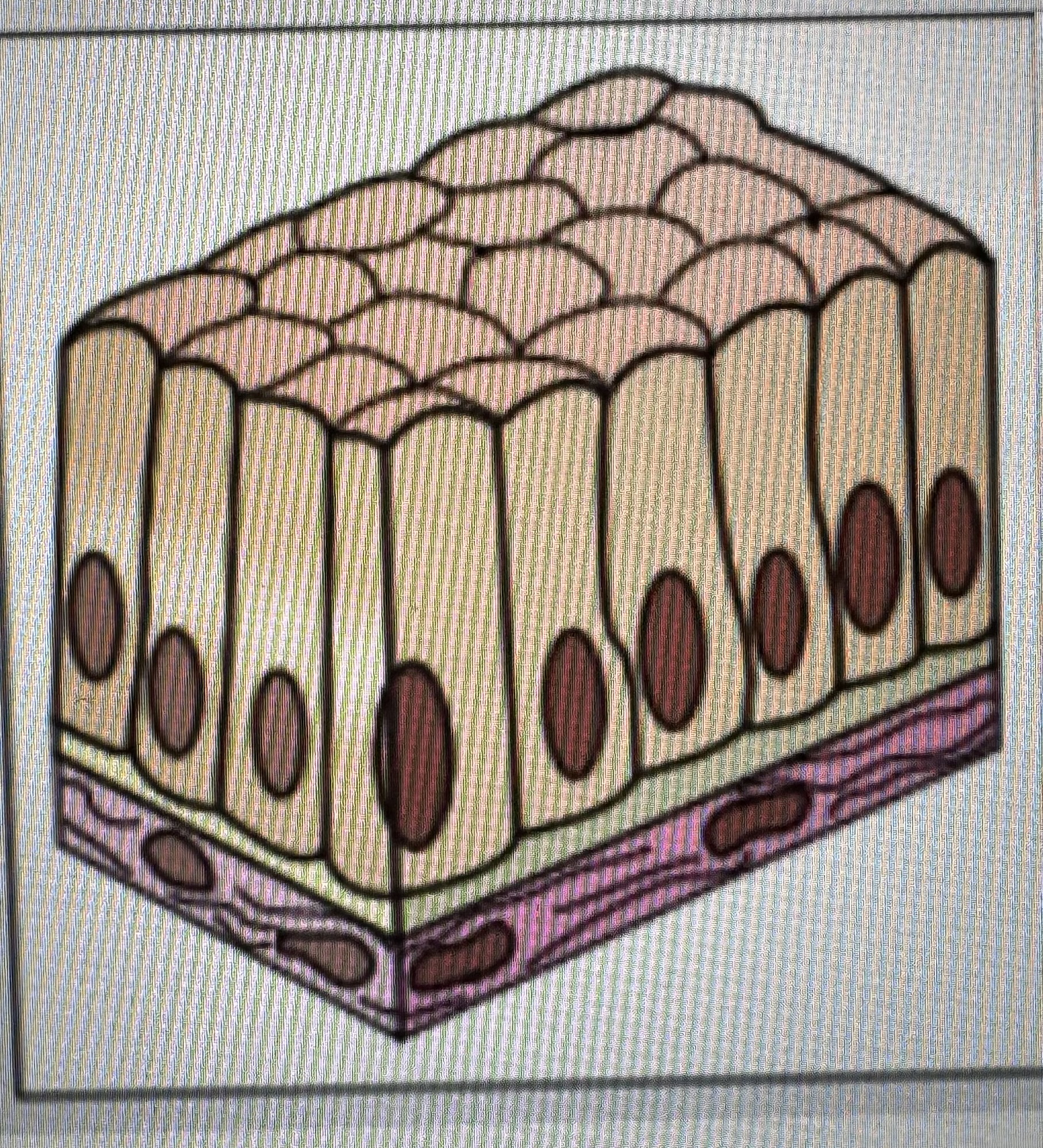
Label identify classify cell type
Simple columnar epithelium
Found in the lining of the stomach
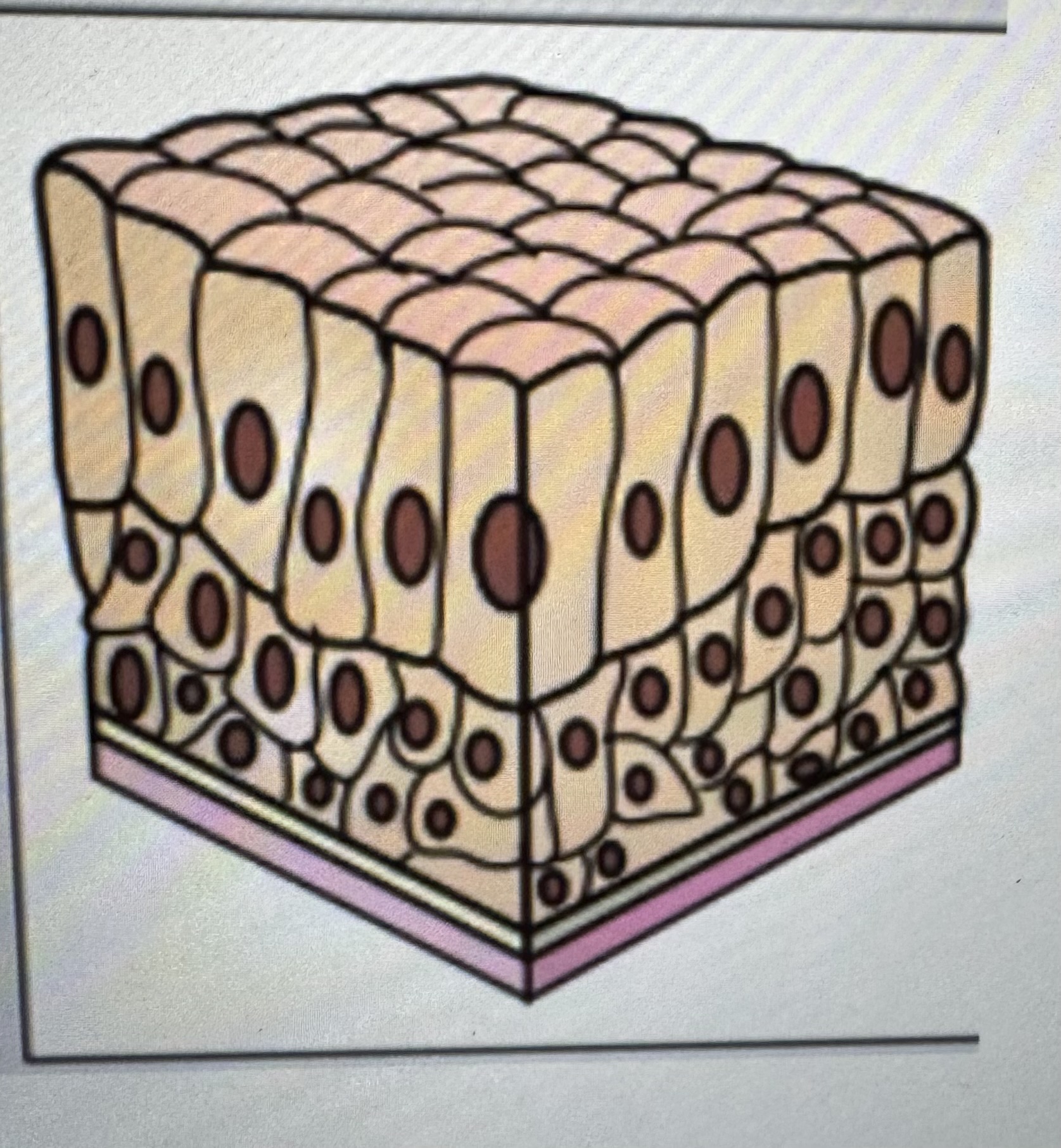
Label identify classify cell type
Stratified squamous epithelium
Found in the epidermis of the skin
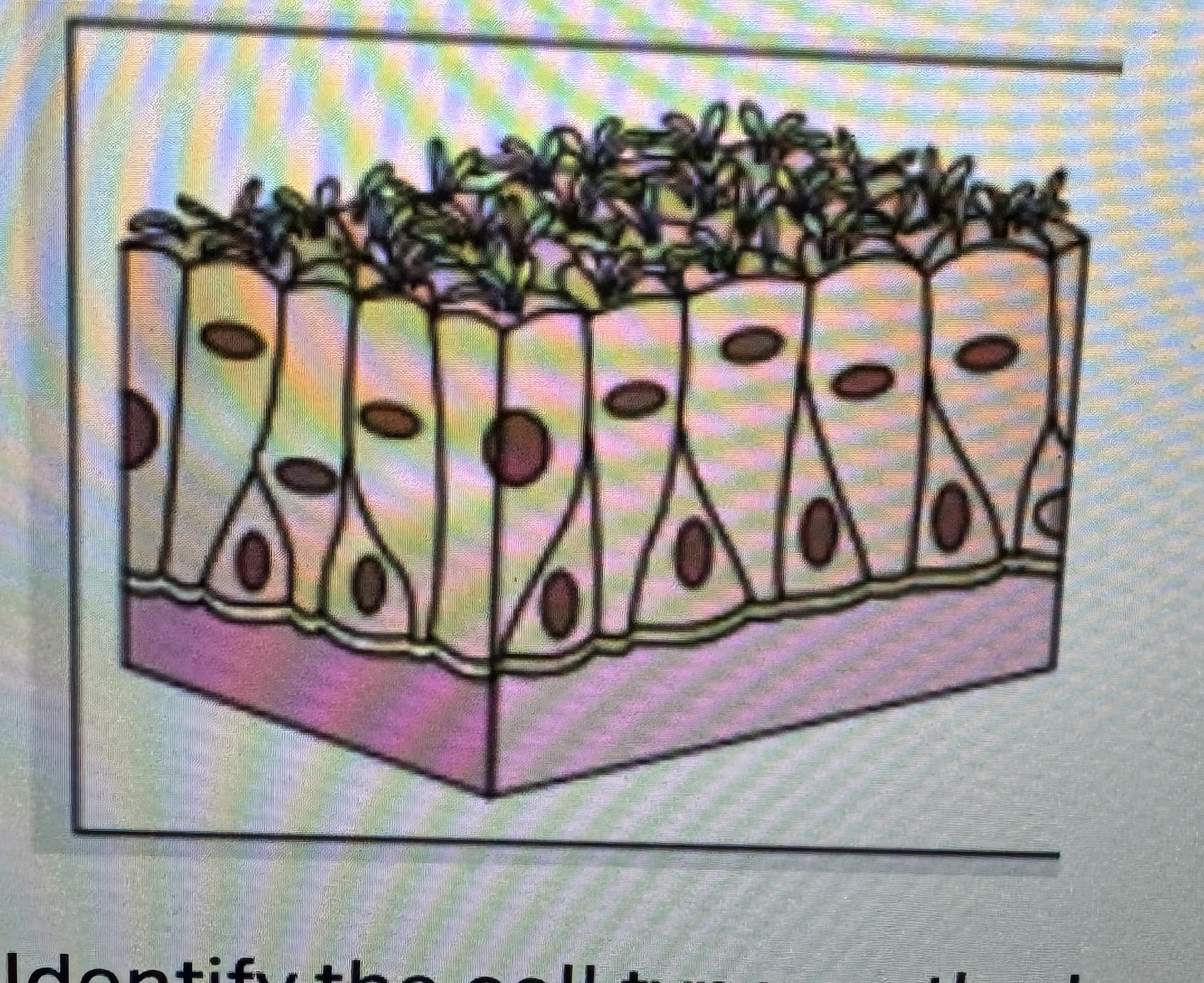
Label identify classify cell type
