Physics-Topic 2 Electricity
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What are ohmic conducters?
Components that follow ohms law
Frequency of Uk mains?
50 Hz
What is current?
The flow of particles (called electrons) though wires and components
Potential difference of uk mains?
230v
What is current measured in?
Amps
What is potential difference?
A measure of the amount of energy needed to move a charges
What is P.D measured in?
Volts
What is resistance?
A measure of the difficulty of passing an electric current through a conducting material
What is resistance measured in?
Ohms
Ohms law?
At a constant temperature, for a fixed resistor, the potential difference across it is directly proportional to the current through it
What is the current and voltage like in series circuits?
Current is the same and voltage is shared
What is the current and voltage like in parallel circuits?
The current is shared but the voltage is the same
Ohmic conductor example?
Fixed resister at constant temp
How does a light bulb work?
Current goes through a filament which heats up and glows, non-ohmic conducter
What is the correlation between temperature and resistance in light bulb?
When the temp increases so does the resistance
What are diodes?
Non-ohmic conducter, only let current flow one way, the resistance is constantly changing
What is the corralation between a current and resistance and current in a diode?
When the current decreases the resistance increases
What is a thermister?
A resister made of semiconductors with a resistance that varies with temp
What is the link between temp and resistance in a thermistor?
The higher the temp the lower the resistance
What is the link between light and resistance in an LDR?
When light shines on it the resistance varies, resitance decreases as light increases
What is the rule about total resistance in Parralel circuits?
total resistance is always less than the smallest individual resistor
Relationship between current and resistance in parralel?
Inversely proportional
What is a D.C?
direct current
Only flows in one direction forever
E.g. cells and batteries
What is A.C?
alternating current
Current constantly change direction
E.g mains like lights and plugs
In uk it switches 50 times a second , uk frequency is 50Hz
Graph for alternating current?
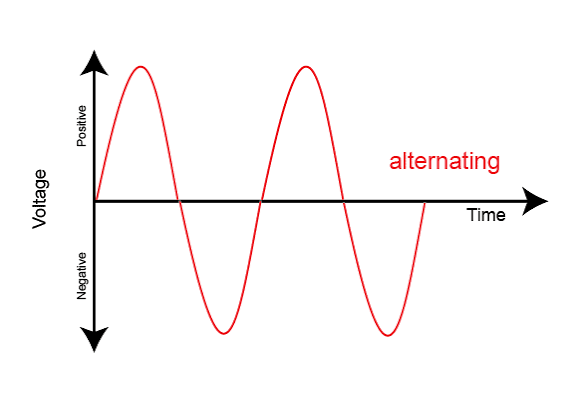
Graph for direct current?

What is the national grid?
A national network of high voltage cables and transformers
Order of the national grid?
power station
Step up transformers
Pylons
Step down transformers
Industry
Homes
What do step up transformers do and why?
raises the P.D from 12,000 volts to 400,000 volts
This reduces the current and so reduces the thermal energy transfer
Making the transmission more efficient
What do step down transformers do?
reduce voltage down to 230V so it can be used in homes safely
Live wire
Brown
Volts 230, provides alternating potential difference
Neutral wire
Blue
Completes circuit , current flows through live and neutral
0v
Earth wire?
0v
Green and yellow
Safety
Carries current to ground if there is a fault
Fuse?
safety measure
Melts if the current is too string
What is static electricity?
friction between rubbing surfaces that causes a transfer of electrons
When does static electricity work?
only word on insulation materials as conducted (e.g metals) have a sea of delocalised electrons and so can just replace any lost electrons