Nucleotide Metabolism in Biochemistry 3022
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What are the primary functions of nucleotides and nucleic acids?
Nucleotides and nucleic acids store genetic information (DNA/RNA), carry and translate genetic information (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA), serve as energy storage molecules (ATP), carry out enzymatic reactions (ribozymes), act as signaling molecules (cAMP, cGMP), and function as redox coenzymes (NADH, NADPH, CoA, SAM).
What are the three parts of nucleotides?
Nucleotides consist of phosphate groups, a pentose sugar (C1', C2', C5'), and a nitrogenous base.
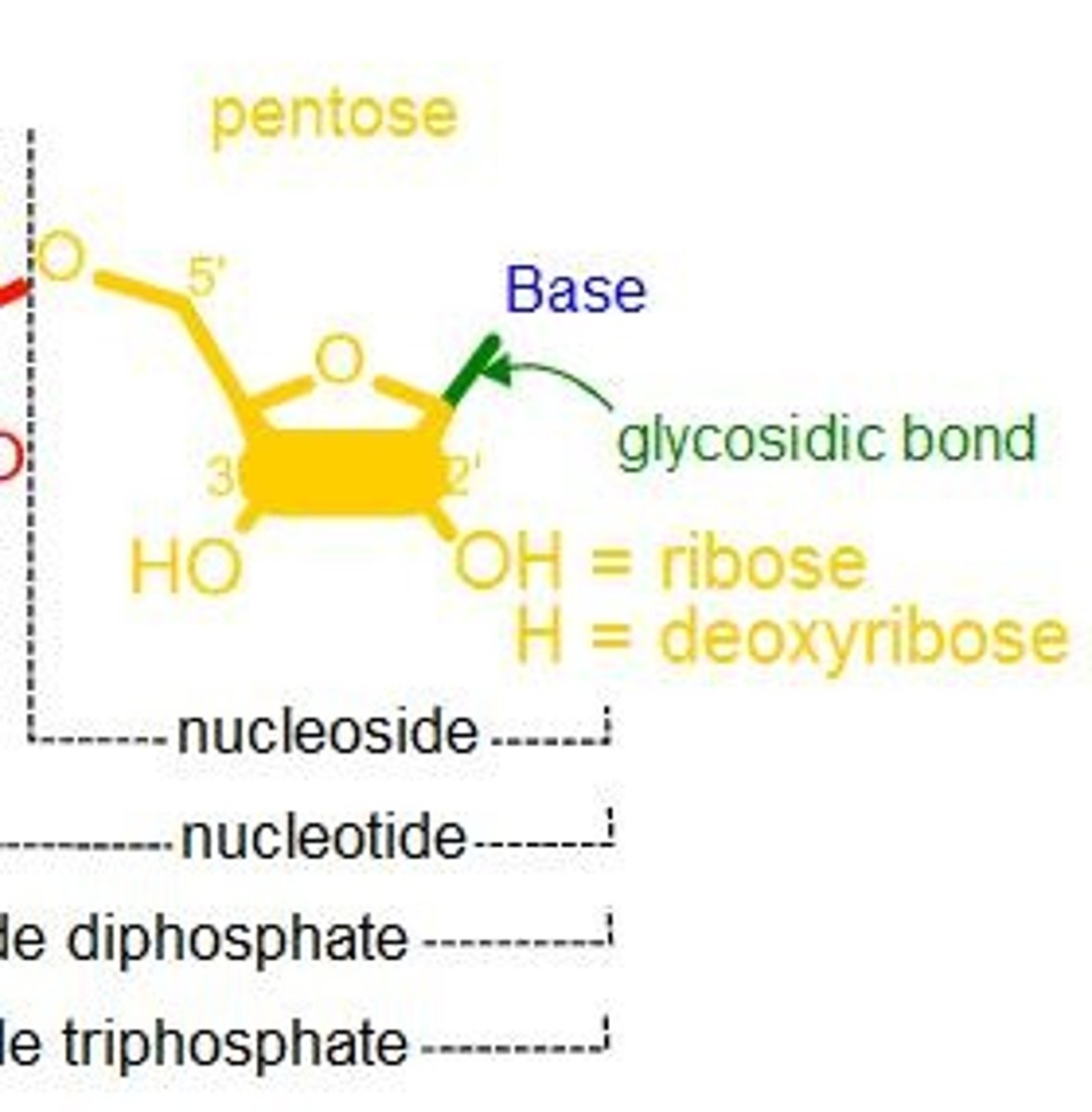
How can nucleosides with different numbers of phosphate groups be interconverted?
Nucleomonophosphate (NMP), nucleoside diphosphate (NDP), and nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) can be interconverted using kinases, with NMP phosphorylated to NDP using ATP and nucleoside monophosphate kinase, and NDP converted to NTP by nucleoside diphosphate kinase.
