THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM & THE VENTRICULAR SYSTEM (Crammed)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Autonomic nervous system and he endocrine system
They control the internal environment of the body
Sympathetic nervous system
It is the larger of the two parts of the autonomic system and is widely distributed throughout the body, innervating the heart and lungs, the muscle in the walls of many blood vessels, the hair follicles and the sweat glands, and many abdominopelvic viscera.
Sympathetic nervous system
prepare the body for an emergency
Parasympathetic nervous system
The activities of this part of the autonomic system are directed toward conserving and restoring energy
Autonomic ganglion
This is the site where preganglionic nerve fibers synapse on postganglionic neurons
Small intensely fluorescent (SIF) cells
Although an autonomic ganglion is the site where preganglionic fibers synapse on postganglionic neurons, the presence of small interneurons has been recognized. These cells exhibit catecholamine fluorescence and are referred to as?
Dopamine
This is thought to be the transmitter of the small intensely fluorescent (SIF) cells
Acetylcholine
The synaptic transmitter that excites the postganglionic
neurons in both sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia
is?
Acetylcholinesterase
The action of acetylcholine in autonomic ganglia is quickly terminated by hydrolysis by?
Nicotinic and muscarinic receptors
Two types of acetylcholine receptors exist and are known as?
fast excitatory postsynaptic potential (fast EPSP)
Acetylcholine activation of the postsynaptic nicotinic receptors on the dendrites and cell bodies of the postganglionic neurons results in a depolarization of the membrane, an influx of Na+ and Ca2+ ions, and the generation of the ____
slow excitatory postsynaptic potential (slow EPSP)
Acetylcholine is also believed to activate small numbers of postsynaptic muscarinic receptors. This results in the development of the?
slow inhibitory postsynaptic potential (slow IPSP)
The activation of postsynaptic muscarinic receptors may also result in the development of the?
Cholinergic
All neurons that release acetylcholine at their endings are called as ____, which works like acetylcholine.
adrenergic endings.
Sympathetic endings that use norepinephrine are called?
alpha and beta receptors
There are two major kinds of receptors in the effector organs, called as the?
alpha-1 and alpha-2 receptors
What are the two subgroups of alpha receptors?
beta-1 and beta-2 receptors
What are the two subgroups beta receptors?
metaproterenol and albuterol
The bronchodilating drugs, such as ___ and ____, mainly act on beta-2 receptors.
phenoxybenzamine
The alpha-adrenergic receptors can be blocked by agents such as?
propranolol
The beta-adrenergic receptors can be blocked by agents such as?
reserpine
The synthesis and storage of norepinephrine at sympathetic endings can be inhibited by?
Hypothalamus
_____ has a controlling influence on the autonomic nervous system and appears to integrate the autonomic and neuroendocrine systems, thus preserving body homeostasis
Diabetes Mellitus
This is a common cause of peripheral nerve neuropathy. This involves sensory and motor dysfunction and may also include autonomic dysfunction. The clinical features of autonomic dysfunction include postural hypotension, peripheral edema, pupillary abnormalities, and impaired sweating. The cause is probably associated with chronic hyperglycemia.
Horner Syndrome
This disease consists of (1) constriction of the pupil (miosis), (2) slight drooping of the eyelid (ptosis), (3) enophthalmos,3 (4) vasodilation of skin arterioles,and (5) loss of sweating (anhydrosis). All these symptoms result from an interruption of the sympathetic nerve supply to the head and neck.
Argyll Robertson Pupil
This is characterized by a small pupil, which is of fixed size and does not react to light but does contract with accommodation
Adie Tonic Pupil Syndrome
the pupil has a decreased or absent light reflex, a slow or delayed contraction to near vision, and a slow or delayed dilatation in the dark.
ventricles
These ____ are four fluid-filled cavities located within the brain; these are the two lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle
Roof, floor, and medial wall
The body of the lateral ventricle consists of?
Third Ventricle
It is a slitlike cleft between the two thalami.
It communicates anteriorly with the lateral ventricles
through the interventricular foramina (of Monro) and posteriorly with the fourth ventricle through the cerebral aqueduct (of Sylvius)
Lateral Ventricles
It is a roughly C-shaped cavity and may be divided into a body, which occupies the parietal lobe and from which anterior, posterior, and inferior horns extend into the frontal, occipital, and temporal lobes, respectively.
