APES: Aquatic Biomes
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
KEY TERMS
1. watershed
2. delta
3. estuary
4. wetland
5. thermocline
6: freshwater zones: littoral, limnetic, profundal, benthic
7. barrier island
8: saltwater zones: euphotic, bathyal, abyssal, coastal
9. upwelling
10. aquifer
11. unconfined aquifer
12. confined aquifer
13. riparian
watershed (drainage basin)
the land area that drains into a particular stream
delta
deposited sediments at the mouth of the river
freshwater
- contains mim salt
- comes from the precipitation which reaches lakes, rivers, and groundwater bodies directly or melting of ice or snow
river mouth
part of the river that flows into the ocean
wetlands
- ecosystems, where the land is at least partially flooded during the year
- can be FRESHWATER or SALTWATER: swamps, marshes, bogs, fens, estuaries
- serve as nurseries many species of birds, fish, shellfish
- plants are adapted to moist conditions - lilies, cattails, iris, cypress, and gum trees
estuaries
- type of wetland
- occur at the river mouth, salt and fresh water mix
- HIGH PRODUCTIVITY AND SPECIES RICHNESS b/c freshwater has a high concentration of nutrients and sediments
- shallow, warm waters so animals receive sunlight
- salmon, sea trout, and migratory birds here, crabs
mangroves
- type of wetland
- trees that grow in salt water
- occur along shallow, calm, tropical coastlines
- help stabilize coastlines and they protect fish, shrimp, species (spawning beds)
- vulnerable to development, overuse
- unlike reefs, mangroves provide commercial timber, and they can be clear-cut to make room for aquaculture
marshes
- wetlands WITHOUT trees
- HIGH PRODUCTIVITY AND BIOLOGICALLY DIVERSE because shallow waters allow for photosynthesis
swamps
- wetlands with trees
- high biological activity because shallow water allows for photosynthesis
bogs
- wetlands w/ deep layers of undecayed vegetation, PEAT
- mainly fed by precipitation
- low biological activy because nutrient-poor soil
fens
- similar to bogs
- except there are mainly fed by groundwater, so they have mineral-rich water and specially adapted plant species
- low biological activity because nutrient-poor soil
wetland losses
- wetlands can gradually convert to terrestrial communities as they fill w/ sediment, vegetation gradually fills towards the center
- process is accelerated by increased sediment loads from human urban development, farms and roads.
- 50% of wetlands in US have been degraded
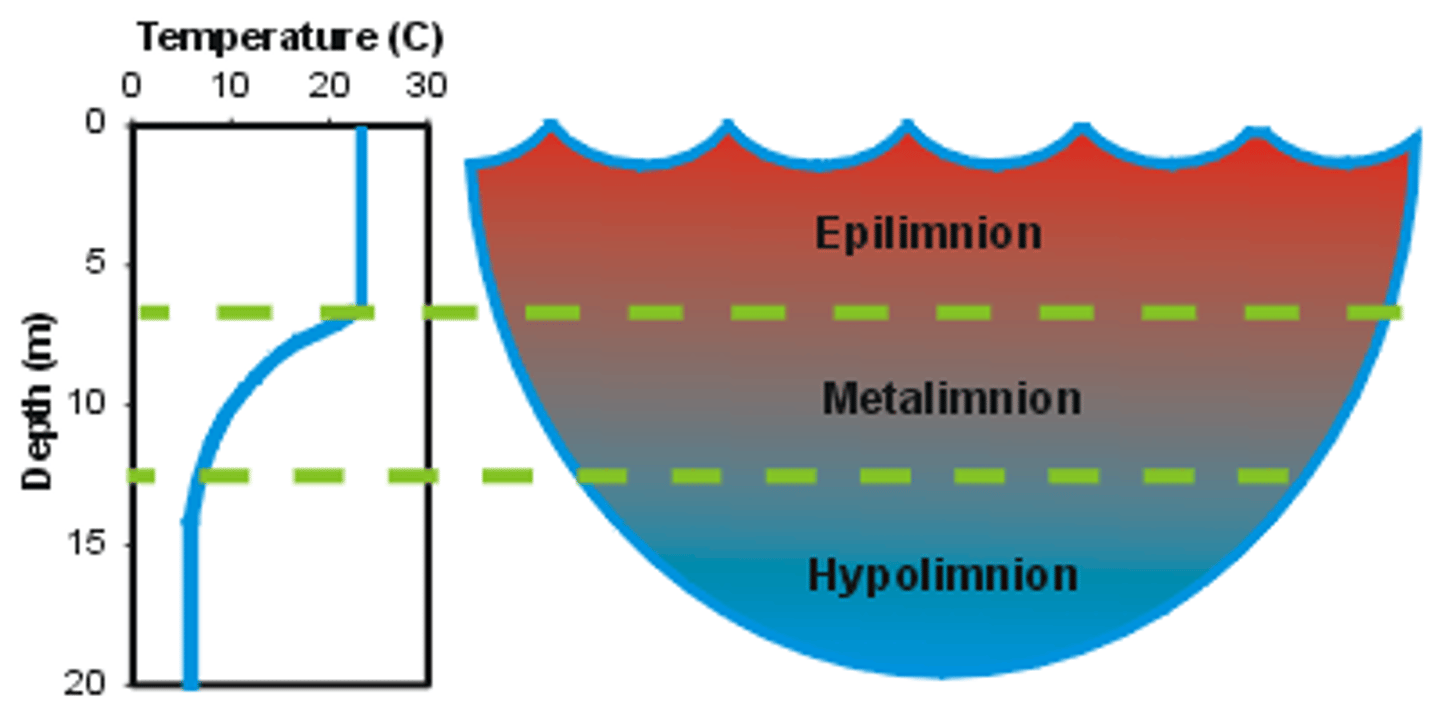
vertical stratification
- in all bodies of water there exist layers that vary significantly in their light, temp, oxygen, and nutrient levels.