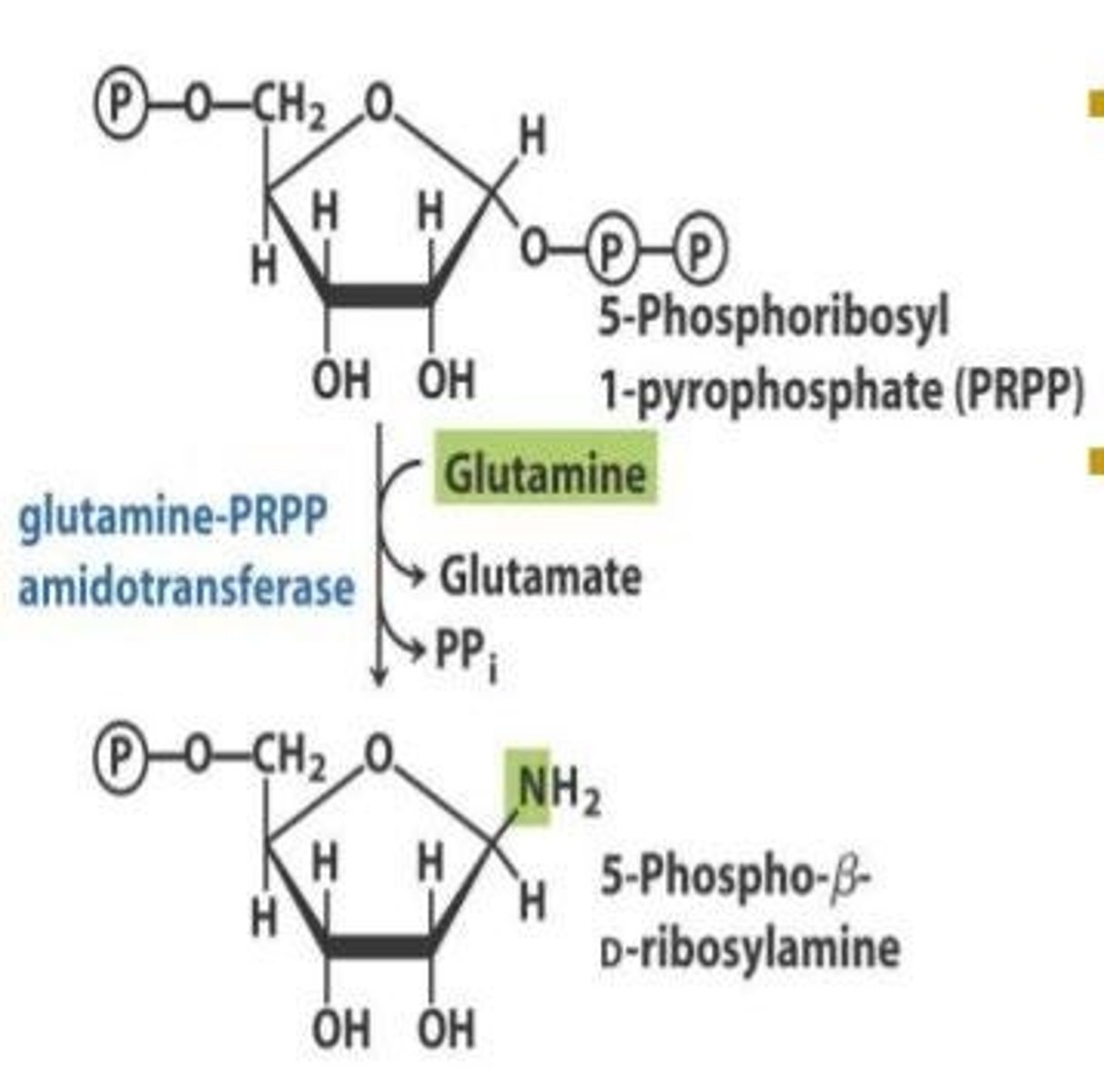
What is the significance of PRPP in nucleotide metabolism?
PRPP (phosphoribosylpyrophosphate) is crucial for nucleotide synthesis, serving as a sugar backbone for all nucleotides and is generated from ribose-5-phosphate.
What is the role of glutamine in purine biosynthesis?
Glutamine reacts with PRPP to initiate the formation of the purine ring, catalyzed by the enzyme glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase, which is the rate-limiting and committed step in purine biosynthesis.
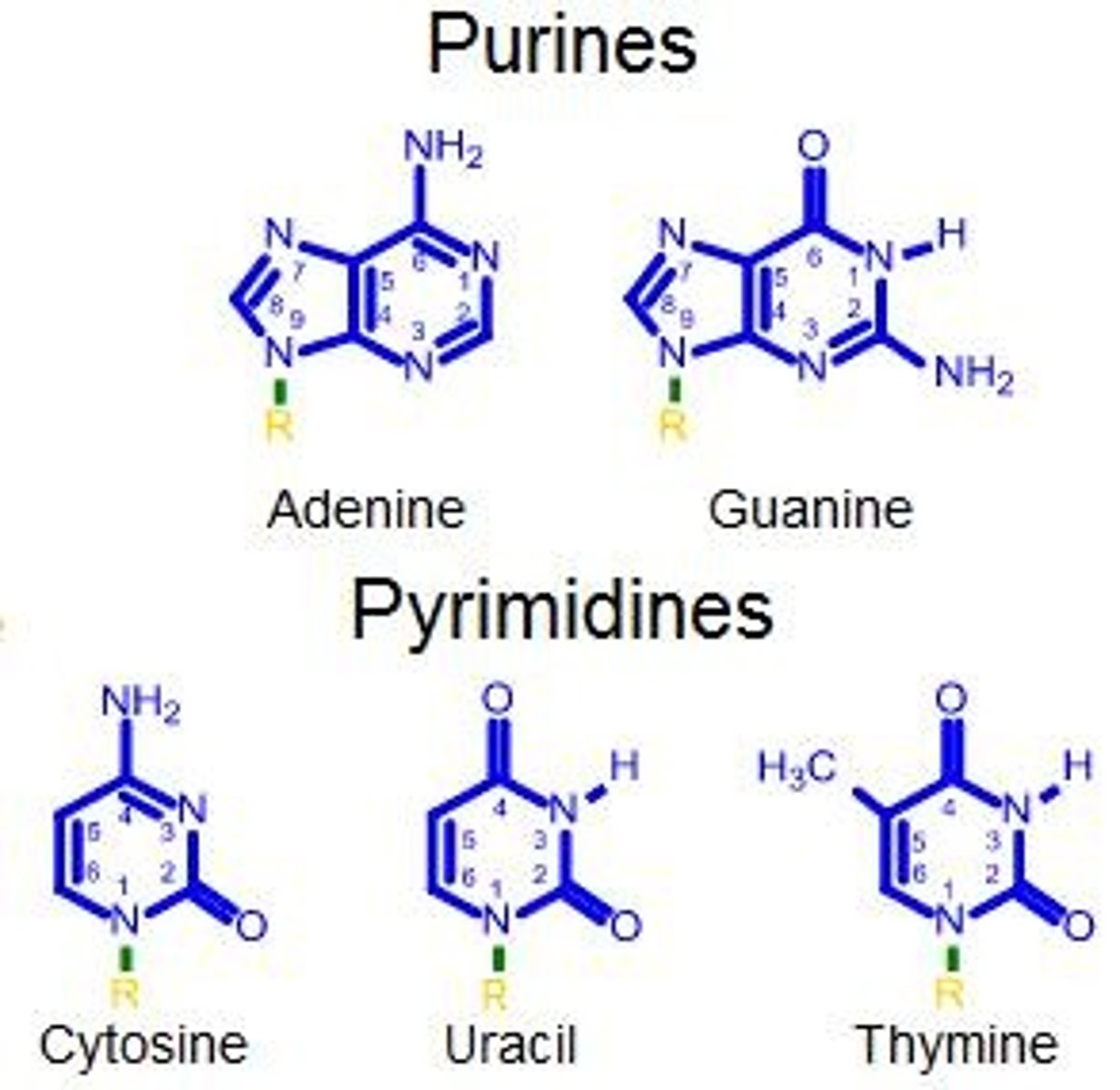
What mnemonic helps remember purines and pyrimidines?
"Pure as gold" helps remember purines, while "CUT the Py" helps remember pyrimidines.