Pseudo stratified epithelium
Found in the respiratory tract
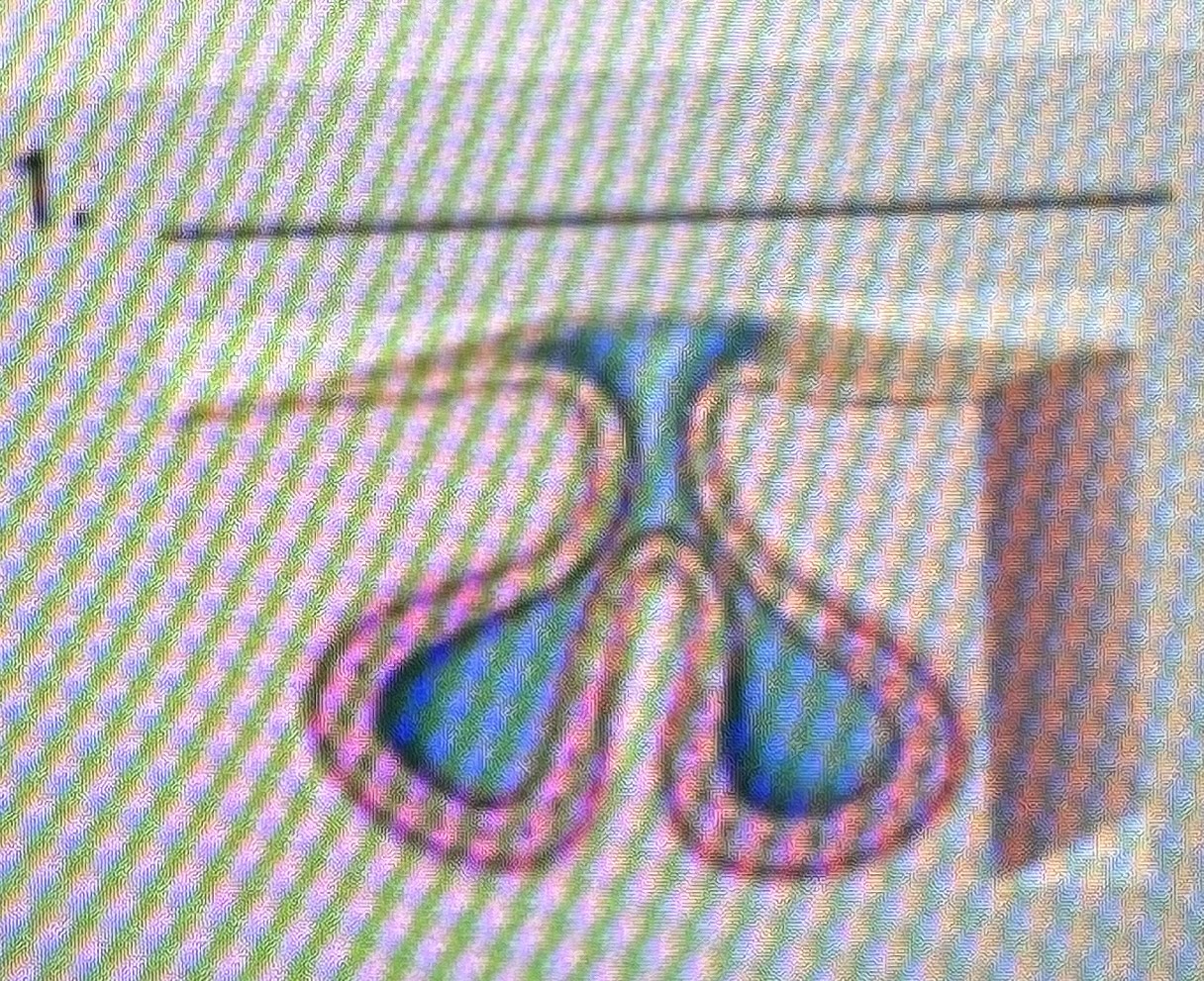
Classify the type of exocrine gland
Simple branched alveolar
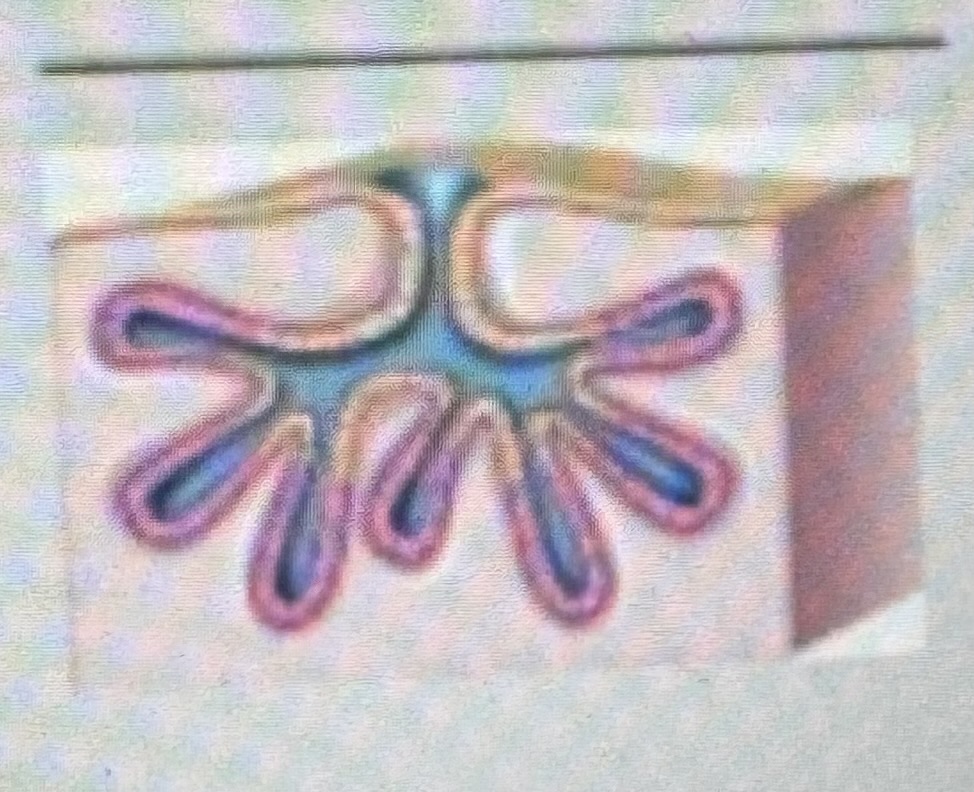
Classify the type of exocrine gland
Branched alveolar
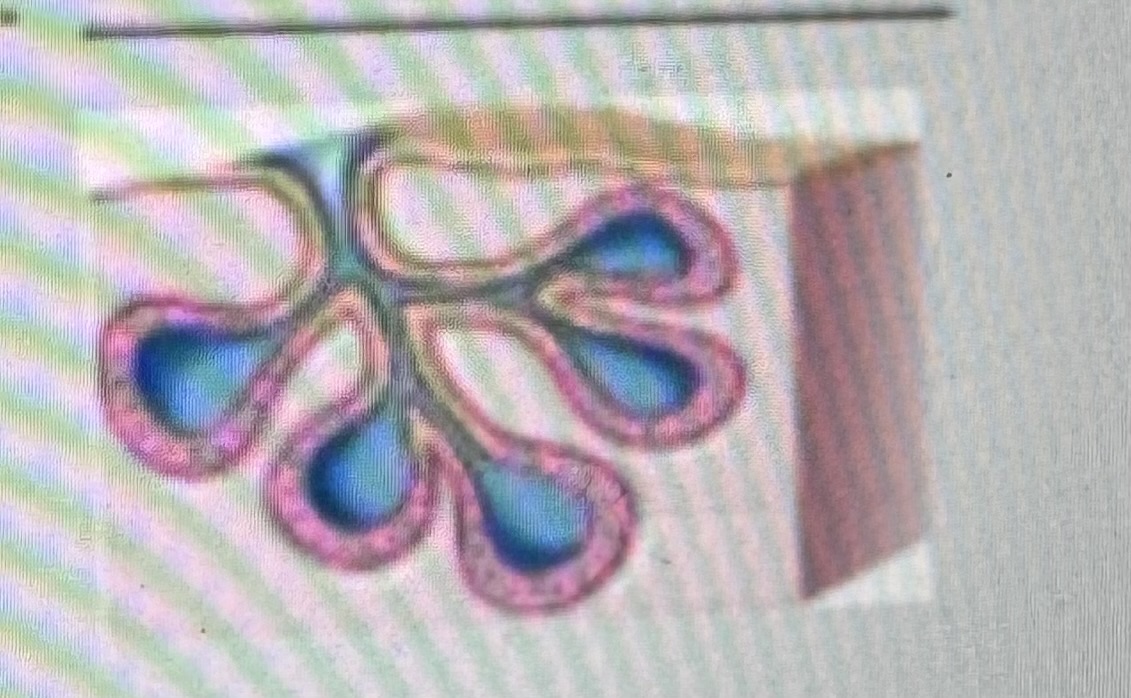
Classify the type of exocrine gland
