GGR112 - Final prep
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/14
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
1
New cards
Soil
A natural mixture of inorganic and organic particles that provide a suitable medium for terrestrial plants to grow
2
New cards
Pedology (soil science)
The study of the description, origin, distribution, and classification of soils.
3
New cards
Pedon
the most basic soil sampling unit (1 to 10 m2). \n - Pedons are described and categorized based on their soil horizons, which are defined as physically and/or chemically distinct sub-units.

4
New cards
Soil Formation
* Soils develop in-situ (in place) from regolith
* Soil evolution depends on __*principle soil forming factors*__
* __passive factors__: parent material type, topography, relief, time
* __dynamic factors__: climate, biology, humans
* Principle soil forming factors vary greatly by latitude and climate
* local differences like aspect, relief, and drainage are also important
* Soil evolution depends on __*principle soil forming factors*__
* __passive factors__: parent material type, topography, relief, time
* __dynamic factors__: climate, biology, humans
* Principle soil forming factors vary greatly by latitude and climate
* local differences like aspect, relief, and drainage are also important
5
New cards
Soil fertitlity
Fertile soil includes the following:
* Clay and organics
* Diverse community of microorganisms
* Basic plant nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium)
* Essential trace elements (Mg, B, Co, Cu, Fe, Mn, Mb, S, Zn)
* Neutral to slightly acidic pH (6.0 - 6.8)
* Good porosity and drainage
\
\- Worms and burrowing organisms help improve porosity and drainage, and breakdown organic materials and return important micronutrients to the solum
* Clay and organics
* Diverse community of microorganisms
* Basic plant nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium)
* Essential trace elements (Mg, B, Co, Cu, Fe, Mn, Mb, S, Zn)
* Neutral to slightly acidic pH (6.0 - 6.8)
* Good porosity and drainage
\
\- Worms and burrowing organisms help improve porosity and drainage, and breakdown organic materials and return important micronutrients to the solum
6
New cards
Soil capability for agriculture (A- O)
A - Mineral soils __***capable of sustained production***__ of field crops, these soils require only normal conservation practices. Crop use __**limitations range from insignificant to moderately severe.**__
\
B - Mineral soils of __***marginal capability for the sustained production of field crops***__. __**Severe limitations**__ influence crop choice, requiring special conservation measures to be employed.
\
C - Mineral soils __***unsuitable for the sustained production of field crops***__. __**Very severe**__ limitations, restricted use to pasture and forage production.
\
D - Mineral soils __***unsuitable for crop use***__ or permanent pasture. E__**xtremely severe limitations**__ don’t allow agriculture
O - Organic soils. not classified according to agriculture capability
\
* Southern Ontario is mostly category A
Classes 1 - 8 no limitation and good to too many limitations and not good / organic
\
B - Mineral soils of __***marginal capability for the sustained production of field crops***__. __**Severe limitations**__ influence crop choice, requiring special conservation measures to be employed.
\
C - Mineral soils __***unsuitable for the sustained production of field crops***__. __**Very severe**__ limitations, restricted use to pasture and forage production.
\
D - Mineral soils __***unsuitable for crop use***__ or permanent pasture. E__**xtremely severe limitations**__ don’t allow agriculture
O - Organic soils. not classified according to agriculture capability
\
* Southern Ontario is mostly category A
Classes 1 - 8 no limitation and good to too many limitations and not good / organic
7
New cards
Soil Properties
* Colour
* Texture
* Structure
* Consistence (cohesion)
* Porosity
* Moisture
* Chemistry
* pH (acidity or alkalinity)
* Texture
* Structure
* Consistence (cohesion)
* Porosity
* Moisture
* Chemistry
* pH (acidity or alkalinity)
8
New cards
Colour Property
* Indicative of composition
* Munsell colour chart standard metric for soil scientists
\
* Red soils - high iron oxide
* Dark brown to black - organic rich (southern Ontario)
* Munsell colour chart standard metric for soil scientists
\
* Red soils - high iron oxide
* Dark brown to black - organic rich (southern Ontario)
9
New cards
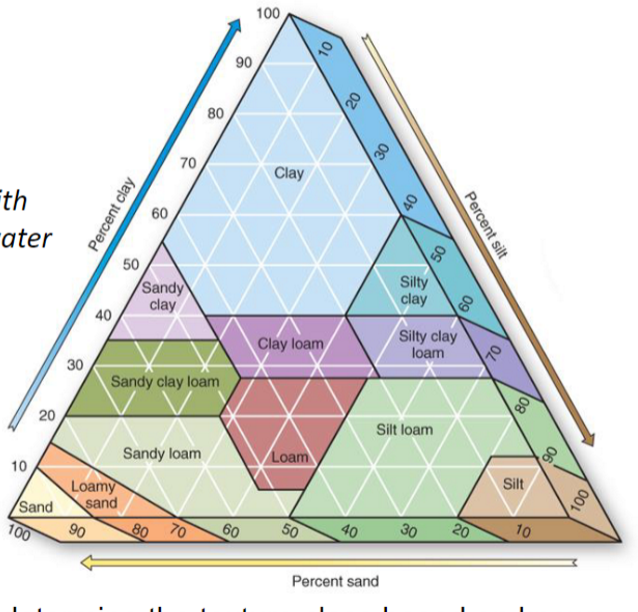
Texture Property
* Soil texture triangle is used to determine the texture class based on known fracitons of sand, silt, and clay
\
Hydrailic Characreristics:
* Sandier soils - faster drainage/low water holding capacity
* Clay-rich soils - slower drainage/ high water holding capacity
\
loam - a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay beneficial for plant growth
* A sandy loam with clay
\
Hydrailic Characreristics:
* Sandier soils - faster drainage/low water holding capacity
* Clay-rich soils - slower drainage/ high water holding capacity
\
loam - a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay beneficial for plant growth
* A sandy loam with clay
10
New cards
Soil ‘Ped’ Structure
* Soil structure - the arrangement of soil particles the smallest natural clump/ cluster of particles is called a ped.
* ped characteristics classify soil structure as granular, platy, blocky, prismatic/columnar
* as well as fine, medium, or coarse
* ped characteristics classify soil structure as granular, platy, blocky, prismatic/columnar
* as well as fine, medium, or coarse
11
New cards
Soil horizons (mineral a, b, c)
Eluviation - leaching of minerals and organics from a horizon
Illuviation - deposition of minerals and organics in a horizon
\
A - eluviation of finer particles/minerals (leaching)
B - illuviation (deposition)
C - recieves little effect from processes in the A and B horizons
Illuviation - deposition of minerals and organics in a horizon
\
A - eluviation of finer particles/minerals (leaching)
B - illuviation (deposition)
C - recieves little effect from processes in the A and B horizons
12
New cards
Soil orders
Regosolic - lacking B horizon, weak, A horizon is thin
Brunisolic - more developed than regosolic
Luvisolic - (toronto)
Podzolic - well developed A and B horizons, significant eluviation/illuviation
Gleysolic and Organic- poorly drained conditions (low oxygen, low rates of decomposition)
\
Brunisolic - more developed than regosolic
Luvisolic - (toronto)
Podzolic - well developed A and B horizons, significant eluviation/illuviation
Gleysolic and Organic- poorly drained conditions (low oxygen, low rates of decomposition)
\
13
New cards
14
New cards
15
New cards