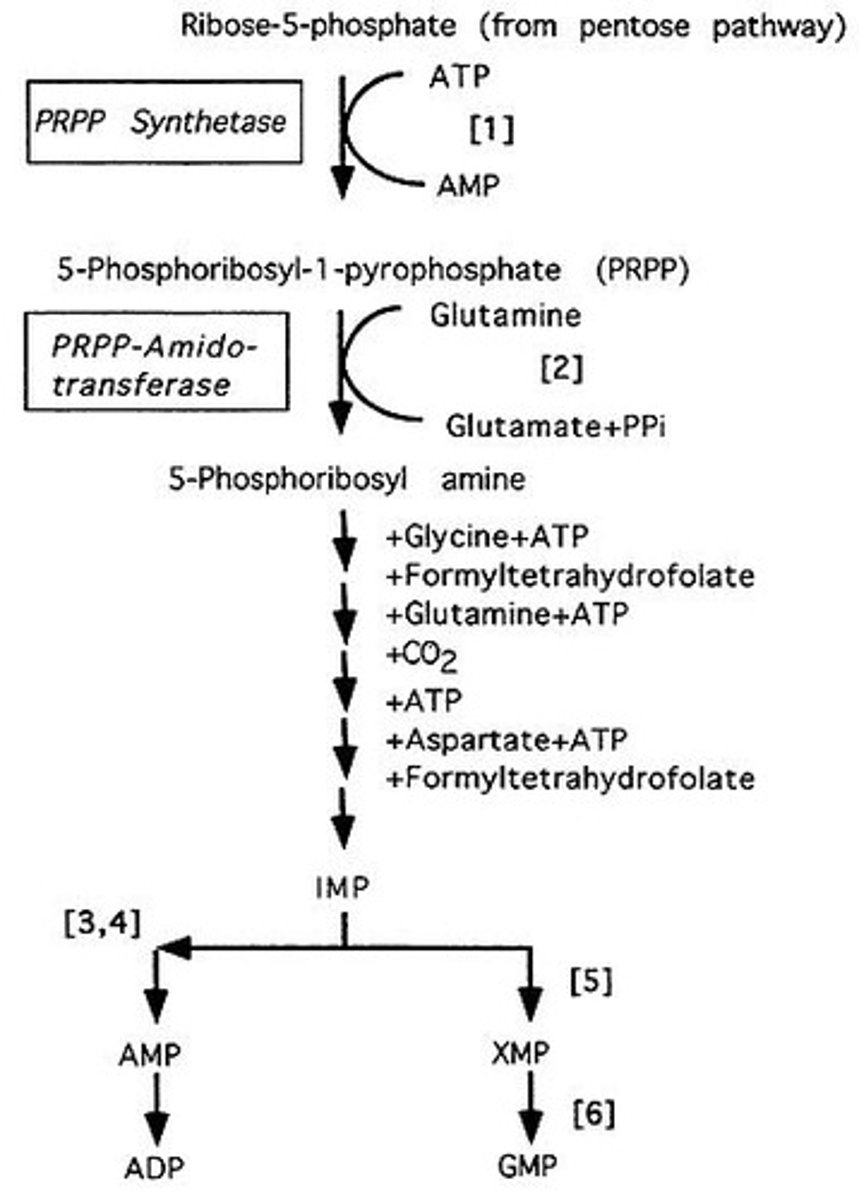
What are the major steps in purine biosynthesis?
The major steps include: 1) Production of PRPP, 2) Production of phosphoribosylamine, 3) Production of IMP (Inosine Monophosphate), and 4) Production of AMP (adenosine monophosphate) or GMP (guanosine monophosphate).
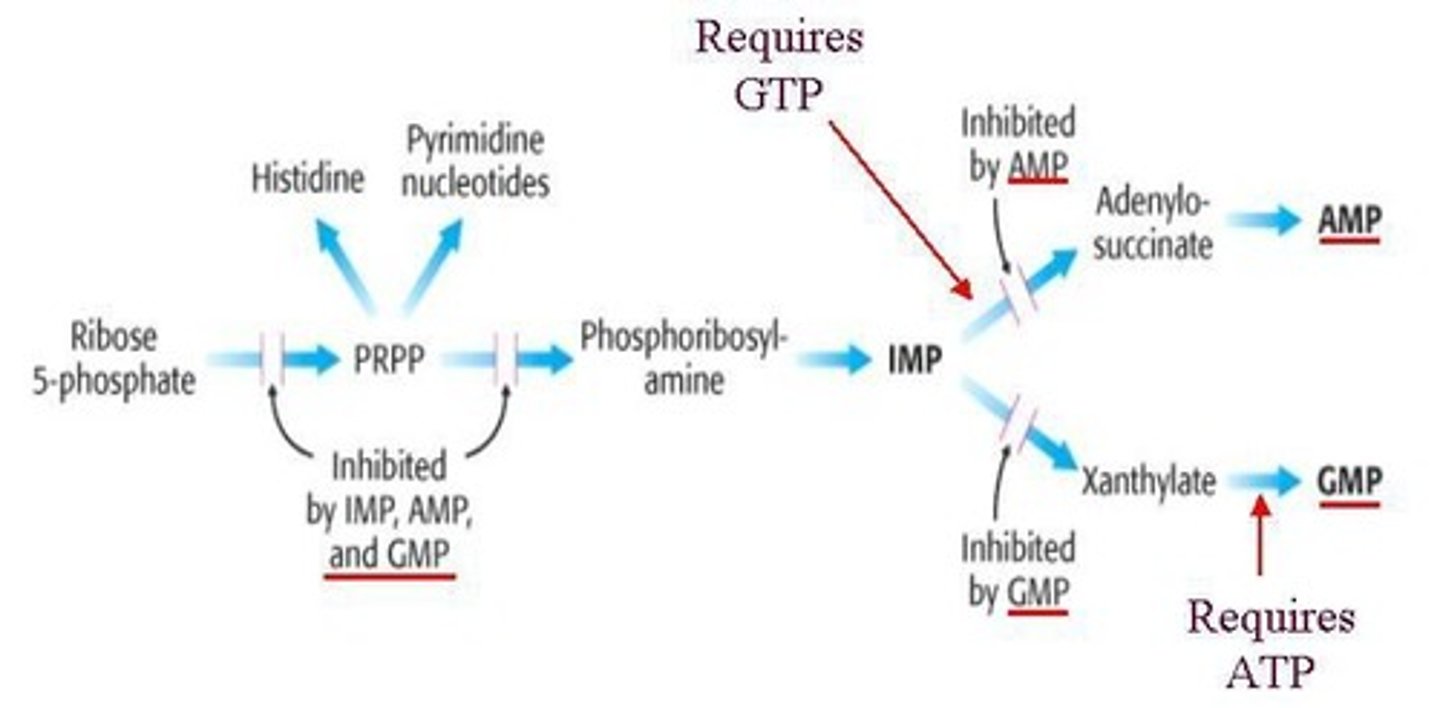
What is the starting product for generating PRPP?