Fourth Ventricle
is a tent-shaped cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid. It is situated anterior to the cerebellum and
posterior to the pons and the superior half of the medulla
oblongata
Subarachnoid Space
This is the interval between the arachnoid mater and pia mater and, therefore, is present where these meninges envelop the brain and spinal cord
Cerebrospinal Fluid
This is found in the ventricles of the
brain and in the subarachnoid space around the brain and
spinal cord. It has a volume of about 150 mL. It is a clear,
colorless fluid and possesses, in solution, inorganic salts
similar to those in the blood plasma
Cerebrospinal Fluid
This fluid, which bathes the external and internal surfaces of the brain and spinal cord, serves as a cushion between the central nervous system and the surrounding bones, thus protecting it against mechanical trauma.
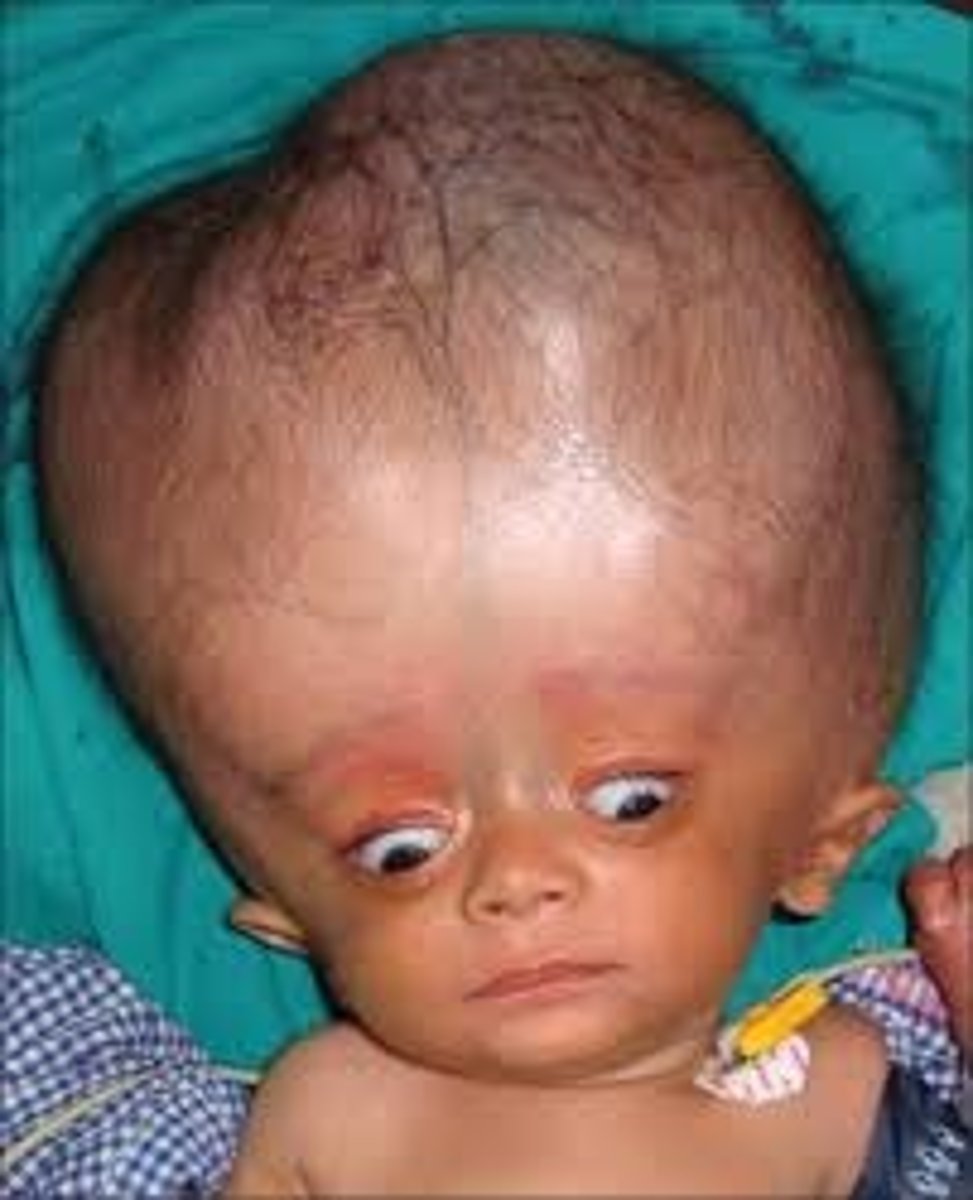
Hydrocephalus
____ is an abnormal increase in the volume of the cerebrospinal fluid within the skull.
Frey Syndrome
This syndrome is an interesting complication that sometimes follows penetrating wounds of the parotid gland.

Hirschsprung Disease
This is a congenital condition in which there is a failure of development of the myenteric plexus (Auerbach plexus)