Biology Semester 1 Final
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/36
Last updated 2:17 AM on 12/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
Population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
2
New cards
Predator
A consumer in a biological community; An animal that preys on other animals
3
New cards
Predation
An interaction in which one organism kills another for food.
4
New cards
Parasites
An organism that lives in or on another organism, deriving nourishment at the expense of its host, usually without killing it
5
New cards
Limiting factors
Environmental factors that restrict population growth
6
New cards
abiotic factors
nonliving parts of an ecosystem
7
New cards
Abiotic factors examples
(1). air
(2). water
(3). sunlight
(4). soil
(5). temperature
(6). climate
(2). water
(3). sunlight
(4). soil
(5). temperature
(6). climate
8
New cards
biotic factors
living parts of an ecosystem
9
New cards
Biotic examples
plants, animals, fungi, bacteria
10
New cards
Producer (autotroph)
An organism that can make its own food.
11
New cards
Consumers (heterotrophs)
incapable of photosynthesis and must obtain their energy by consuming other organisms
12
New cards
decomposers/detritivores
An organism that breaks down wastes and dead organisms
13
New cards
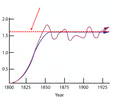
Carry capacity
the maximum size of population the environment will support
14
New cards
Photosynthesis
process by which plants and some other organisms use light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and high-energy carbohydrates such as sugars
15
New cards
cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
16
New cards
Photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O \------\> C6H12O6 + 6O2
17
New cards
cellular respiration equation
C6H12O6+6O2\---\> 6CO2+6H2O+ATP
18
New cards
anaerobic respiration
Respiration that does not require oxygen
19
New cards
Types of fermentation
alcohol and lactic acid
20
New cards
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
21
New cards
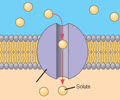
facilitated diffusion
the transport of substances through a cell membrane along a concentration gradient with the aid of carrier proteins
22
New cards
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
23
New cards
hypotonic solution
Solute concentration is less than that inside the cell; cell gains water
24
New cards
hypertonic solution
Solute concentration is greater than that inside the cell; cell loses water
25
New cards
isotonic solution
a solution whose solute concentration is equal to the solute concentration inside a cell
26
New cards
facilitate transport (facilitated diffusion)
27
New cards
carry capacity
28
New cards
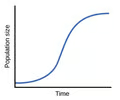
logistic growth
29
New cards
exponential growth
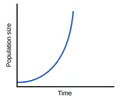
30
New cards
Phospholipids
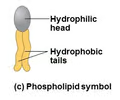
31
New cards
prokaryotic cell
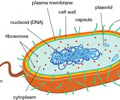
32
New cards
Eukaryotic cells
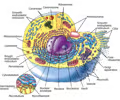
33
New cards
plant cell
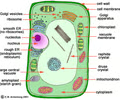
34
New cards
cell wall
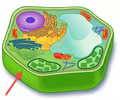
35
New cards
hypertonic solution

36
New cards
hypotonic solution
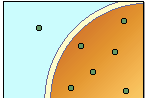
37
New cards
isotonic solution