Oncology 7 (canine soft tissue sarcoma)
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
what are soft tissue sarcomas (STS)?
heterogenous population of mesenchymal tumors
where do STS originate?
connective tissue (muscle, adipose, neurovascular, fascial, fibrous)
what is the typical signalment of STS?
most occur in middle-aged to older dogs
no specific sex or breed predilection

what are occurrences of STS associated with?
radiation
trauma
foreign bodies
orthopedic implants
parasite (spirocerca lupi)
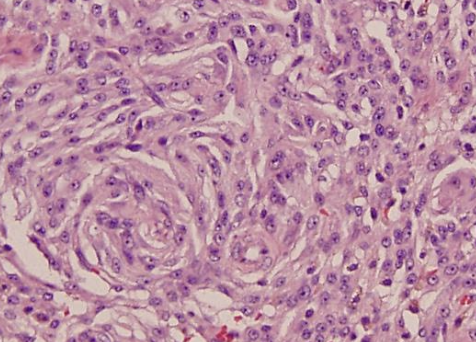
what is the biologic behavior of cutaneous/SQ STS?
-locally expansile mass (grow between fascial planes or infiltrate)
-often surrounded by pseudocapsule
-low to moderate local recurrence and low distant metastatic rate
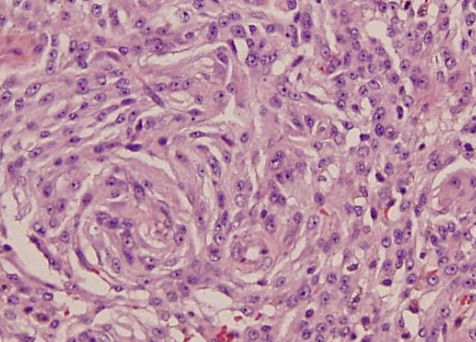
how is the pseudocapsule of STS formed?
formed by compression of peritumoral connective tissue
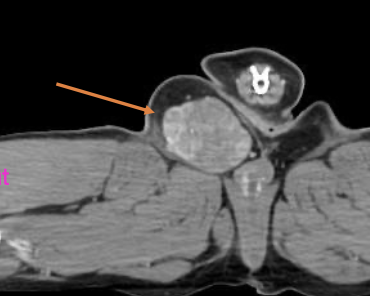
how are STS subclassified?
subclassified by tissue of origin or phenotype:
-fibrosarcoma
-perivascular wall tumor
-peripheral nerve sheath tumor
-liposarcoma
-etc.
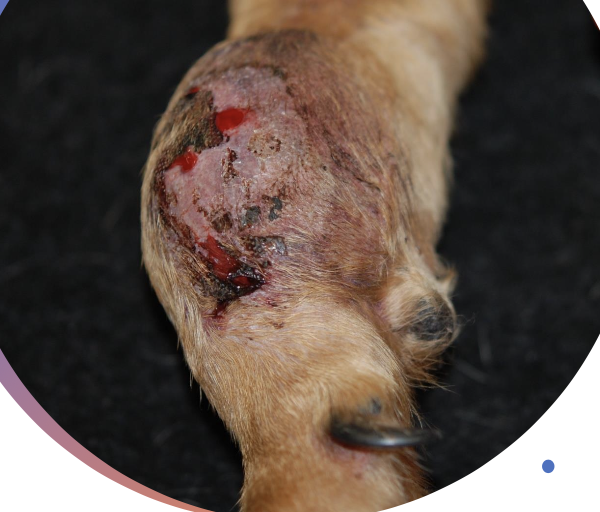
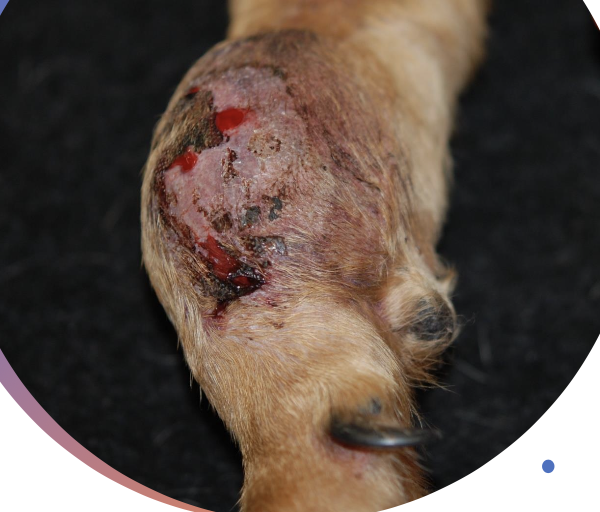
what is the clinical presentation of STS?
