IB Biology Year 1 - Cell Theory, Water, and Microscopes
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Which living structures are an exception to the cell theory?
An aseptate fungal hyphae
Striated muscle fiber
A red blood cell is 8 μm in diameter. If drawn 100 times larger than its actual size, what diameter will the drawing be in mm?
800 micrometers → 0.8mm
Compare & contrast the terms adhesion and cohesion in the context of water molecules in biological tissues
Adhesion and cohesion are both used in capillary action which is when water is transported from the roots of the plant to it leaves, through the xylem. Adhesion, however, is used so that the water molecules can latch onto the xylem itself, while cohesion is rather for the water molecules to bond with each other; despite their differences, both of them work in harmony to ensure capillary action works.
A student draws a white blood cell with a length of 5.8cm. She was viewing it under oil immersion (1000x). She already determined that the low power (40x) had a FOV diameter of 3.6mm.
a) What is the FOV diameter under high power (1000x)?
b) What is the magnification of the white blood cell sketch if you learn the WBC is actually 14 micrometers long?
a) The FOV diameter under high power is around 0.1mm.
Formula: FOV diameter = Field Number / (Objective Magnification x Eyepiece Magnification)
b) The magnification of the WBC is 4100x.
Which of the following will not dissolve in water?
Nonpolar substances (oil, sand, and most plastics) AND lipids
Between air and water, which has greater:
buoyancy
thermal conductivity
viscosity
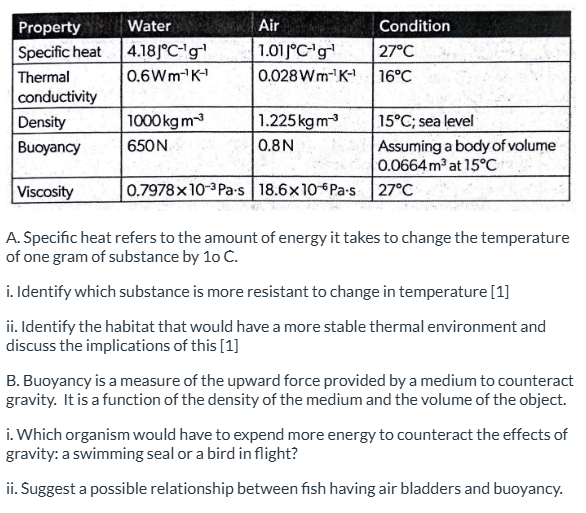
Air has less density than water; thus, it has less buoyancy, so water has greater buoyancy
Water has a significantly higher thermal conductivity than air, meaning it can conduct heat much more efficiently.
Water is more viscous than air
Viscosity = thickness!!
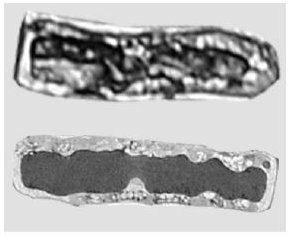
The images are microscopic views of two similar cells. What is a reason for the differences between the two micrographs?
The lower image has greater resolution.
Consulting the hierarchy of life, what is the basic unit of life?
the cell!
What fall into the respective categories:
Common to all cells
Not common to all cells
Common to all cells
Ribosomes
DNA
Cytoplasm
Cell Membrane
Not common to all cells
Chloroplast
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Cell wall
What is Inductive Reasoning and what is Deductive Reasoning? Give examples of each.
Inductive Reasoning:
SIG (Specific, Inductive, General)
Ex: My dog loves bacon, your dog loves bacon so all dogs must love bacon
Deductive Reasoning:
Ex: All humans being have a pancreas. Titus is a human, therefore he has a pancreas.
What is:
Magnification?
Resolution?
Magnification: how much larger an object appears compared to its real size.
Resolution: the smallest interval distinguishable by the microscope, which then corresponds to the degree of detail visible in an image created by the instrument.