- they are affected diff by seasonal changes and other disturbances
vertical stratification in freshwater biomes
1. eplimnion
2. thermocline
3. hypolimnion
eplimnion
- uppermost layer, warmer, most oxygen so photosynthesis
thermocline
temperature boundary between the epilmnion and hypnion
hypolimnion
- deeper layer, colder NO photosynthesis
freshwater lake zones
1. LITTORAL - plants
2. LIMENTIC - ample light
3. PROFUDAL ZONE - dark
4. BENTHIC
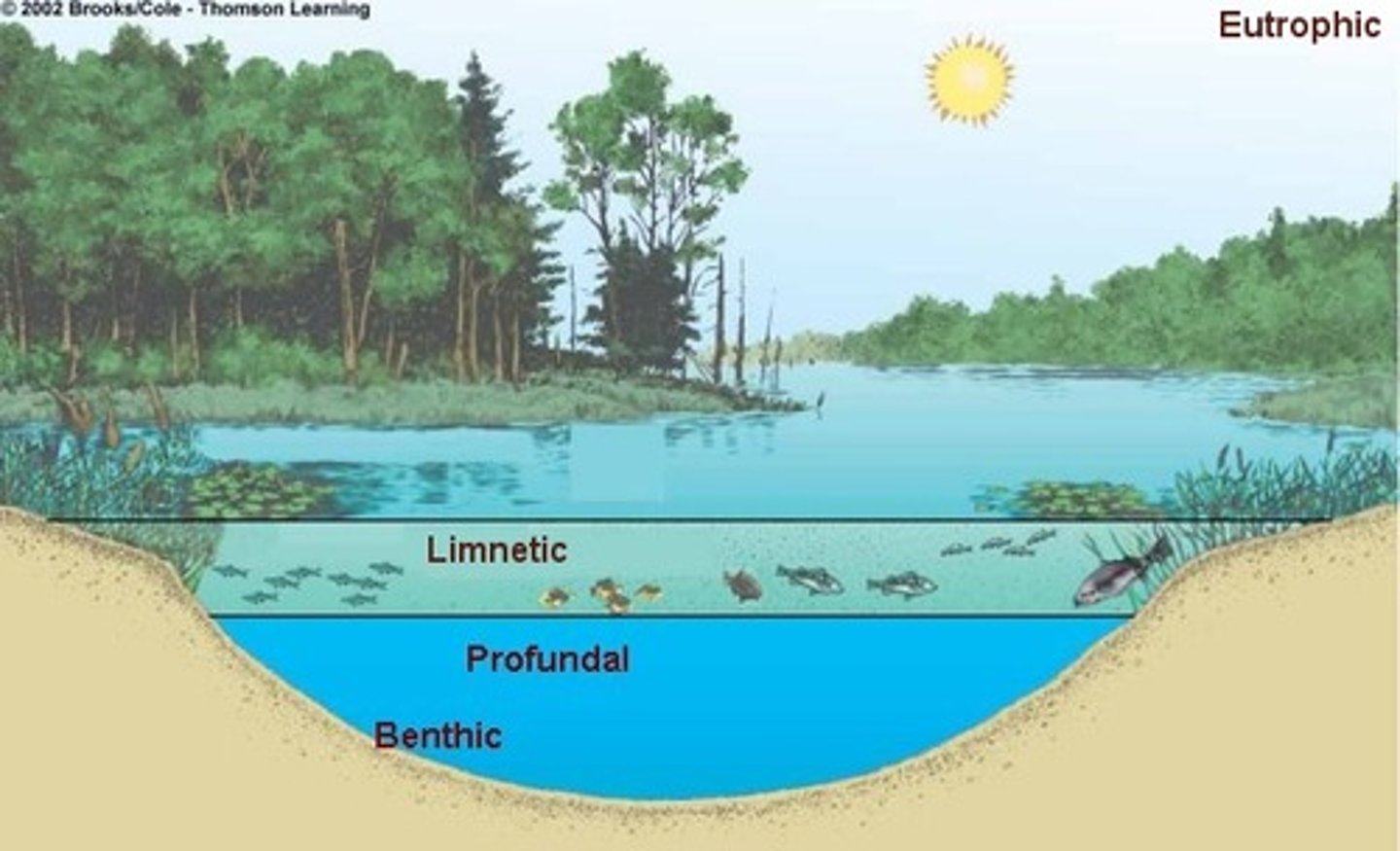
Littoral zone
- near the shore, lots of sunlight
- amphibians here and emergent plants such as cattails, primary productivity
limnetic zone
surface of open water, euphotic zone
- organisms that are here are short-lived and rely on photosynthesis
profudal zone
aphotic zone, no photosynthetic plants here
benthic zone
- deepest layer, characterized by very low temps and low O2 levels
- build up of nutrient rich sediments, organisms are scavengers and detritus feeders, such as worms, mollusks, ground fish
marine biomes
1. oceans
2. barrier islands
barrier islands
- landforms that lie off coastal shores
-important buffers for for the shoreline behind them
- because they are created by the buildup of deposited sediments their boundaries are constantly shifting aground them so its not the best place to build property, hit hard by storms
intertidal
- shoreline uncovered at low tides
types of coral reefs
1. fringing reefs: grow directly from a shore, there is no lagoon between the reef and the shore
2. barrier reefs: linear reefs, parallel a shore, but separated by a lagoon
3. atolls: circular reefs + surrounded by a central lagoon
pelagic
the water column
ocean zones
1. Coastal Zone
2. Euphotic Zone - warm + light