slow growing mass that is usually non-painful
clinical signs depend on location of mass and invasiveness
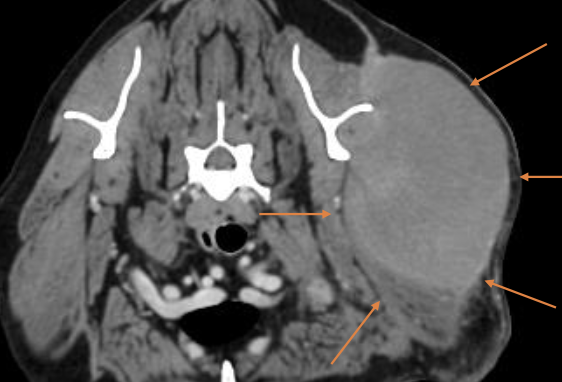
what is rapid growth of STS due to?
cell proliferation, necrosis, and hemorrhage (if aggressive, but this is rare)
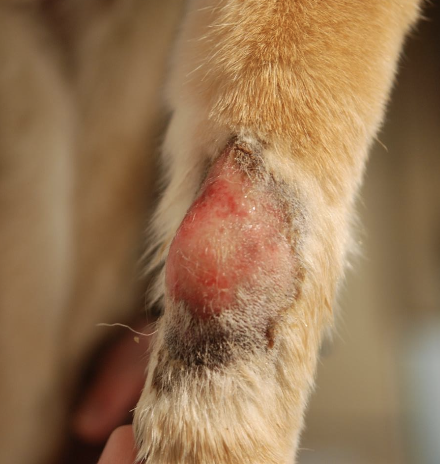
how will STS feel when palpated?
-generally firm and well-circumscribed
-can be mobile or fixed
-can also be soft and lobulated, mimicking lipomas
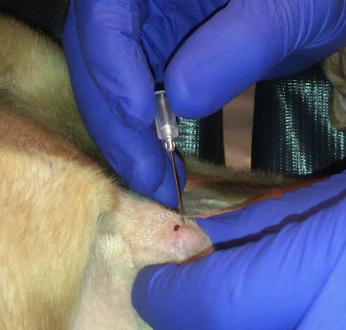
how are STS diagnosed with sampling?
cytology or biopsy
how is cytology useful when diagnosing STS?
FNA is recommended for cytologic diagnosis, can exclude diagnosis of readily exfoliating tumors
why may cytology not be best for definitive diagnosis of STS?
exfoliation with STS can be an issue:
-non-diagnostic or false-negative results more common due to poor exfoliation
-inflammation can hide the tumor
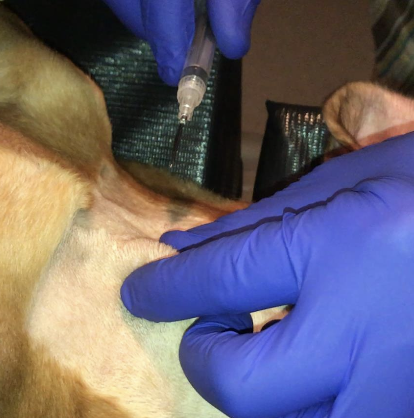
is biopsy useful for diagnosing STS?
yes, it is often necessary for definitive diagnosis and to subtype STS
what is included in the diagnostic work-up of STS?
-routine lab work (CBC, chem, UA)
-imaging
-FNA or biopsy of regional lymph node
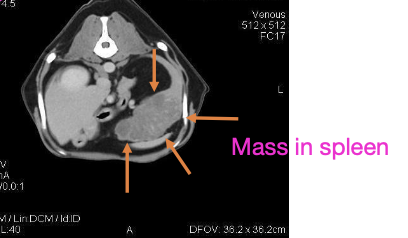
what imaging modalities are used in the diagnostic work-up for STS?