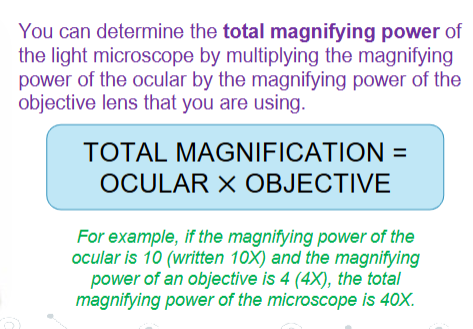
How do you calculate the total magnifying power of the light microscope?
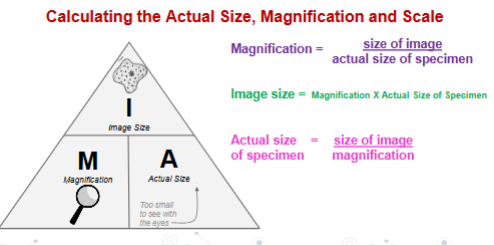
How do you calculate the Actual Size, Magnification and Scale?
This type of imaging makes use of antibodies to target specific proteins for staining?
Immunofluoresence
This type of imaging uses electrons and a technique to split membranes open to view structures within the plasma membrane.
Freeze-Fracture
Compound Light Microscope
Benefits and Limitations
Use multiple lenses to bend light and magnify images.
Benefits:
● Ease of use
● Less expensive to buy