Ribose-5-phosphate from the Pentose Phosphate Pathway is the starting product for generating PRPP.
What enzyme is responsible for generating PRPP?
Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase is responsible for generating PRPP.
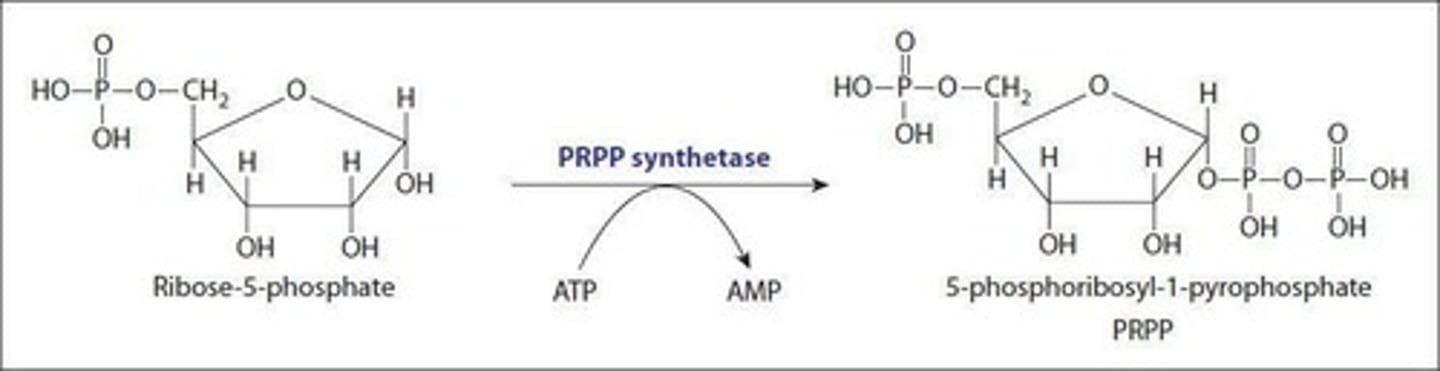
What is the committed step in purine biosynthesis?
The committed step in purine biosynthesis is the formation of phosphoribosylamine from PRPP and glutamine.
What is the significance of the ribose sugar in purine synthesis?
Purine synthesis begins on the ribose sugar, which is essential for constructing the purine ring.
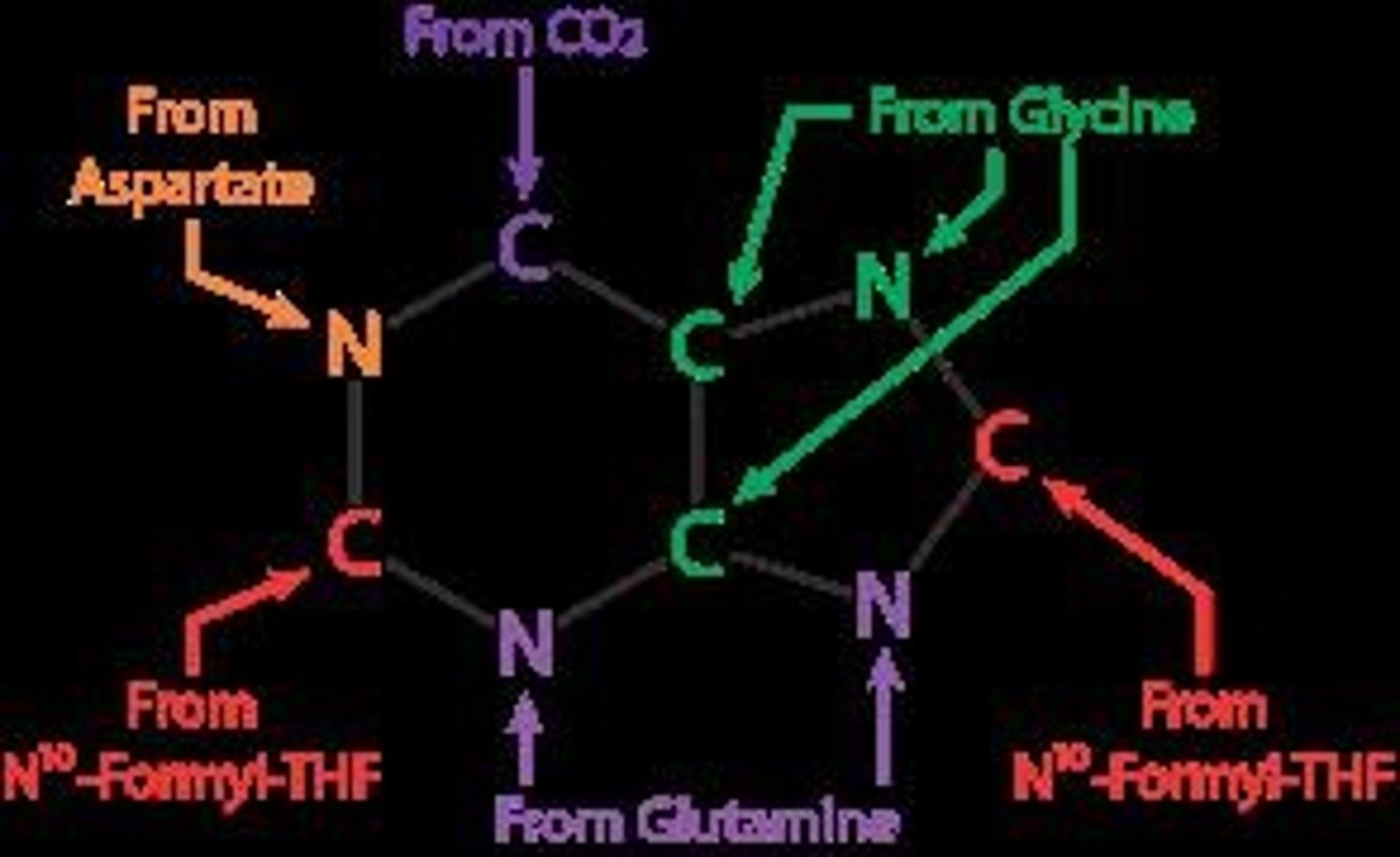
What is the difference between purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?
