Plasma Membrane & Diffusion
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/23
Last updated 6:02 AM on 3/29/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
1
New cards
Extracellular fluid
Fluid present outside of the cells of a multicellular organism.
2
New cards
Intracellular fluid
Fluid present inside of the cell.
3
New cards
Net Movement
When the flow of solute particle moving in one direction is bigger than the flow of solute particles moving in the opposite direction.
4
New cards
Name of the Model of the Plasma Membrane
Fluid Mosaic Model
5
New cards
Roles of the Plasma Membrane
* Movement of substances in and out of the cell.
* Providing structural support.
* Facilitating cell communication.
* Providing structural support.
* Facilitating cell communication.
6
New cards
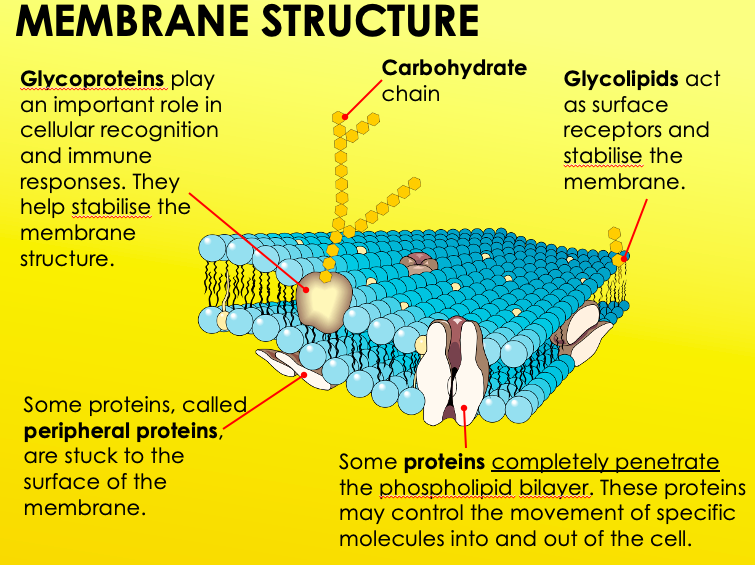
Phospholipid Bilayer
Quite fluid, with proteins flowing within it. Glycoproteins, glycolipids, and cholesterol are also apart of membrane structure.
7
New cards
Glycoproteins
Have an important role in cellular recognition and immune responses. They help stabilise the membrane structure.
8
New cards
Glycolipids
Act as surface receptors and stabilise the membrane.
9
New cards
Cholesterol
Makes the membrane more stable.
10
New cards
What can pass through the plasma membrane? (Hydrophobic or hydrophilic)
Hydrophobic molecules, eg: wateralcoholoxygen
11
New cards
What cannot pass through the plasma membrane? (Hydrophobic or hydrophilic)
Hydrophilic molecules, eg: ionslarge molecules
12
New cards
4 Types of Diffusion
Simple diffusion, Facilitated diffusion, Osmosis, Active transport
13
New cards
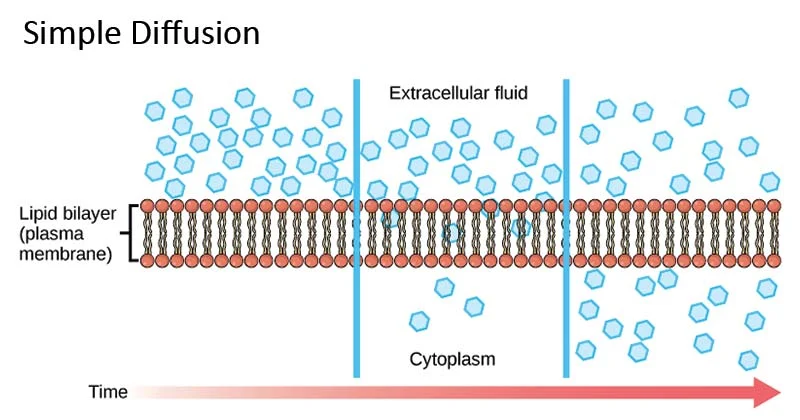
Simple diffusion
The net movement of a substance from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration. Movement occurs down a concentration gradient, passive process.
14
New cards
Factors affecting rate of diffusion
* Distance
* Concentration gradient
* Physical barriers
* Surface area
* Concentration gradient
* Physical barriers
* Surface area
15
New cards
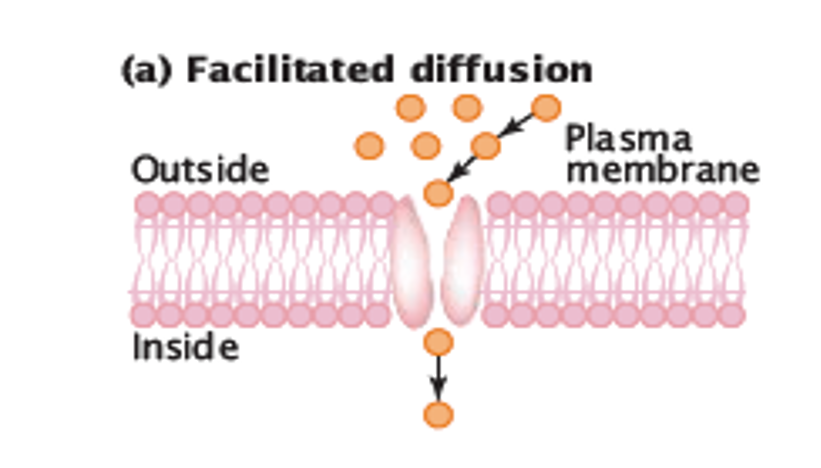
Facilitated Diffusion
When a protein channel and/or carrier is used to help pass proteins through the membrane.