● Can observe dead or living cells in color
● Cell movement can be studied
● Quick specimen preparation (minutes to hours)
● No need for high voltage electricity
Limitations:
● Maximum magnification of about 1500X
● Low resolving power (0.25μm to 0.3μm)
Electron Microscope
Benefits and Limitations
Use electron beams focused by electromagnets to magnify and resolve.
Benefits:
● Magnification of 100,000X to 300,000X
● High resolving power (0.001μm)
Limitations:
● Expensive to use
● Requires cells to be killed and chemically
● No movement can be seen
● Without stain or dye, no color* can be seen
● High voltage electric current is required
● Specimen preparation usually takes few days
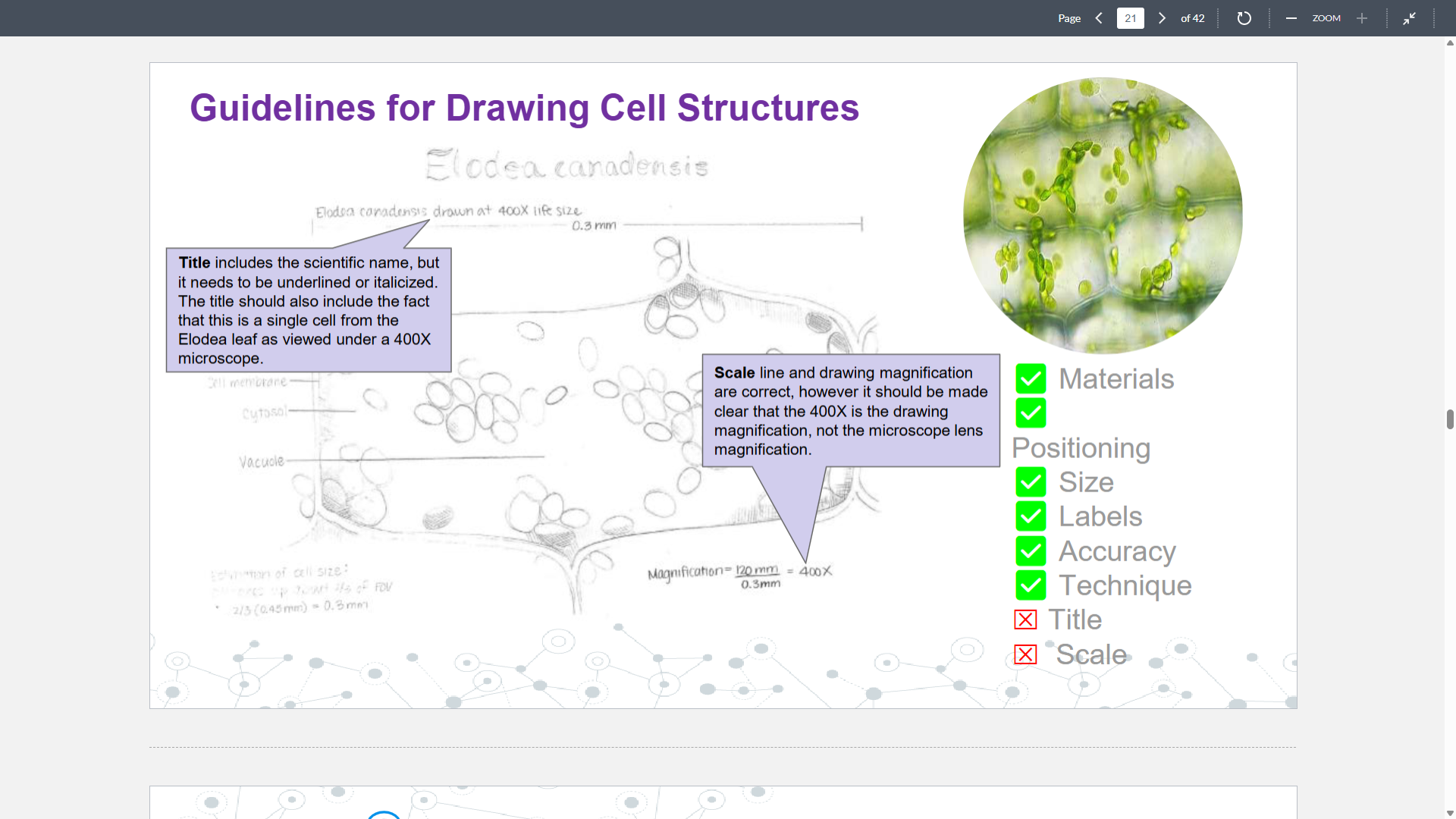
Draw dis cell man!! And label it!!
(Keep in mind of what IB wants…)
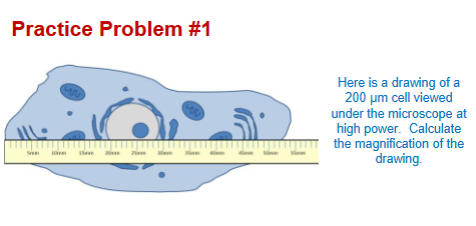
How do you calculate high or medium power FOV?

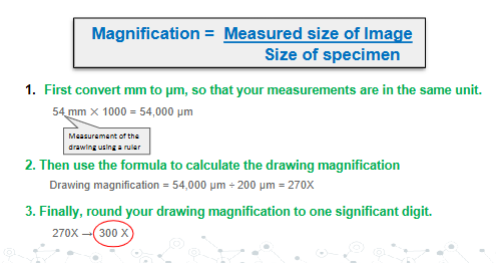
Answer #1

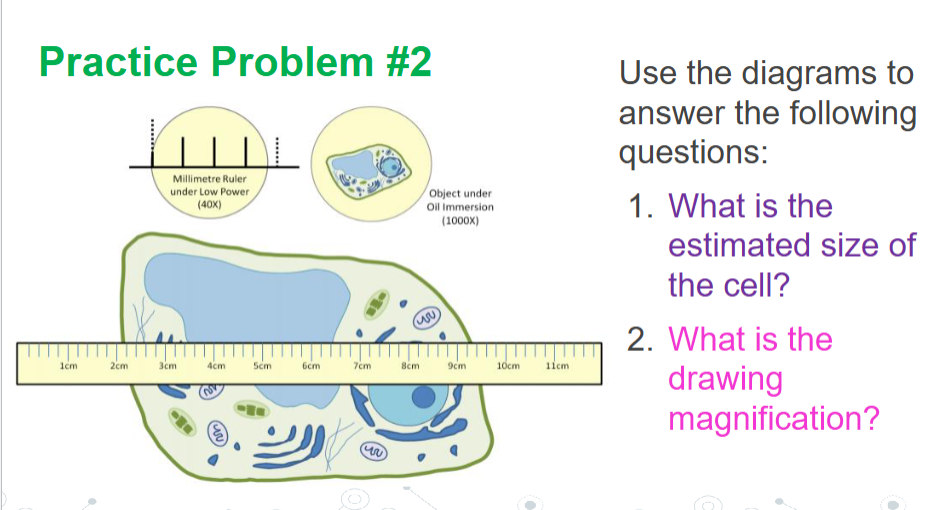
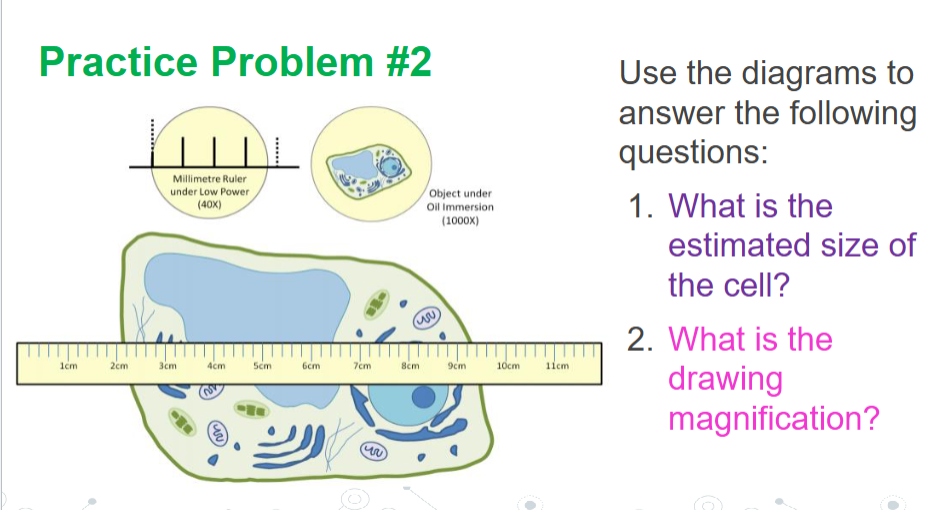
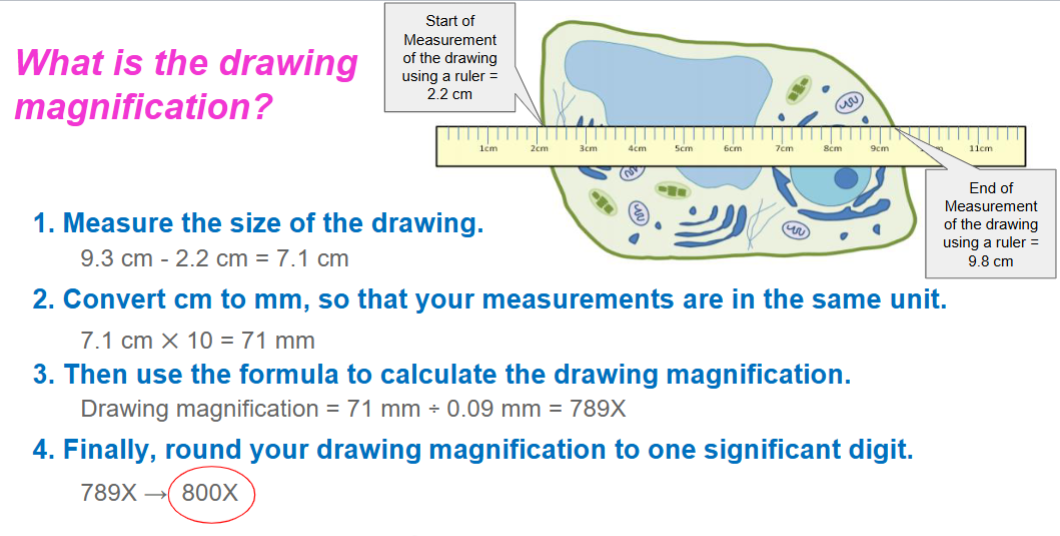
Answer #2
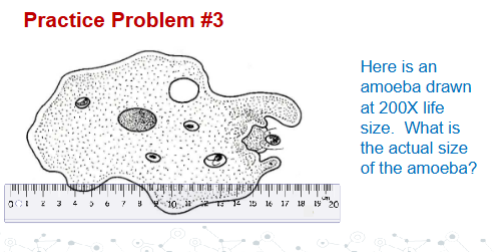

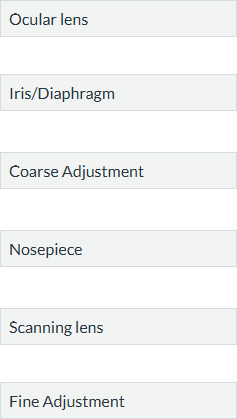
Connect the structures to their respective functions in a microscope

A.