-3 view chest rads
- +/- abdominal imaging (consider with subtype, high grade pelvic limb STS)
- +/- advanced imaging (CT or MRI) for tx planning
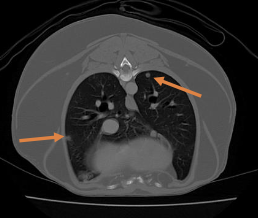
what is the most common site of metastasis of STS?
lungs most common
(in general, STS mets are rare, but depends on grade)
when is LN FNA/biopsy considered for STS?
consider FNA/biopsy with subtype, if LN is abnormal on PE, or grade 3 STS
(LN metastasis is uncommon, but depends on subtype)
how are STS staged?
based on TNM staging (tumor, lymph node, metastasis)
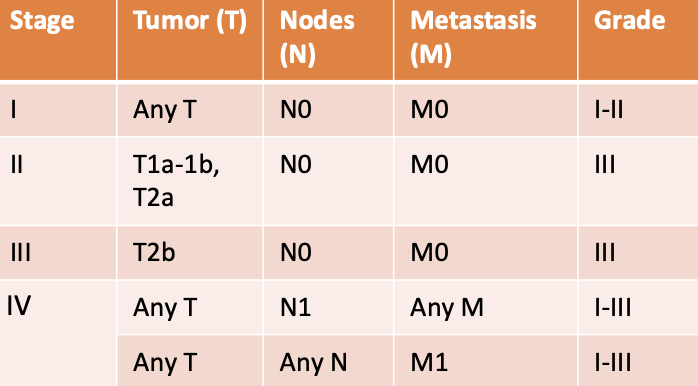
how is the primary tumor assessed for STS staging?
T1: tumor less than or equal to 5cm in diameter
-T1a: superficial tumor
-T1b: deep tumor
T2: tumor over 5cm in diameter
-T2a: superficial tumor
-T2b: deep tumor
how are lymph nodes assessed for STS staging?
N0: no regional LN metastasis
N1: regional LN metastasis
how is distant metastasis assessed for STS staging?
M0: no distant mets
M1: distant mets
what is the predominant challenge in STS treatment?
local tumor control (via sx, radiation)
what does treatment for STS depend on?
location
tumor size
degree of infiltration
histologic grade
completeness of excision
when is systemic therapy (chemo) for STS indicated?
high grade (grade 3) or metastatic STS
typically with doxorubicin
how is surgery done to achieve treatment of STS?
complete excision: margins should be 2-3cm lateral, and 1 facial plane deep
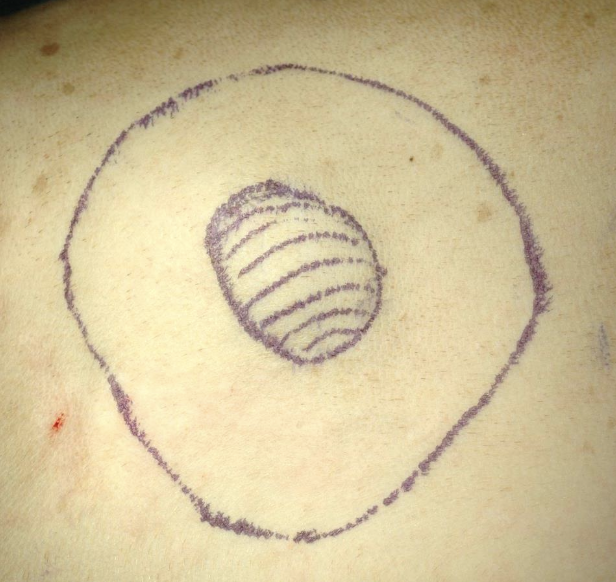
what are the treatment options for incomplete excision of original STS?
-second surgery (excise scar with same margins)
-radiation therapy
-active surveillance
-metronomic chemo or electrochemo (only done if high grade)
what are the 3 histologic features assessed when grading STS with histopath?
1. differentiation score (0-3)
2. mitotic activity (0-3)
3. tumor necrosis (0-2)
how are the histologic features used to assign a grade to STS?
add the scores of each histo feature up to get grade:
-grade 1= 3 or less
-grade 2= 4-5
-grade 3= 6 or more
what is the best adjuvant therapy for incomplete excision of STS?
radiation therapy
what is the overall MST for STS with surgery and radiation therapy?
MST= 2270 days (~6 yrs)
what is the overall response rate of radiation alone to treat STS? complete response rate?
ORR= 46-50%
complete response= 30%
what is the overall MST for hypofractioned radiation for macroscopic STS?
206-513 days (6.8-17 months)
what STS is chemotherapy indicated for?
-grade 3 tumors
-metastatic disease
-intra-abdominal disease
-some subtypes (histiocytic, hemangiosarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma)
what chemotherapeutic agents are used for STS? what are their ORR/CR?