Compound alveolar
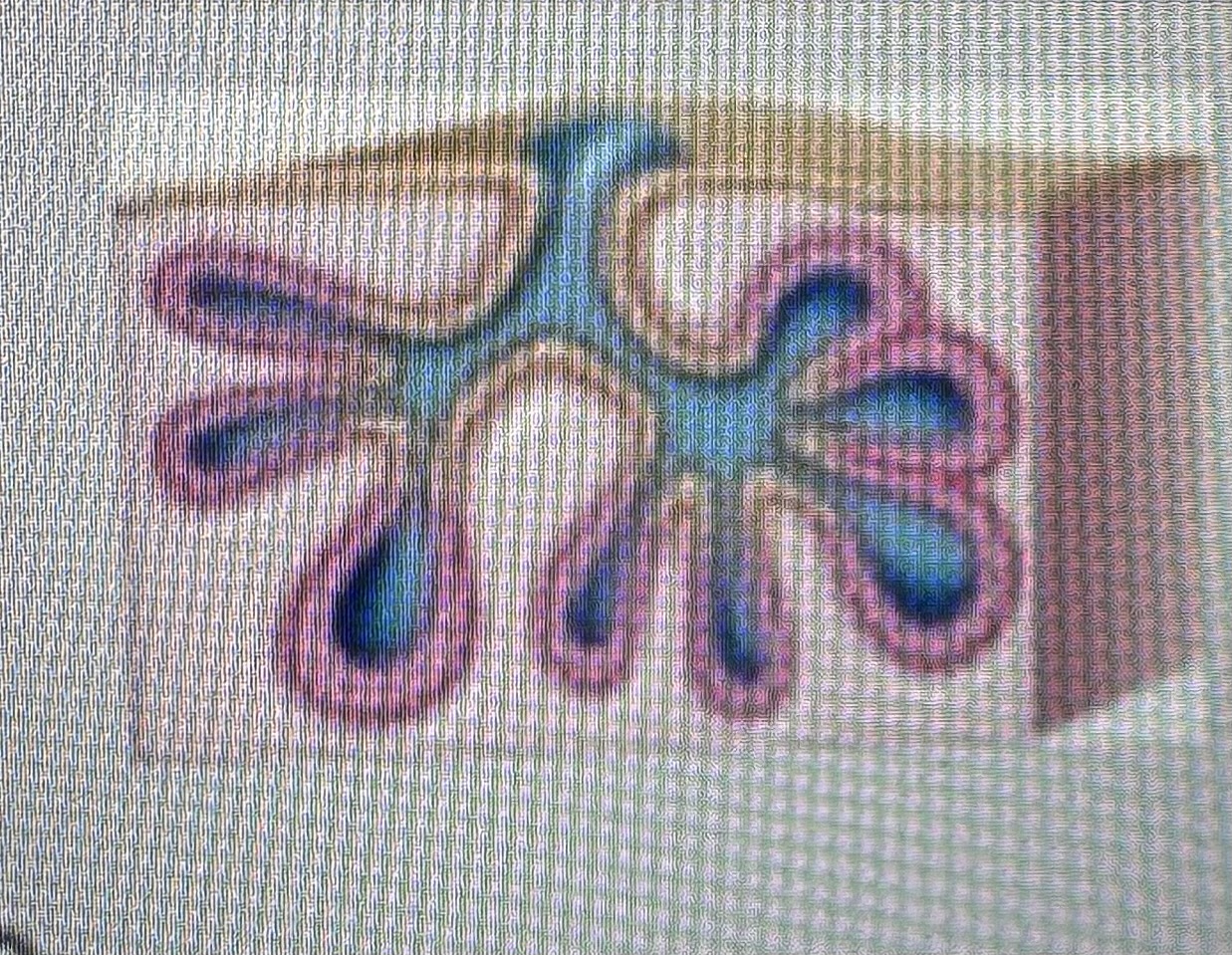
Classify the type of exocrine gland
Compound tubuloaveolar
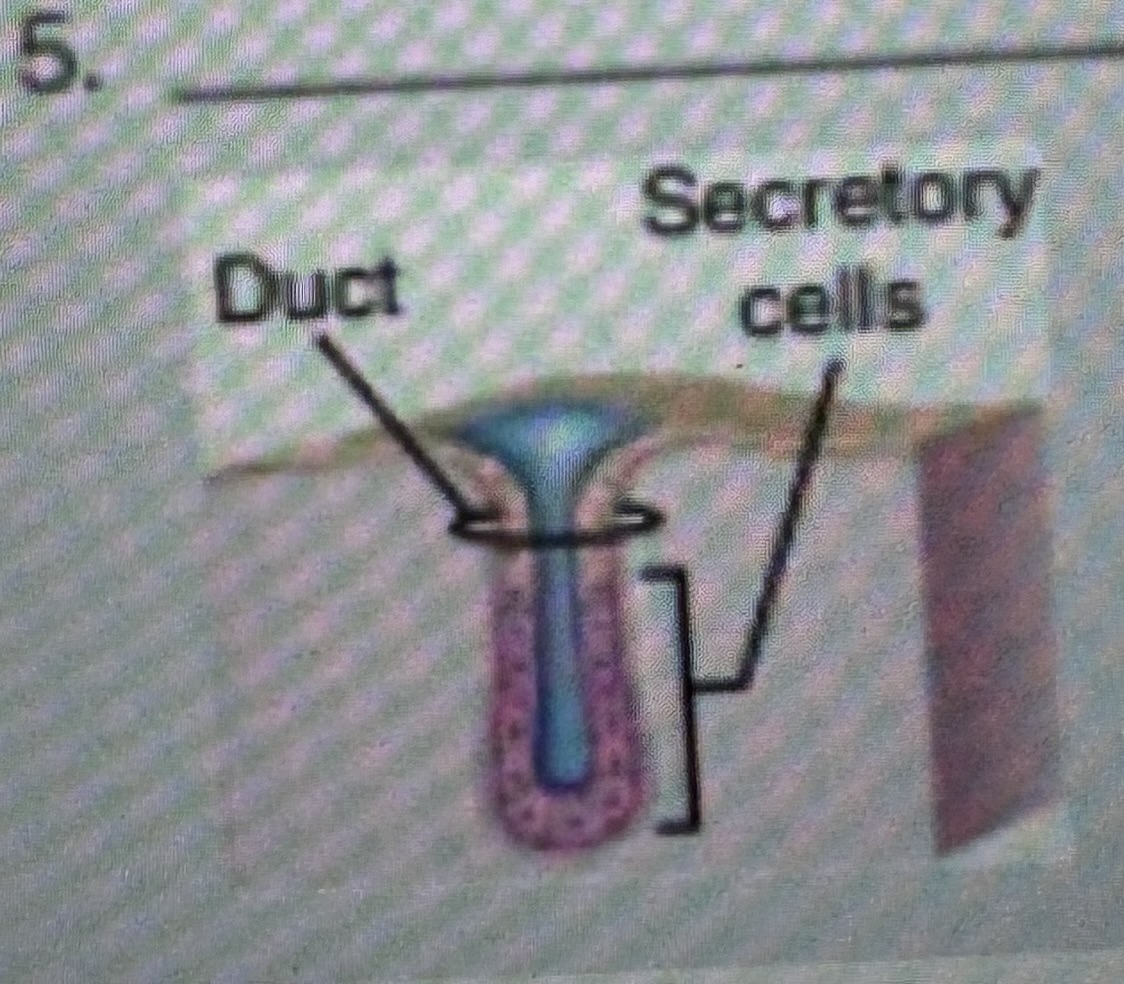
Classify the type of exocrine gland
Simple tubular
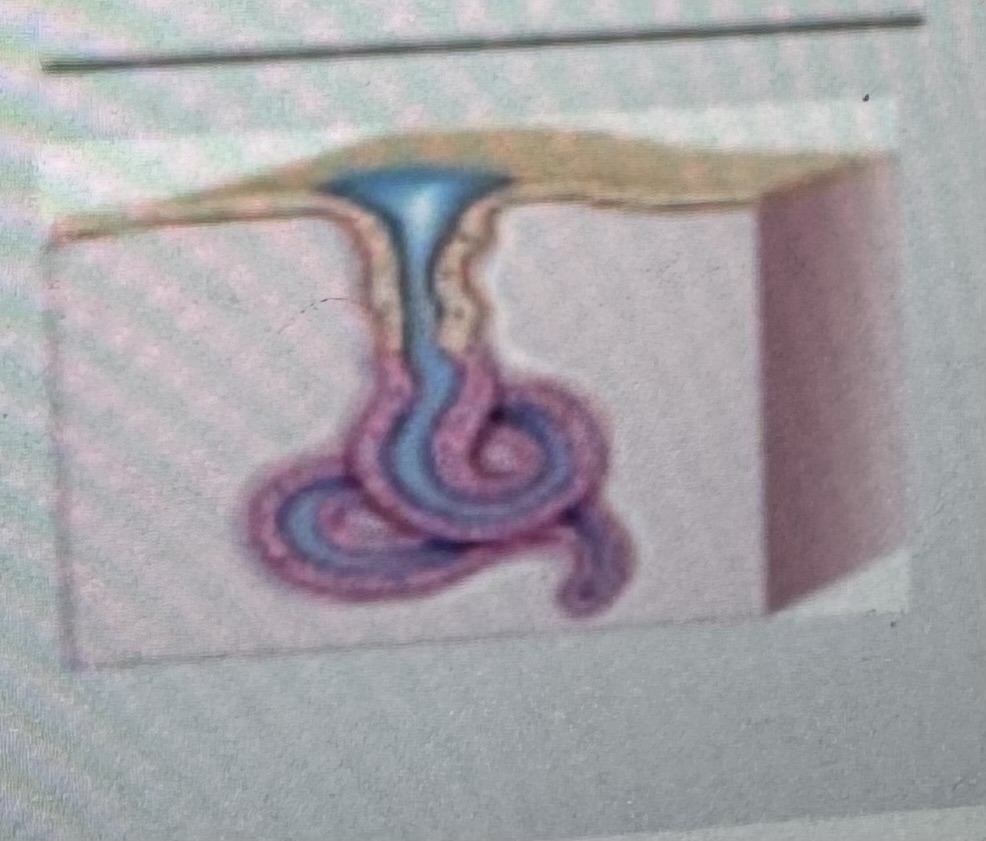

Classify the type of exocrine gland
Simple coiled tubular
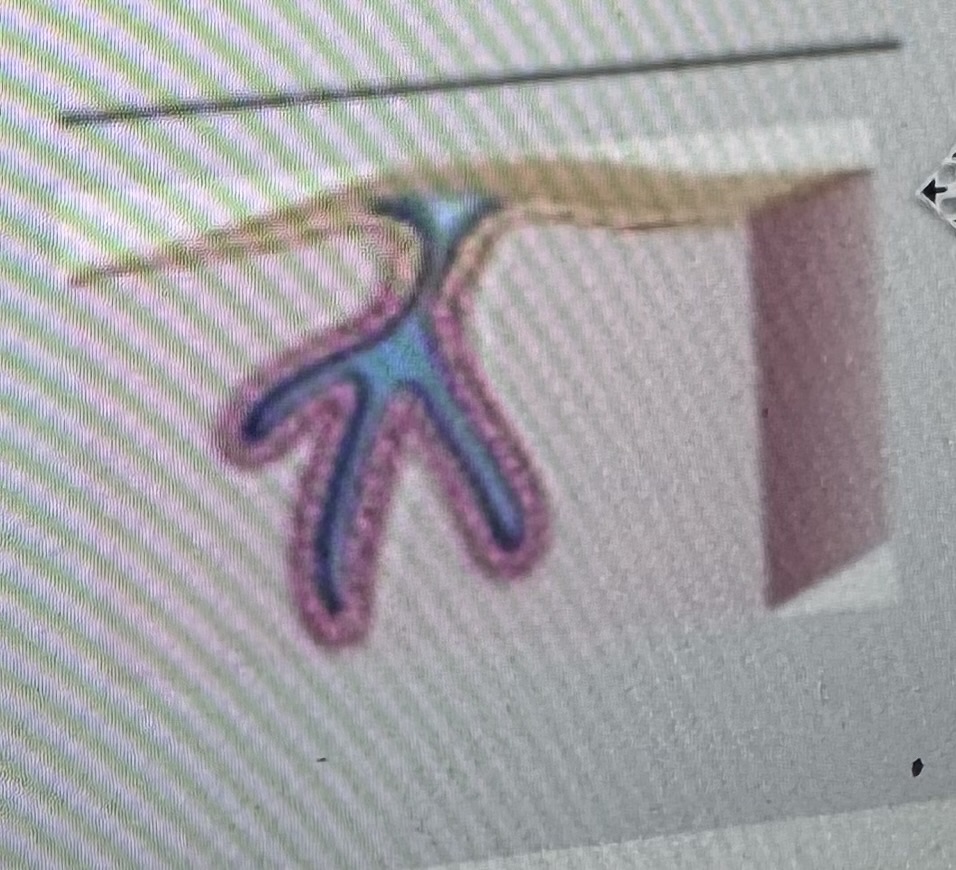