3. Bathal Zone - cool water, little light
5. Abyssal/Benthic Zone - dark, cold, high pressures
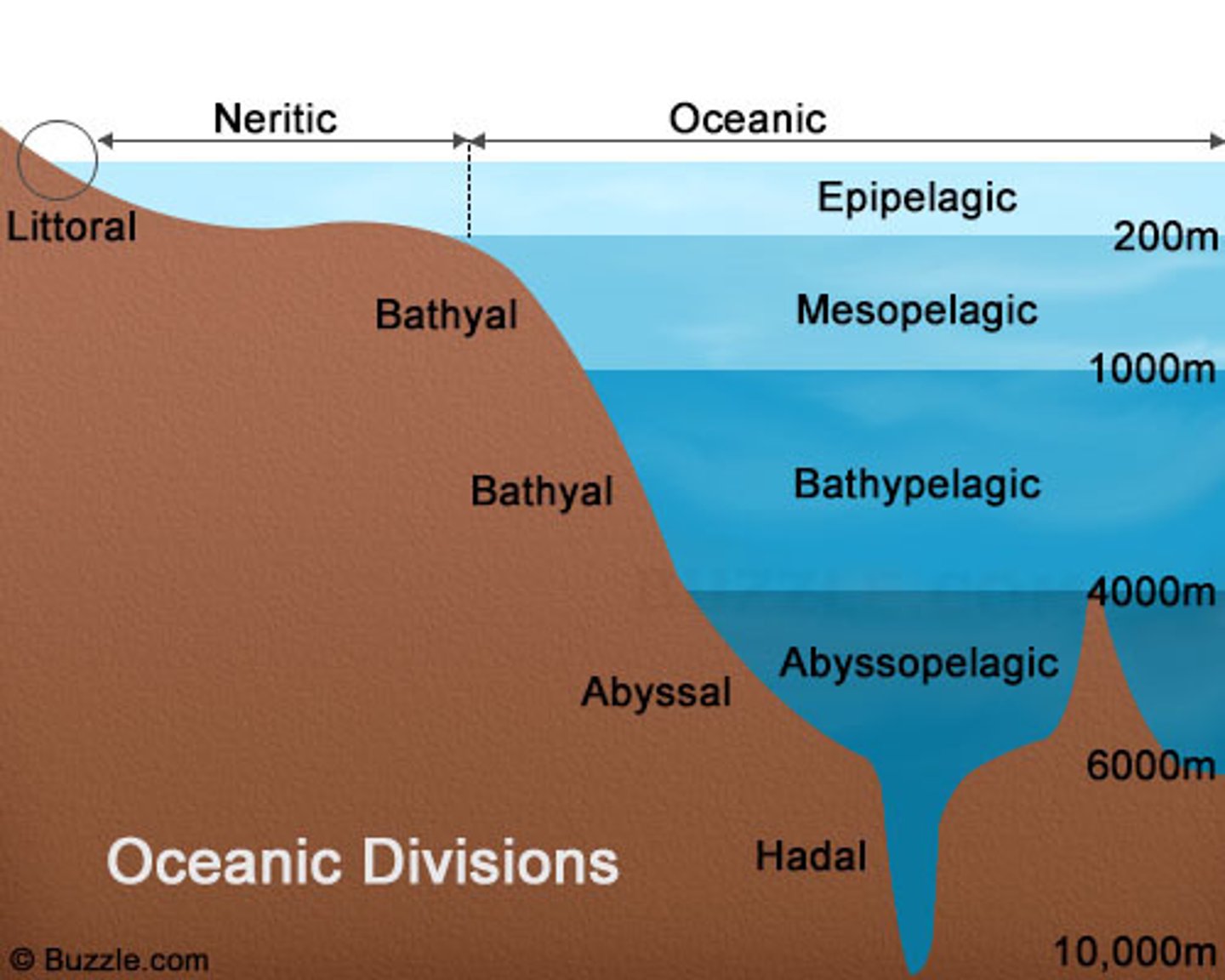
coastal zone
- ocean water closet to land
- the shore at the end of the continental shelf
euphotic zone
-warmest region of ocean water, highest levels of dissolved 02
abyssal zone
- deepest region of ocean
bathyal zone
- the middle region, cold, not enough light for photosynthesis
deep-sea thermal vents
- releases H2S; this chemical energy is then used by organisms that live around it
-tube worms, mussels, microbes are adapted to extreme heat (350°C) and extreme pressure
coral reefs
- type of barrier island
- occur in clear, salty, shallow waters, for photosynthesis
- formed from a community of living things: cnidarians which secrete calcium rich skeletons
- PROTECT shorelines and SHELTER countless species of fish
- but EXTREMELY DELICATE; most ENDANGERED BIOME b/c polluted urban runoff, introduced pathogens, and GLOBAL WARMING
coral bleaching
- caused by elevated water temps
- corals expel their algal partner and then die
- b/c dissolved CO2 creates carbonic acid - water becomes more acidic
upwelling
- seasonal movement of water from the cold and nutrient rich bottom to surface
- prove a new nutrient supply to organism in the photic regions; followed by exp growth esp. single cell algae which form blooms
- RED TIDES: recurring toxic algal bloom that kill fish and poison beds of filter feeders (oysters and muscles)
lake turnover
. - Water is densest at 4°C. In tropical regions, after spring ice melts, the water surface temp of lakes will rice from 0°C to 4°C where the dense surface water will sink to the bottom of the lake.