i. Water is more resistant to temperature change.
ii. The environment that is most stable for temperature change is water, meaning aquatic organisms are able to resist drastic changes in their environment due to water’s high specific heat.
B.
i. A bird expends more energy.
ii. Fish inflating it’s bladder combats water’s higher density, as it makes the fish less dense, allowing the density of the fish to reduce as well and making it more buoyant.

Identify the 3 parts of the cell theory
Cells are the basic unit of life
All livings things are made of at least one cell
Cells arise from preexisting cells
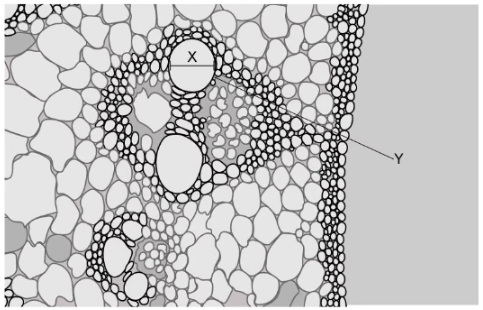
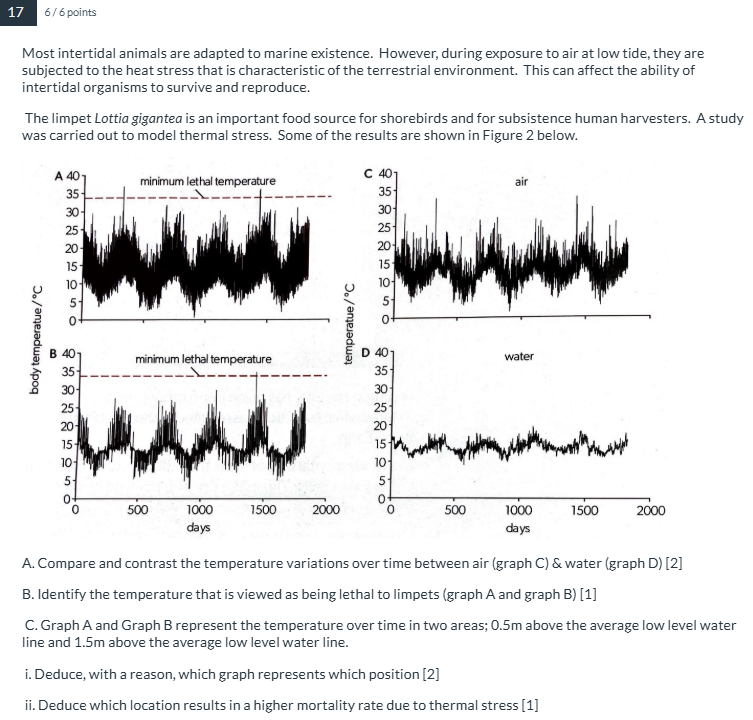
The electron micrograph below shows a root vascular system. The magnification of the image is x200. A student uses a ruler to measure distance X and finds it to be 10 mm. What is the diameter of the cell labelled Y?
50 micrometers
Which functions of life are carried out by all unicellular organisms?