Classify the type of exocrine gland
Simple branched tubular
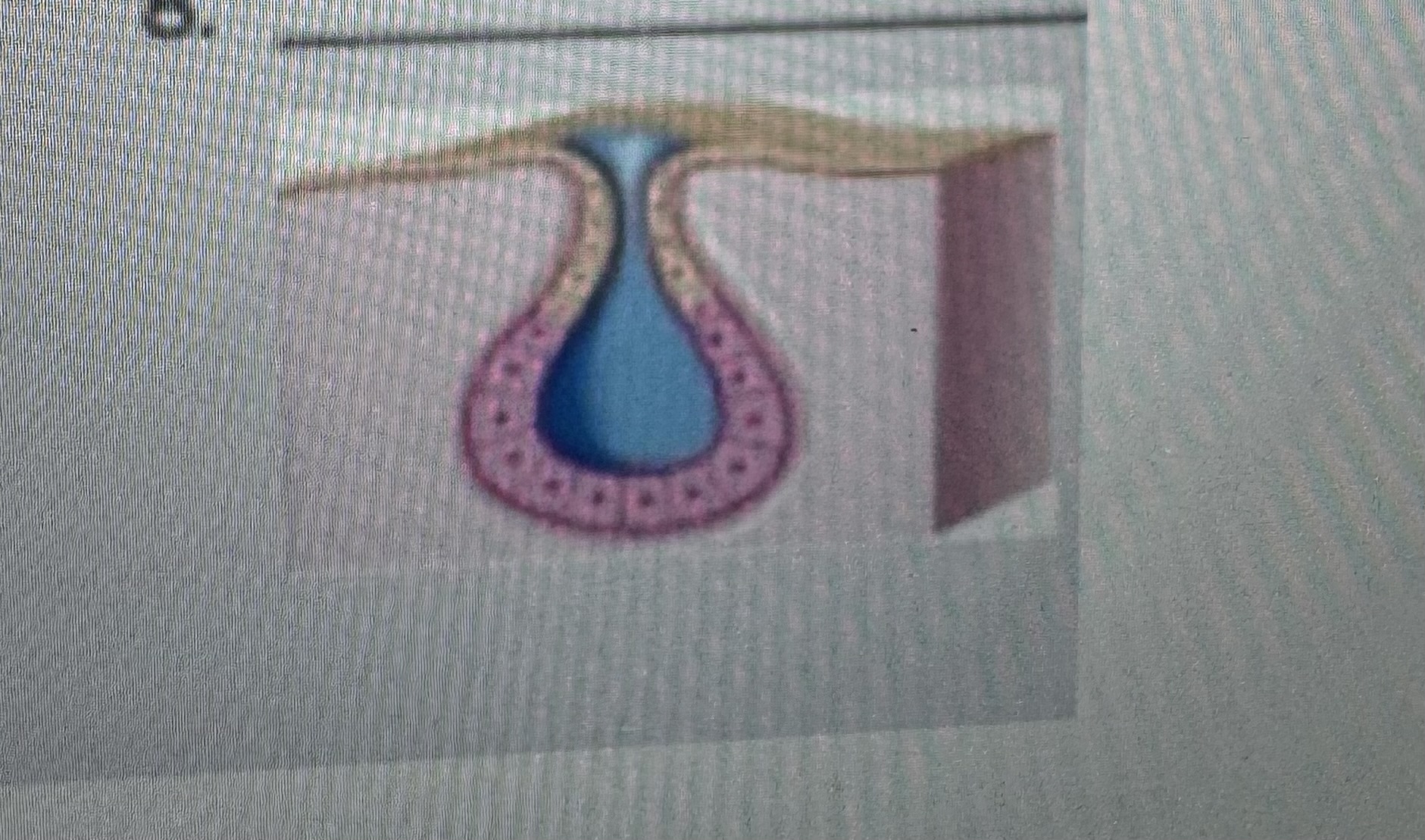
Classify the type of exocrine gland
Simple alveolar
Cranial nerve l - Olfactory Nerve
Function: sense of smell
Type of nerve: sensory
Cranial Nerve ll - optic nerve
Function: vision
Type of nerve: sensory
Cranial nerve lll - Oculomotor
Function : controls the superior oblique muscles, pupil constriction, and lens shape
Type of nerve : motor
Cranial Nerve V - Trigeminal
Function: sensation of the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing.
Type of nerve: both sensory and motor.
Cranial Nerve VI - Abducens
Function: controls the lateral rectus muscle; responsible for outward gaze.
Type of nerve: motor.
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial
Function: controls facial expressions, taste sensations, and production of saliva and tears.
Type of nerve: both sensory and motor.
Cranial Nerve VIII - Vestibulocochlear
Function: responsible for hearing and balance.
Type of nerve: sensory.
Cranial Nerve IX - Glossopharyngeal
Function: taste from the posterior one-third of the tongue and assists in swallowing.
Type of nerve: both sensory and motor.
Cranial Nerve X - Vagus
Function: regulates heart rate, controls digestive tract, and affects voice.
Type of nerve: both sensory and motor.
Cranial Nerve XI - Accessory
Function: controls the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles; responsible for head movement and shoulder elevation.
Type of nerve: motor.
Cranial Nerve XII - Hypoglossal
Function: controls tongue movements for speech and swallowing.
Type of nerve: motor.
Cranial Nerve I - Olfactory
Function: sense of smell.
Type of nerve: sensory.