Purine rings are synthesized starting from ribose sugar, while pyrimidine rings are synthesized separately from the sugar and then attached.
What are the roles of ribonucleotide reductase in nucleotide metabolism?
Ribonucleotide reductase is involved in the conversion of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides, which is essential for DNA synthesis.
What are the sources of carbon and nitrogen for nucleotide biosynthesis?
The sources of carbon and nitrogen for nucleotide biosynthesis include amino acids, one-carbon donors, and CO2.
What happens to ADP during nucleotide metabolism?
ADP is reconverted to ATP using mitochondrial ATP synthase.
What are the end products of purine biosynthesis?
The end products of purine biosynthesis are AMP (adenosine monophosphate) and GMP (guanosine monophosphate).
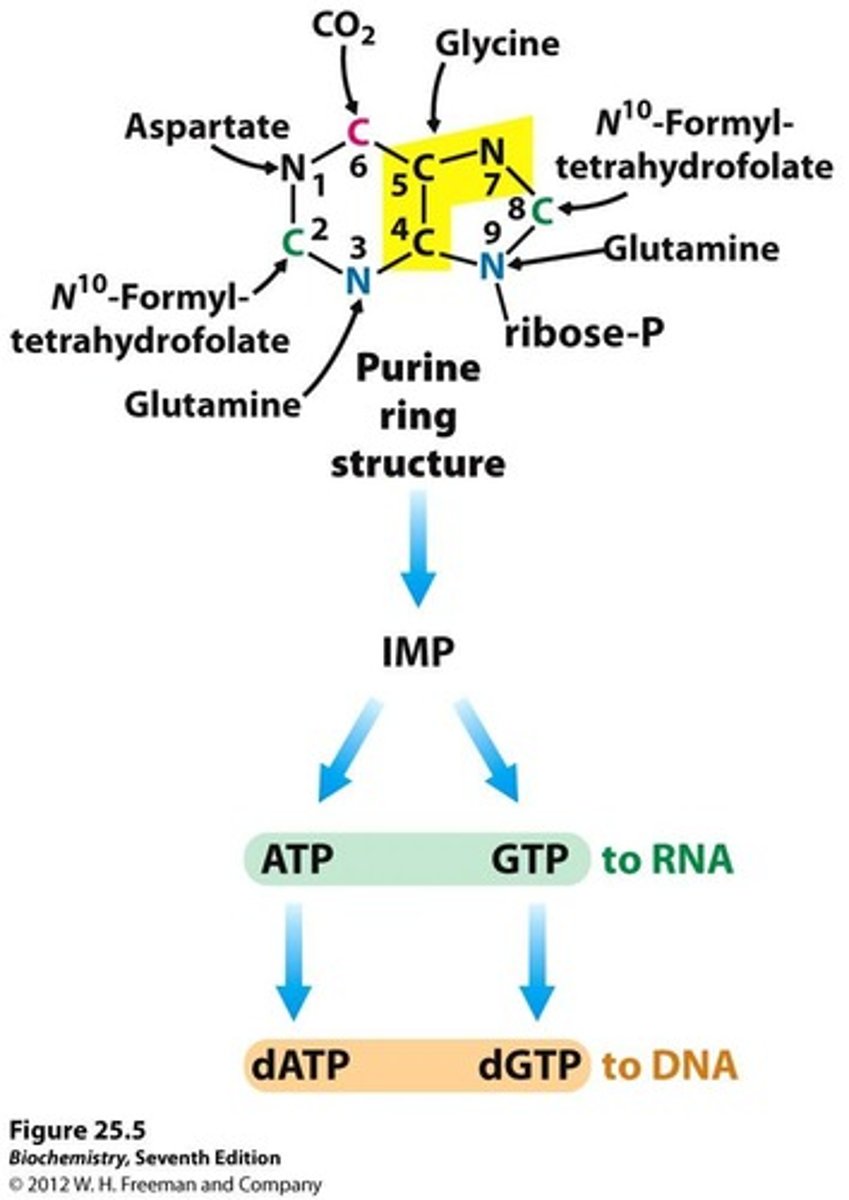
How is the synthesis of nucleotides regulated?
Nucleotide synthesis is tightly regulated to prevent imbalances that could favor mutations.
What is the significance of the glycosidic bond in purine biosynthesis?
The formation of the glycosidic bond is crucial for linking the nitrogenous base to the sugar in nucleotides.
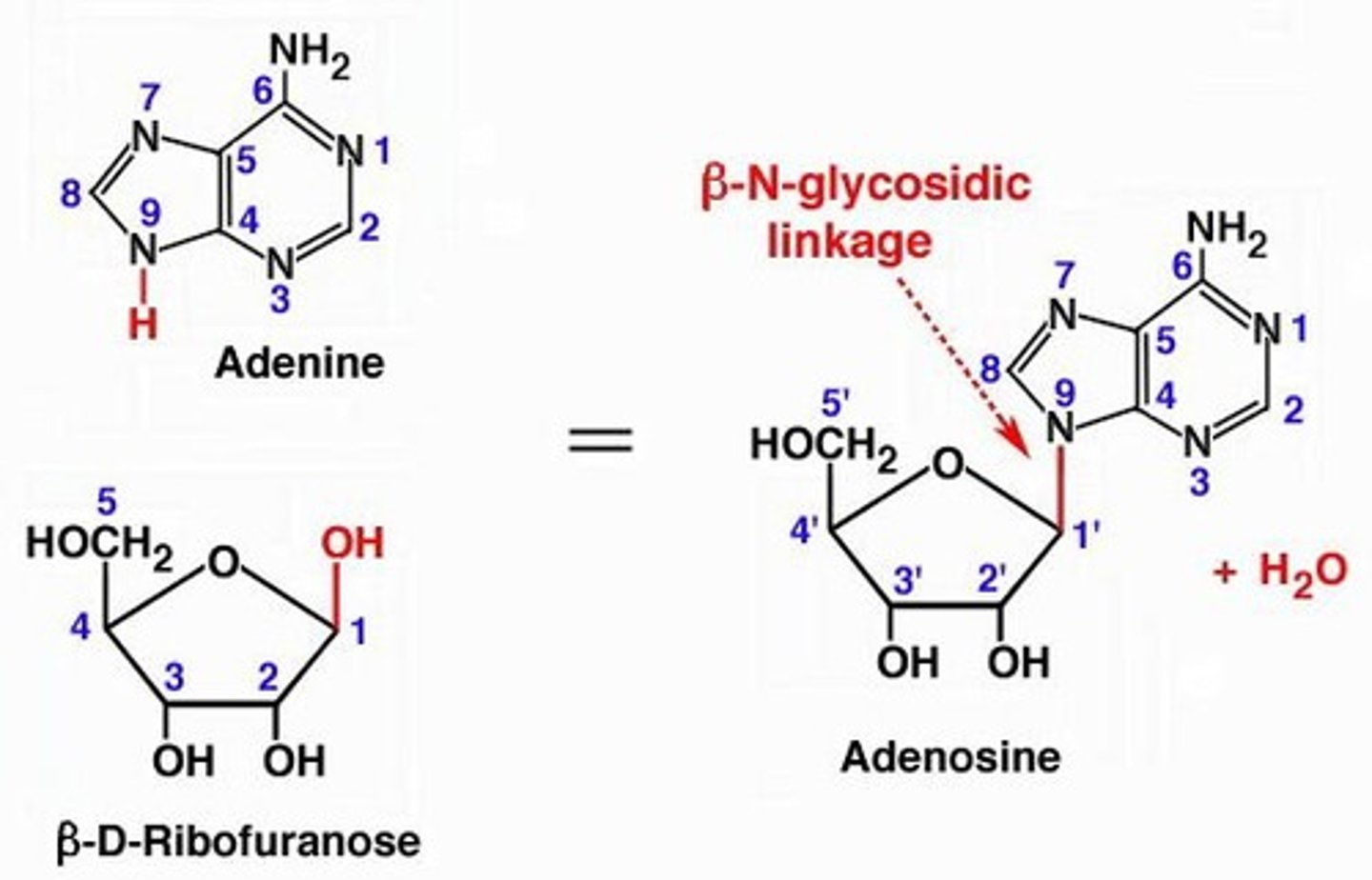
What is the role of ribozymes in nucleotide function?