Response, homeostasis, metabolism and growth
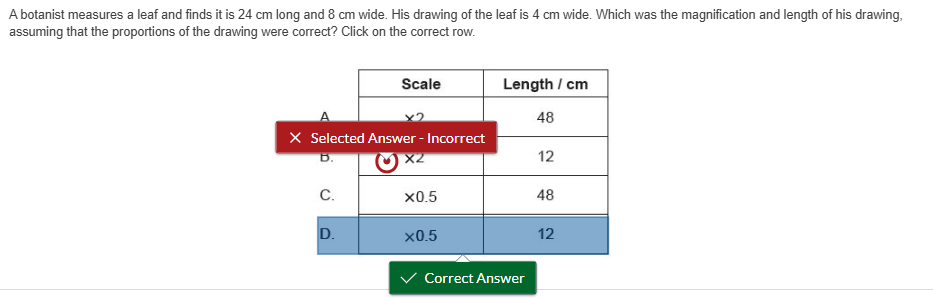
A botanist measures a leaf and finds it is 24 cm long and 8 cm wide. His drawing of the leaf is 4 cm wide. Which was the magnification and length of his drawing, assuming that the proportions of the drawing were correct? Click on the correct row.
This method of microscopy would be best suited to determining the shape of a protein while it performs a function, such as contracting.
cryogenic electron microscopy

The diagrams show a virus and a bacterium. The length of the scale bar with a ruler of the virus is measured to be 25 mm. The length of the scale bar with a ruler of the bacterium is measured to be 40 mm. Calculate the magnification of the virus.


The diagrams show a virus and a bacterium. The length of the scale bar with a ruler of the virus is measured to be 25 mm. The length of the scale bar with a ruler of the bacterium is measured to be 40 mm. Calculate the magnification of the bacterium. Do not include units.
40,000x
Which property of water accounts for its moderating effects on the Earth’s atmosphere?
Thermal capacity—specifically high specific heat capacity
Water striders of the Gerridae family of insects have areas of their legs covered with a hydrophobic substance. What property of water makes it possible for them to walk on its surface?
Cohesion of water molecules
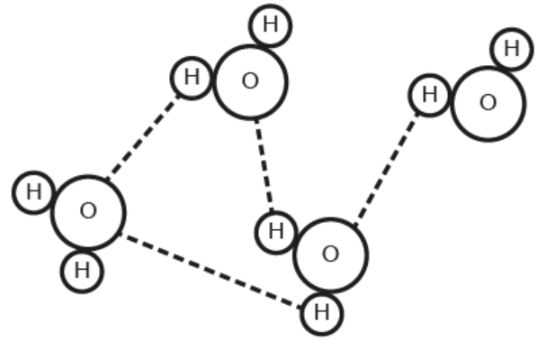
The diagram shows water molecules. Which property of water is not illustrated?
Adhesion
Which of the following substances are transported in lipoprotein complexes because they cannot dissolve in the blood plasma?
Fat molecules (non-polar)
Cholesterol (non-polar)
What property of water accounts for its usefulness as a coolant in sweat?
High latent heat of vaporization
latent is converting liquid to gas which is what sweating does
High specific heat isn’t what is doing the cooling.
What allows the movement of water under tension in the xylem?
Cohesion of water molecules due to hydrogen bonding
At room temperature, water is a liquid and methane is a gas. Which molecular property explains this difference?
Higher boiling point of methane
When it talks about states of matter, just thinking about boiling point only
Biological systems are sensitive to temperature changes, so they have mechanisms to resist temperature changes.
Distinguish between one thermal property of air and water as they relate to the habitat of animals. Include an example.
As it becomes winter, air tends to have lower specific heat capacity and is colder than water.
Water also has high thermal conductivity, which is not beneficial for people, as it would take away human heat, animal seals have fat (blubber) to resist temperature change → water has higher thermal conductivity even though it has lower specific heat. Put seal on land, blubber would overheat it
Where do hydrogen bonds form between water molecules?
Hydrogen bonds form between the oxygen of one water molecule and the hydrogen of another.
What is the term for the attraction of water molecules to other water molecules?
Cohesion