3.3: nervous system
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
CNS is responsible for
integration, processing, coordination, higher cognitive functions (thinking & memory)
PNS is responsible for _____
-sensation:
-integration:
-response:
delivering sensory info to CNS, carrying motor commands to body, monitor internal & external changes, processes sensory input & determine responses, activate effector organs
subcategories of peripheral nervous system
sensory PNS, motor PNS
types of sensory PNS
somatic & visceral
sensory PNS is responsible for ____
-made up of ___ signals
carrying info from receptors to CNS, afferent
somatic sensory PNS receives sensations from:___
receptors for: ___
skin, bones, muscles, etc,
touch, pressure, vibration & special senses like taste, smell, hearing
*visceral sensory PNS
sensation from organs, mainly touch, temp, etc (like drinking water and feeling its temperature go down the esophagus and stomach and bladder expanding)
motor PNS transmit info from ____ to ____
made up of ___ signals
CNS, body, efferent
somatic motor PNS
-contraction of:
-____ movement,
-____ reflexes
skeletal muscles, voluntary, somatic
autonomic, aka ___ motor PNS:
-regulates autonomic nervous system, specifically: ____
-used for ___ movement
-sympathetic & parasympathetic
visceral, smooth & cardiac muscles & glands, involuntary
glia function
cell support
types of glia for CNS
astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells
astrocytes:
-provides ___ ___
-regulate ____ environment
-regulation of substances in ___ & ___
-___ & ___ damaged tissue
--glia of PNS or CNS?
structural support, extracellular, blood, brain, divide, replace, CNS
oligodendrocytes
-glia of PNS or CNS?
wrap around axons to form myelin sheath, CNS
microglia:
-glia of PNS or CNS?
phagocytic defense cells, clean up debris & eliminate pathogens, CNS
ependymal cells function
-part of CNS or PNS
form & help circulate cerebral spinal fluid, CNS
glia of PNS
satalite & schwann cells
satelite cells function:
part of CNS or PNS?
provide structural support, regulate extracellular environment, PNS
schwann cells
--glia of PNS or CNS?
form myelin sheath & help repair damaged axons, PNS
neurons:
-excitability:
-conductivity:
-secretion:
-extremely long-lived
-amitotic:
-high metabolic rate
respond to stimuli, produce & transmit electrical signals, release neurotransmitters, don’t reproduce through mitosis
anatomy of neuron:
-soma:
-dendrites:
-axon terminal:
cell body, receive signals, communicate with target cell
anatomy of a nerve:
-axon:
-fascicle:
-nerve:
surrounded by myelin sheath, group of axons, group of fascicles & blood vessels
-myelin sheath:
-plasma membrane of schwann cells/ oligodendrocytes facilitate:
-segmented:
insulation around axons, signal transmission, unmyelinated nodes & myelinated internodes
myelinated PNS: ____
begins prenatally or postnatally?
schwann cells spiral around axon, prenatally because babies need to set up good sensory system when they’re born (think “babies don’t have brains, so that’s why they don’t have high CNS control””
myelinated CNS: _____ ___ wrap around axons
begins prenatally or postnatally?
oligodendrocyte process, postnatally
categories of neurons:
sensory (afferent) neurons, motor (efferent) neurons
sensory (afferent) neurons:
-conduct ____ from ___ to ___
-CNS interneurons integrate ___ ___ & mediate ____
signals, receptors, CNS, incoming signals, responses
motor (efferent) neurons conduct ___ from ___ to ___
signals, CNS, effectors
types of neuron shapes
multipolar, pseudounipolar, bipolar
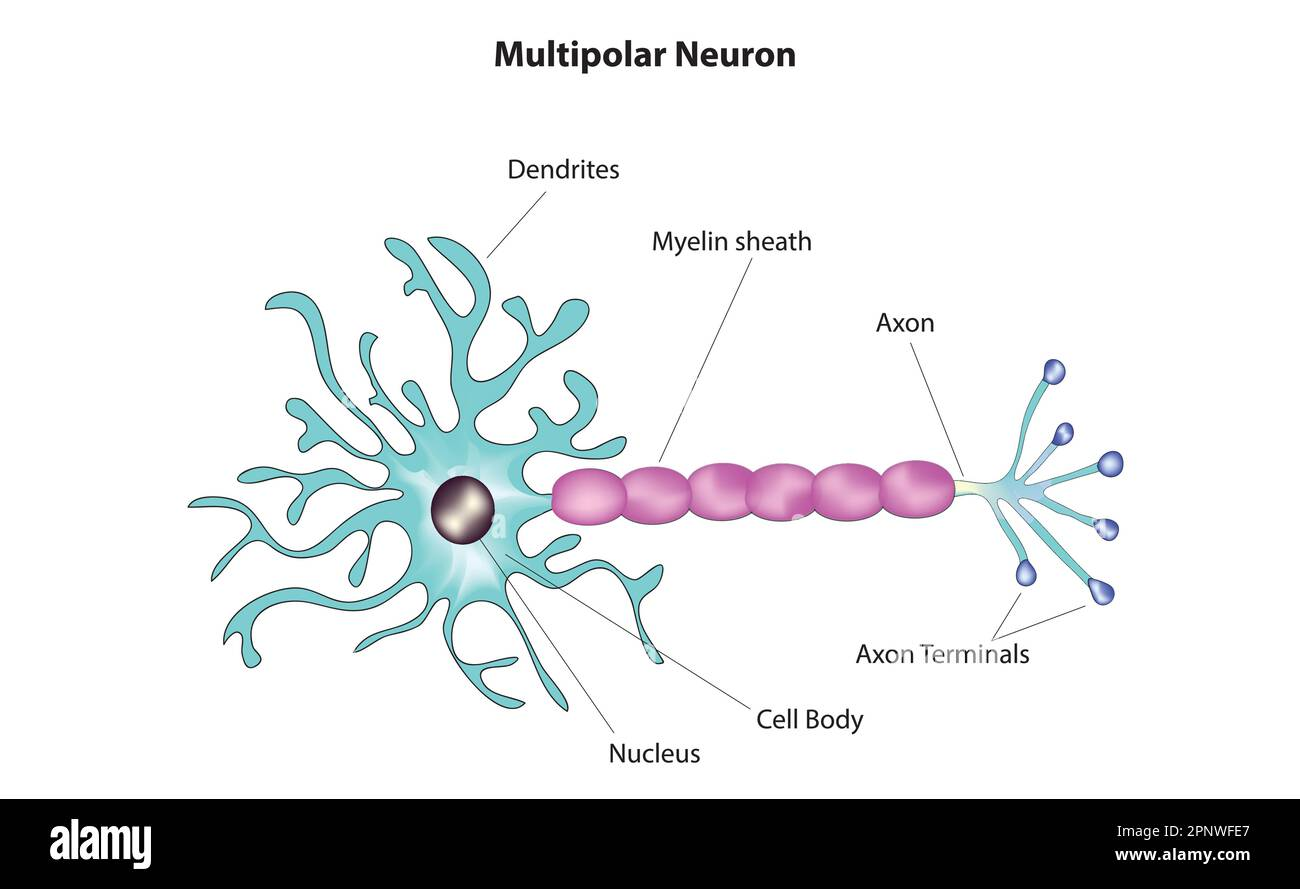
multipolar neurons
typical motor neurons, interneurons
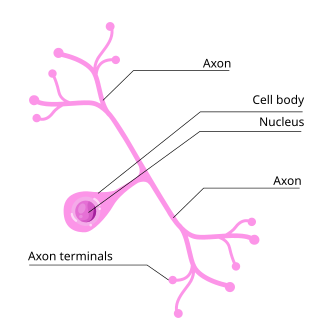
pseudounipolar neurons
sensory neurons
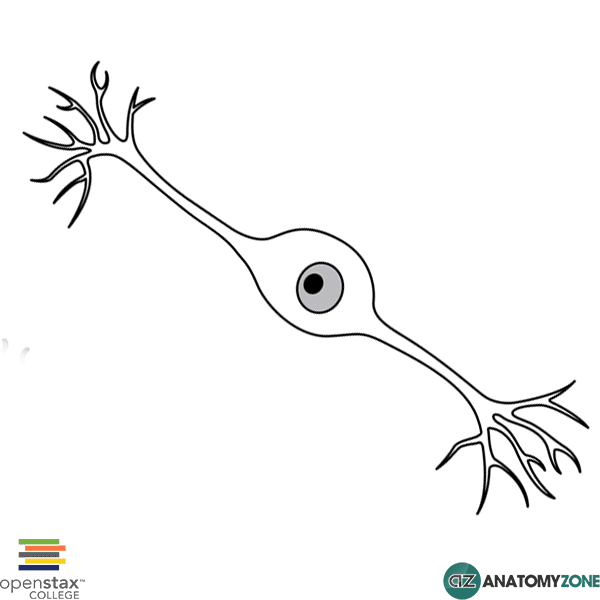
bipolar neurons are found in this type of neuron:
special sensory neuron
gray matter consists of:
soma, dendrites, unmyelinated axons
white matter is made up of
myelinated sheaths
synapes
connection point between neuron & adjacent cell (post synaptic cells)
electrical synapses: ___
-allowing for ____ ____
gap junctions join adjacent cells, rapid transmission
chemical synapses
neurotransmitters released from synaptic vessels to receptors on postsynaptic cell membrane on receiving cell
neurotransmitters: __
types: ___ & ___
-can vary based on ___ ___
chemical signals that alter postsynaptic cell physiology; excitatory, inhibitory, receptor type