Ribozymes, such as ribosomal RNA, carry out enzymatic reactions.
What are some examples of signaling molecules derived from nucleotides?
Examples of signaling molecules include cAMP and cGMP.
What is the role of PRPP in histidine biosynthesis?
PRPP is also utilized in histidine biosynthesis, in addition to its role in nucleotide synthesis.
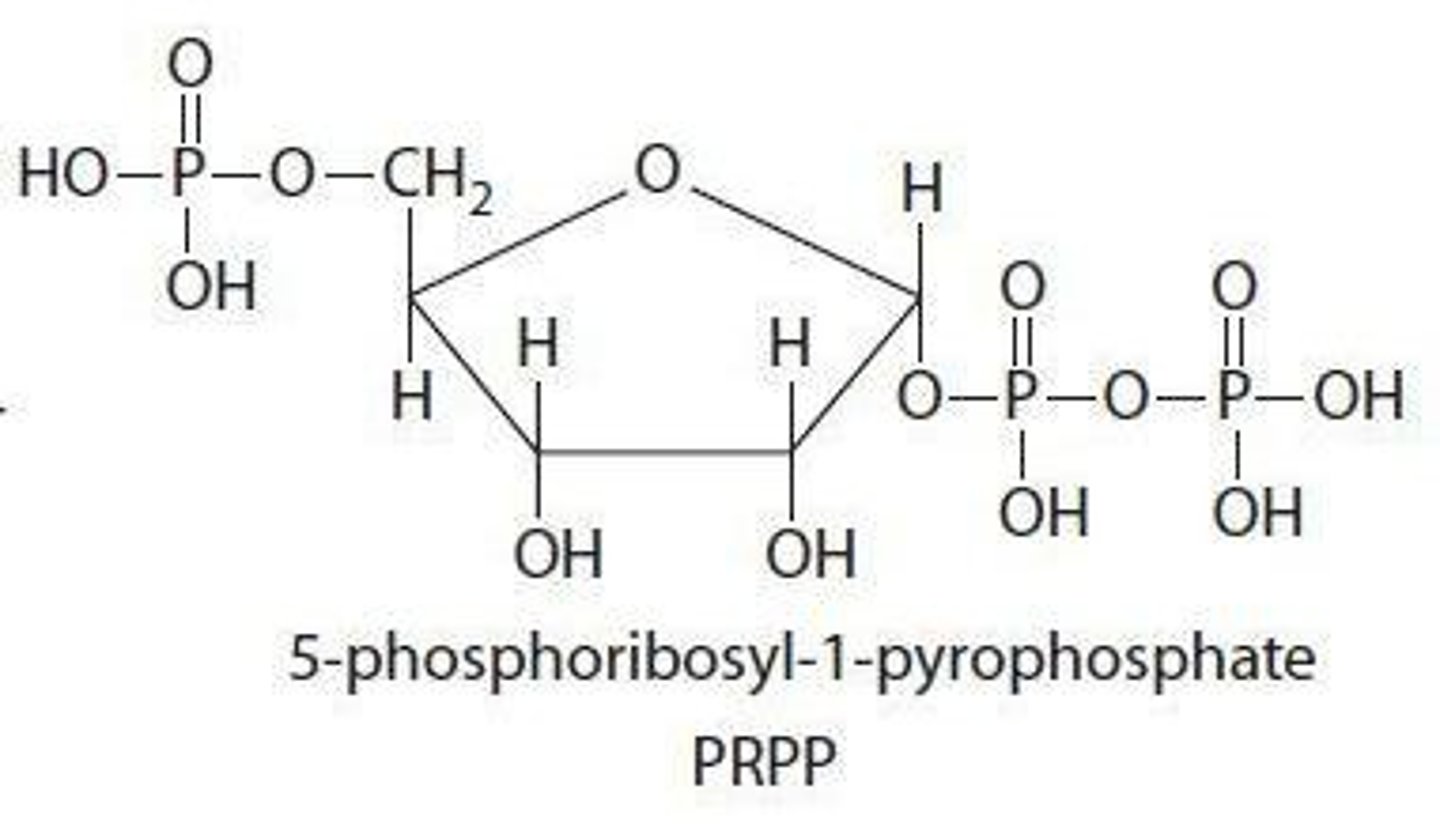
What is the basic structure of a purine ring?
The basic purine ring is formed through a multi-step pathway beginning with ribose-5-phosphate.
What is the importance of the pentose phosphate pathway in nucleotide metabolism?
The pentose phosphate pathway provides ribose-5-phosphate, which is essential for generating PRPP and subsequently for nucleotide synthesis.
What is the first step in the production of Inosine Monophosphate (IMP)?
Production of PRPP (phosphoribosylpyrophosphate)
How many reactions are involved in building the purine base onto the amine group?
11 reactions
What molecule donates a methyl group during purine biosynthesis?