1. doxorubicin (ORR= 23%)
2. mitoxantrone (ORR= 0-33%)
3. ifosfamide (CR = 15%)
what is the metronomic chemotherapy used for STS?
low dose of cytoxan and piroxicam
improved OST in dogs with macroscopic STS tx with hypofractioned radiation
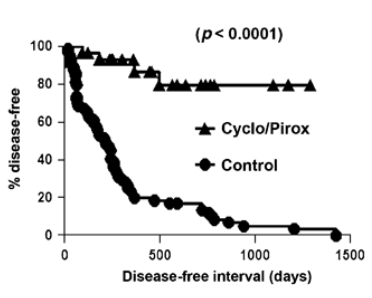
what determines the prognosis of STS?
histologic grade
what are the recurrence rates of STS with incomplete margins?
grade 1: 7%
grade 2: 34%
grade 3: 75% (recurrence mostly occurs in grade 3)
what is the overall survival times with grades 1-3 STS?
grade 1: over 48 months
grade 2: 36 months
grade 3: 7 months
what are the metastatic rates of grade 1-3 STS?
grade 1: 0-13%
grade 2: 6-27%
grade 3: 22-44%
median time to metastasis is around 1 year
how much more likely is a STS to metastasis if the mitotic index is over 20?
5x more likely to met
how does mitotic index affect MST?
MST is associated with mitotic index:
<10= 1444 days (3.9 years)
10-19= 532 days (1.4 years)
>20= 236 days (0.6 year)
what are the unique locations of STS?
-distal elbow or stifle
-oral (most commonly maxilla, esp in goldens)
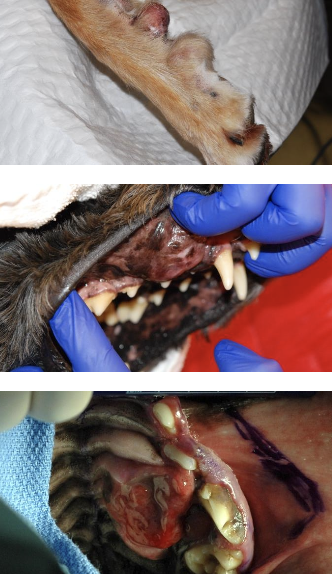
how are distal to elbow/stifle STS treated? what is the recurrence?
marginal excision of low-grade STS
recurrence rate of 11%
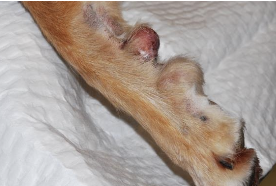
what is the biologic behavior of oral STS?
low/high fibrosarcoma:
-histologically low grade, biologically high grade oral tumors
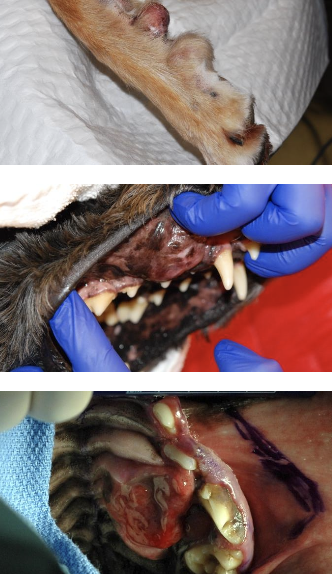
what are the sites of metastasis for oral STS?
pulmonary (12% on necropsy), lymph nodes (20% on necropsy)
what are the prognostic factors of STS?
-surgical margins
-tumor size and location
-recurrence
how do surgical margins affect prognosis of STS?
most important factor for local recurrence
how does tumor size/location affect prognosis of STS?
-tumors <5cm have better prognosis with surgery +/- radiation
-tumors of oral location have worse prognosis
-tumors of lower extremities often have better prognosis
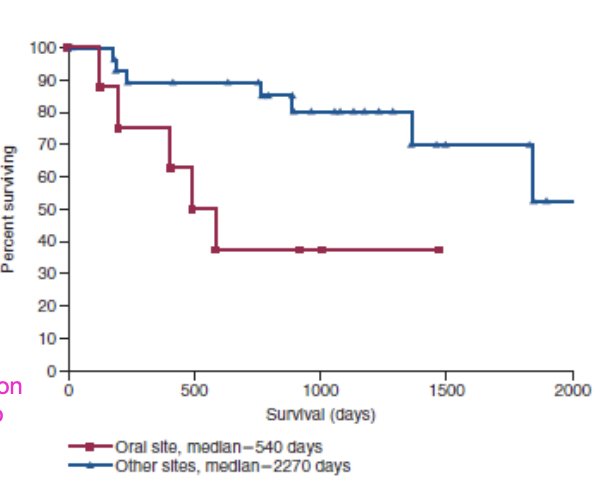
what is the MST of oral STS?
540 days (1.4 yrs)
how does tumor recurrence affect prognosis of STS?
local disease may be more difficult to control and have increased metastatic rate