hearing science quiz
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
masking
interference that one stimulus causes in the production of another stimulus
masking efficiency
difficulty that the masker provides in the detection of the signal
2 types maskers
tonal and noise
psychoacoustic tuning curve
threshold of tonal detection with tonal masker
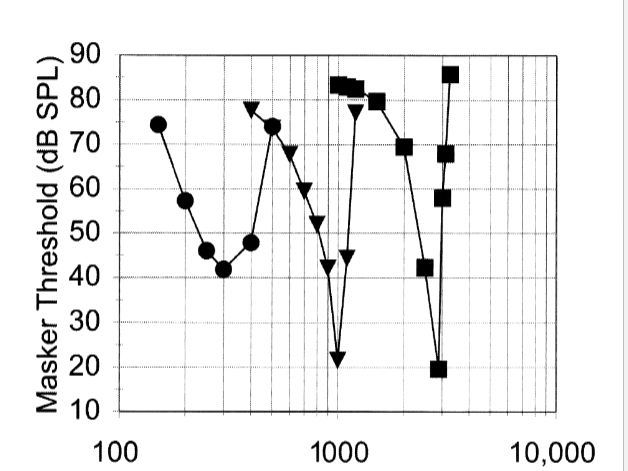
factors influencing masking efficiency
noise frequency and noise level
auditory filter
process where the ear separates different sound frequencies, allowing us to perceive and distinguish various sounds
broad bandwidth
range of frequencies a hearing device can process and amplify
equivalent rectangular bandwidth (ERB)
gives an approximation to the bandwidths of the filters in human hearing
auditory filter function
determines frequency selectivity
notch noise method
varying the width and position of the notch relative to the signal frequency and measuring the signal threshold
simultaneous masking
signal and masker are present at the same time
forward masking
signal follows the masker
backwards masking
masker follows the signal
loudness
attribute of auditory sensation where a sound is ranked based on a scale of quiet to loud
2 ways to measure loudness
matching and scaling
matching method
listeners are asked to adjust the level of the target sound to match the loudness of the reference sound
reference sound: 1 kHz
tone: 40, 50…db SPL
scaling method
listeners are asked to scale a sound relative to the loudness of the reference sound
reference sound: 1 kHz
tone: 40 db SPL defined as 1 sone
equal loudness contour
matching method, frequency dependent
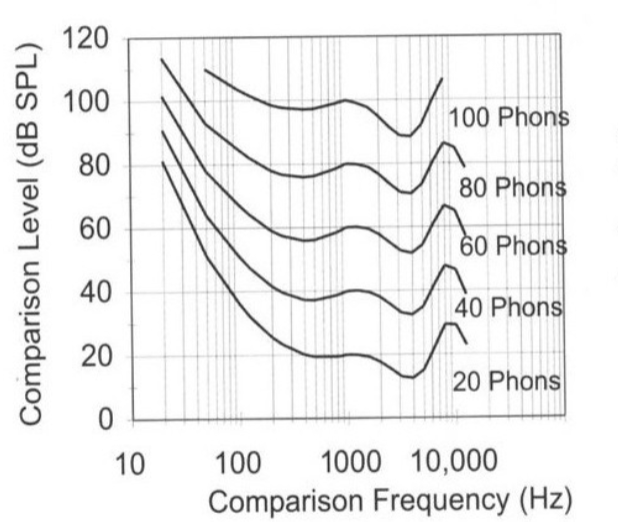
loudness growth function
describes how the perceived loudness of a sound changes as its intensity increases
factors influencing loudness
frequency (broadband/narrowband), intensity level, duration