16
New cards
Protein Channel
A channel in membrane that some substances need to move through protein instead of passing straight through.
17
New cards
Protein Carrier
A carrier that is supplied in addition to a protein channel, in order to pass through the membrane.
18
New cards
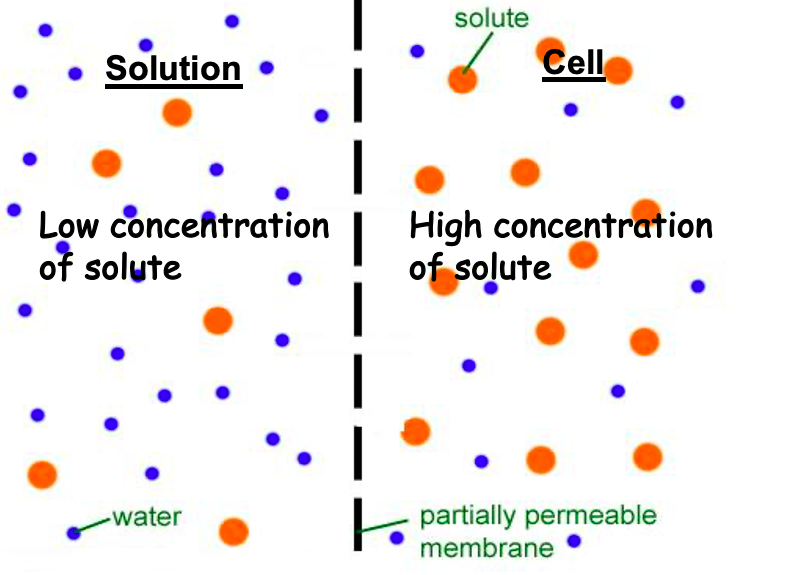
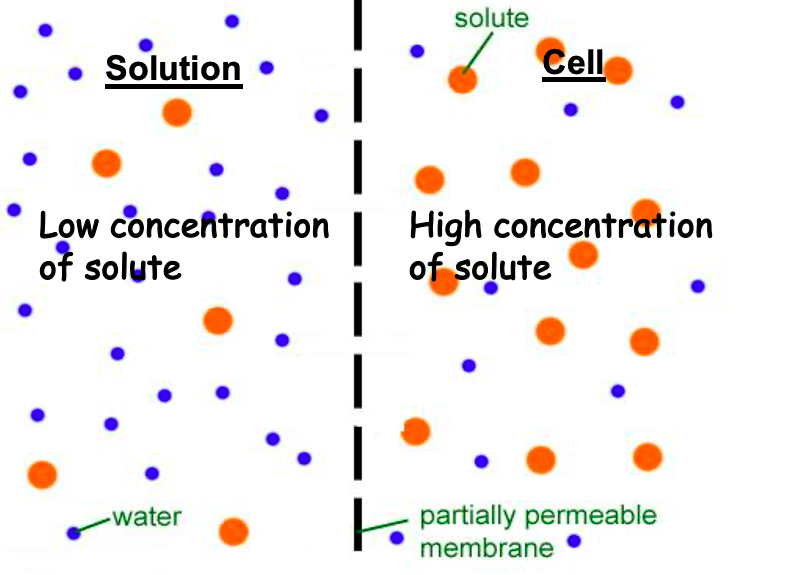
Hypertonic Solution
The solution has a higher concentration of solute than the cell or solution that it is being compared to.
19
New cards
Hypotonic Solution
The solution has the lower concentration of solute as the cell or solution it is being compared to.
20
New cards
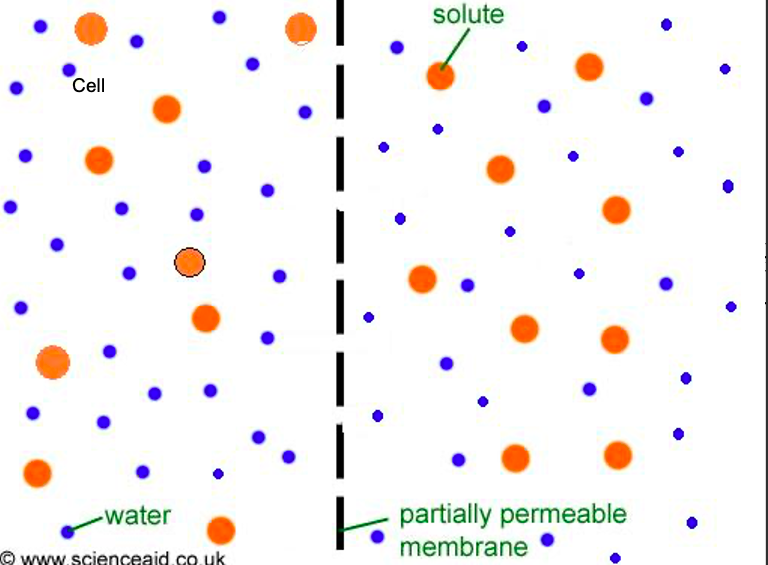
Isotonic Solution
The solution has the same concentration of solute as the cell or solution it is being compared to.
21
New cards
Osmosis
The movement of water from a dilute solution to a more concentrated one.
22
New cards
Dilute
A solution with a low concentration of solute, more water molecules than the solute.
23
New cards
Why do cells need osmosis?
It is how they gain water, making them turgid. (swollen, full)
24
New cards
Active Transport
Substances are moved across a membrane against a concentration gradient. It is an active process as it requires energy (ATP). Used to pump substances in or out of the cell with specific protein carrier molecules.