N10FH4 (tetrahydro folate from one-carbon metabolism)
From how many different locations is nitrogen sourced to form the purine ring?
Four locations
What is the significance of the rate-limiting step in purine biosynthesis?
The pathway is subject to several redundant systems and metabolites will not be invested unless all conditions are favorable.
What leads to the production of AMP in purine biosynthesis?
Addition of aspartate
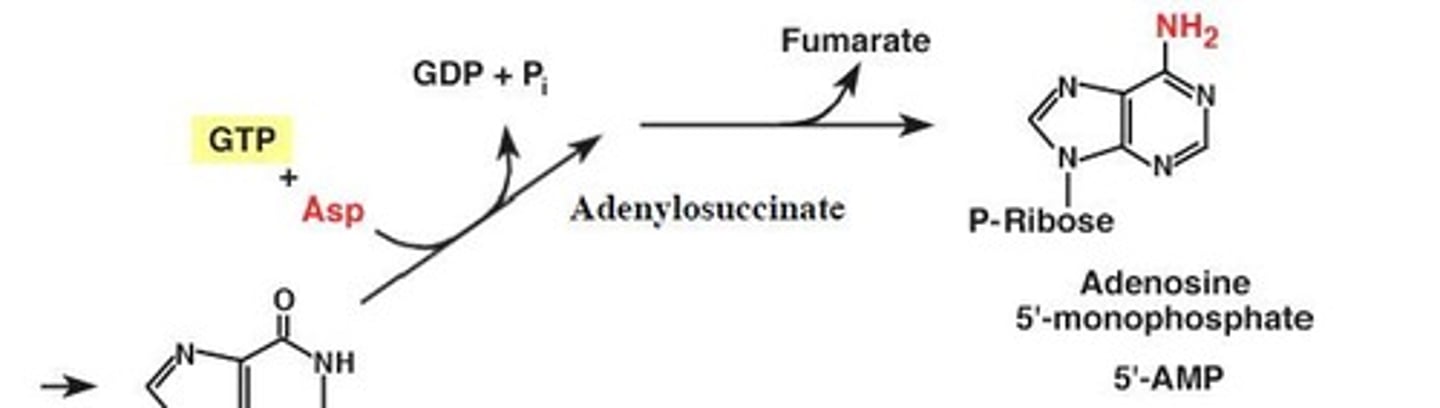
What leads to the production of GMP in purine biosynthesis?
Addition of glutamine
What is the starting substrate for generating AMP or GMP?
Inosine monophosphate (IMP)
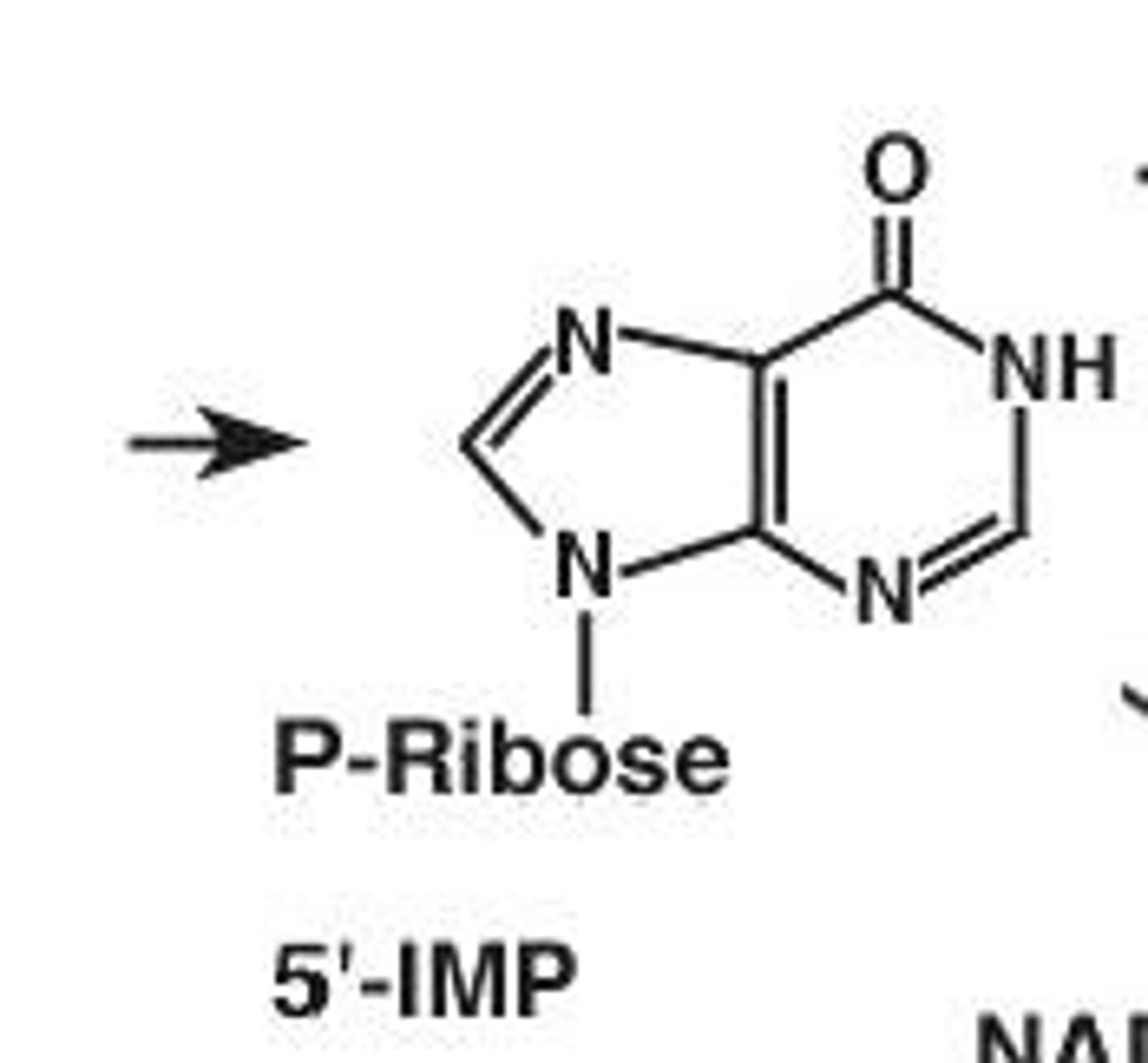
What is the first step in pyrimidine biosynthesis?
Start with glutamine to make carbamoyl phosphate.
