Animal Anatomy and Physiology
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 1 flash cards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
List the components of the mammalian cell
Mammalian cells consist of several key components:
Nucleus - contains genetic material
Mitochondria - ATP production
Ribosomes
Rough ER - has ribosomes on surface and synthesises proteins
Smooth ER - Synthesis of lipid & steroid production
Golgi apparatus - modification of some proteins
Lysosomes - digestion of foreign debris
Centrsome
Plasma Membrane
separates cell from environment
Controls passage of substances
Phospholipid bilayer
What are the 4 types of selective permeability
Simple diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Exocytosis & Endocytosis
Active Transport
Simple Diffusion
Passive
small components easily pass
Exocytosis & Endocytosis
Active
Taking or bringing something
Uses vesicles (small membrane bound structure that holds things)
Active Transport
requires pumping of molecules against their concentration gradient, using energy (ATP) to move substances into or out of the cell.
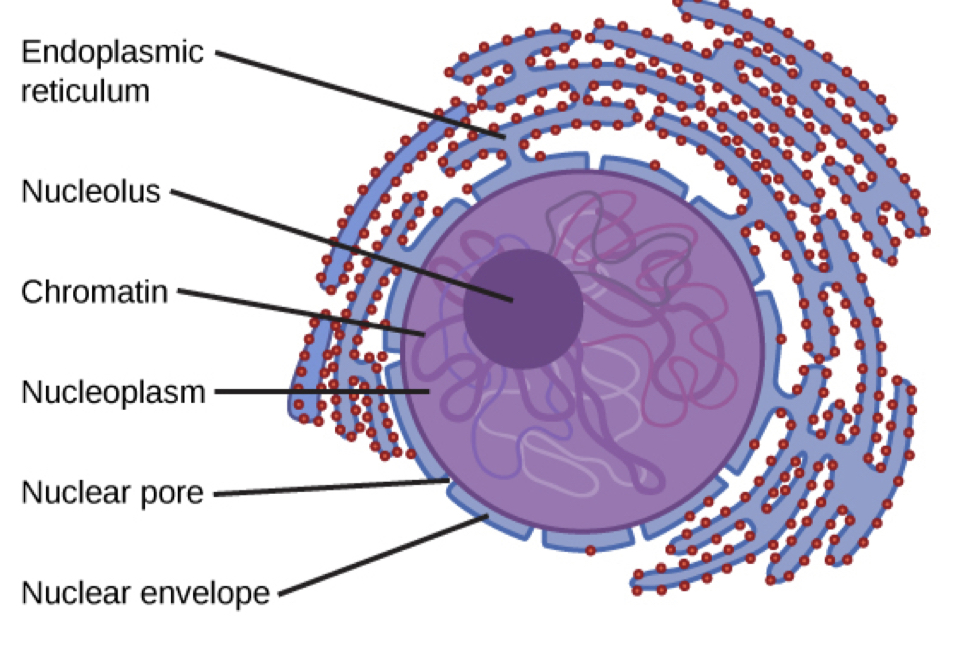
The Nucleus contains (6 total)
Endoplasmic reticulum
Nucleolus - produces ribosomal subunits and rRNA, and loosely hanging genetic material (chromatin)
Chromatin - condenses into chromosomes at division
Nucleoplasm - gel like substance in the nucleus
Nuclear pore - allows mRNA to escape into the cytoplasm
Nuclear envelope (membrane) - is continuous with ER membrane
Mitochondria contains…
Smooth outer membrane
highly folded inner membrane
electron transport chain enzymes
ATP Production
the process of generating adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through cellular respiration, which occurs in the mitochondria and involves glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Glycolysis
Location: Cytoplasm
Start: Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆)
End: 2 Pyruvate (3C)
ATP Yield: Net 2 ATP (4 produced, 2 used)
Other Products: 2 NADH (used in aerobic respiration)
Fate of Pyruvate:
Aerobic: Converts to Acetyl-CoA for Krebs cycle
Anaerobic: Converts to Lactate (animals) or Ethanol + CO₂ (yeast)
each step is catalyzed by its own enzyme ( 10 total enzymes)
Pyruvate Oxidation
Pyruvate oxidation is the linking step between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle in aerobic respiration. It occurs in the mitochondrial matrix and is catalyzed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC).
What reaction converts pyruvic acid into acetyl CoA and where does this occur in the cell?
Pyruvate+NAD++CoA→Acetyl-CoA+CO2+NADH
Mitochondrial Matrix
Kreb’s/Citric Acid/ Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle
-3CO2
-3 NADH
-1 IAOH
-1 ATP
2 x
Electron Transport Chain
Location: Inner mitochondrial membrane
Start: NADH, FADH₂, O₂, ADP + P
End: ATP, H₂O, NAD⁺, FAD
ATP Yield: ~34 ATP per glucose
Process Steps:
NADH & FADH₂ donate electrons to the ETC.
Electrons move through complexes, pumping H⁺ into the intermembrane space.
O₂ is the final electron acceptor, forming H₂O.
H⁺ flows through ATP synthase, generating ATP (chemiosmosis).
Other Products: H₂O, recycled NAD⁺ & FAD
Requires Oxygen? ✅ Yes (Aerobic Process)
What are transcription factors?
Transcription factors - proteins that regulate transcriptions of genes
What are the two types of transcription factors, and what do they do?
Enhancer - bind stimulatory (activator) factors
Repressor - bind inhibitory (silencer) factors
In what 3 ways can activators stimulate transcription factors?
Recruit transcriptional machinery
Chromatin remodeling
Stimulate RNA polymerase
What are the 3 big steps of translation?
Initiation (starting it)
Elongation
Termination
What are Post-Translational Modifications?
Regulates protein compartmentalization/trafficking and activity
What is Phosphorylation of a transcription factor?
A common way to turn things on/off (change activity of a protein)