- This overturn brings oxygen to the bottom and nutrients to the top and occurs during spring and fall
tide pools
- depressions in a rocky shoreline that are flooded at high tide but retain some water at low tide
- wave action prevents most plant growth
- but there are specialized animals and plants here
stuff that affects aquatic community
1. nutrient availability (or excess) such as N + P
2. suspended matter, such as silt, affects photosynthesis
3. depth
4. temp
5. currents
6. bottom characteristics - muddy, sandy, rocky floor
7. internal currents
8. connections to, or isolations from, other biomes
human destruction
- human take over 40% of the net primary productivity
- arctic tundra/desert is the least disturbed
- temperate broadleaf forests are the most disturbed
secondary succession
existing community is disturbed, a new one develops from the nutrients of the old
rainshadow effect
- causes the leeward side to have little precipitation due to the effect of a mountain range
- leeward side is usually a desert
leeward side
- of a mountain, is the dry area that doesn't receive water
windward side
- of a mountain, receives the rain and wind
what effect does living near a large ocean have on average air temps?
oceans and lakes create a "moderating effect" bc of high specific heat. They take longer to heat hup and longer to cool down, making summer and springs cooler, and winters warmer
lagoon
stretch of salt water separated from the sea by a coral reef
eutrophication
- excess of nutrients which stimulate growth, and depletes oxygen in water
two types of organisms that can live in low oxygen environoments
geoducks and catfish
winter kill
ice freezes the top of the lake in the winter, all the organisms in the top are dead