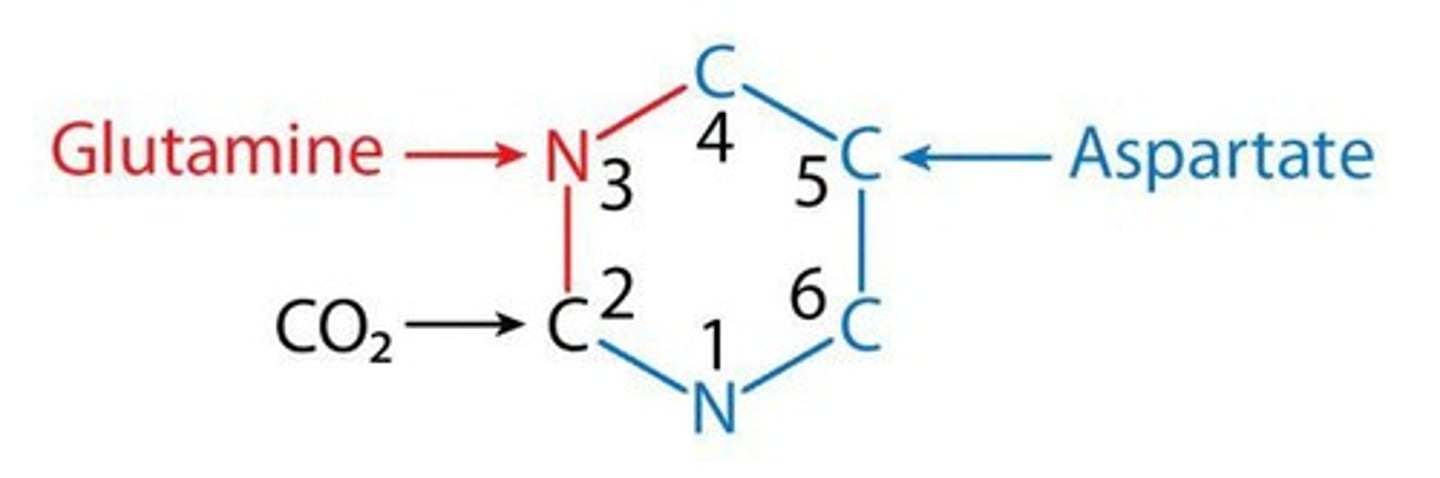
What is the regulatory step in pyrimidine biosynthesis?
CPSII (Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase II) is activated by PRPP.
What is the role of Aspartate Transcarbamoylase in pyrimidine biosynthesis?
It attaches aspartate to carbamoyl phosphate and removes the phosphate group.
What is the product formed after the decarboxylation of OMP?
UMP (uridine monophosphate)
What is required to convert UMP to CMP?
CTP synthase aminates UMP using ATP and glutamine.
What is the precursor for dTMP synthesis?
dUMP (deoxy uridine monophosphate)
Why does the synthesis of dTMP require extra steps?
It is linked to one-carbon metabolism.
What is the role of thymidylate synthase in dTMP synthesis?
It catalyzes the reaction between 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate and dUMP to produce dTMP.
What is one-carbon metabolism?
A system that moves one-carbon units around for synthetic or degradative processes.
What is the final product of the decarboxylation reaction in pyrimidine biosynthesis?
UMP (uridine monophosphate)
What is the difference between purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?
Purine synthesis builds the base on PRPP, while pyrimidine synthesis assembles the ring completely before adding PRPP.
What two amino acids are sources of nitrogen for AMP and GMP?
Aspartate and glutamate.
What is the function of OMP decarboxylase?
Converts OMP to UMP by removing CO2.
What is the significance of the metabolites in purine biosynthesis?
All metabolites needed to form the ring must be abundant enough to carry out the synthesis reactions.
What are the two true statements regarding the reactions generating AMP and GMP?
A. Aspartate and glutamate are sources of nitrogen; B. These reactions are regulated by levels of AMP and GMP.
What is the primary function of One-Carbon Metabolism in nucleotide synthesis?
It provides carbons for nucleotide synthesis.
Which enzyme is primarily controlled at the Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase II step in pyrimidine biosynthesis?
CPS II.
What inhibits and activates Orotate phosphoribosyl transferase?
Inhibited by CTP and activated by PRPP.
What is the rate-limiting step in the pyrimidine biosynthesis pathway?
The commitment to the first nitrogen.
What is the role of Ribonucleotide Reductase (RNR) in deoxyribonucleotide synthesis?
It converts ribonucleotides into deoxyribonucleotides.
Why is Ribonucleotide Reductase important for cells?
It generates precursors for DNA replication and repair, vital for cell proliferation and genome maintenance.
What is the starting substrate for Ribonucleotide Reductase?
Nucleoside diphosphates.
What reducing agent is used by Ribonucleotide Reductase?
NADPH.
What are the two subunits of Ribonucleotide Reductase and their functions?
The large subunit (R1) has two allosteric sites and the active site; the small subunit (R2) has a radicalized tyrosine involved in the reaction.
What is the purpose of the Purine Salvage Pathway?
To recycle bases that are already formed back into nucleotides.
What enzyme is required in the Purine Salvage Pathway?
PRPP transferase.
What is the outcome of the Purine Degradation Pathway?
It leads to uric acid synthesis, which is the primary mechanism to eliminate excess nitrogen.
What is the role of nucleoside phosphorylase in purine degradation?
It breaks the glycosidic bond in nucleosides.
What are the products of the Pyrimidine Degradation Pathway?
β-alanine, β-aminobutyric acid, ammonia, and CO2.
What distinguishes the salvage pathway from the degradation pathway?
Salvage recycles nucleosides back to nucleotides, while degradation eliminates excess nitrogen.
What are the atom sources of C and N for purine ring formation?
The specific sources are not detailed in the notes.
What are the atom sources of N for pyrimidine ring formation?
The specific sources are not detailed in the notes.
What key facts should be known about Ribonucleotide Reductase?
It is a conserved enzyme in all living organisms and is crucial for deoxyribonucleotide synthesis.
What is the role of PRPP in nucleotide biosynthesis?
It acts as a ribose sugar backbone in the salvage pathway.
What are the differences between CPSI and CPSII?
The specific differences are not detailed in the notes.
What are the allosteric controls of Ribonucleotide Reductase?
RNR controls the balance of deoxyribonucleotides with complex allosteric controls.
What is the significance of thioredoxin in the Ribonucleotide Reductase reaction?
Thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase are used as intermediates in the reduction reaction.
How does Ribonucleotide Reductase contribute to DNA synthesis?
It produces deoxyribose, which is essential for DNA synthesis.