Final Review-Bio 181
1/237
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
238 Terms
Which of the following best describes a hypothesis?
a plausible, testable explanation for a single natural event
Plasma membranes are selectively permeable. This means that
the plasma membrane allows some substances to enter or leave a cell more easily than others.
What determines the number of bonds an atom will make?
The number of electrons in the outermost electron shell
The process by which a cell engulfs a foreign particle is known as:
phagocytosis
Plasma membranes are selectively permeable. This means that
the plasma membrane allows some substances to enter or leave a cell more easily than others.
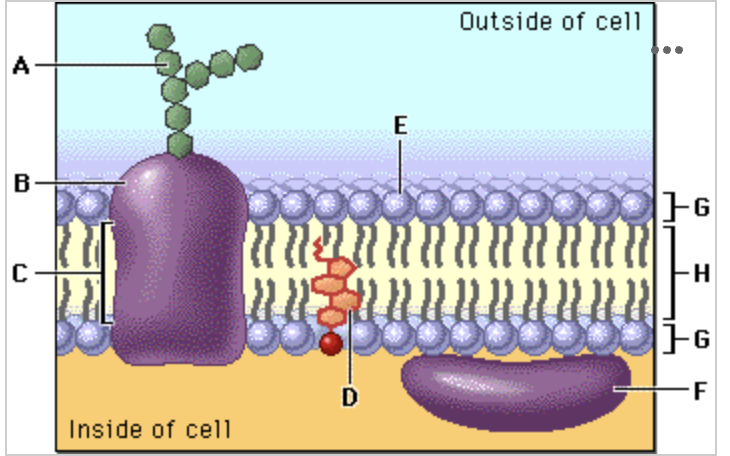
In the diagram, what is the charge of E and H, respectively?
E: negative, H: neutral (no charge)
Which of the following cellular processes is coupled with the hydrolysis of ATP and move a solute against its concentration gradient (low to high)? ?
active transport
Carbohydrates primary function in our bodies is for
fuel source
Carbon is able to form an immense diversity of organic molecules because of carbon’s tendency to form covalent bonds.
Ability to bond with up to four other atoms.
Ability to bond together to form extensive, branched, or unbranched “carbonskeletons.”
Capacity to form single and double bonds.
What is a buffer and why is it important?
The buffer maintains the ph system and and is important so there isn't rapid change in the ph
If animal cells were immersed in distilled water, what is likely to happen?
The cells will burst
An atom that normally has ___ in its outer shell would tend not to form chemical bonds with other atoms.
8 electrons
Starches are polymers of _____.
fatty acids
What is the goal of diffusion?
to have an equal concentration throughout an area
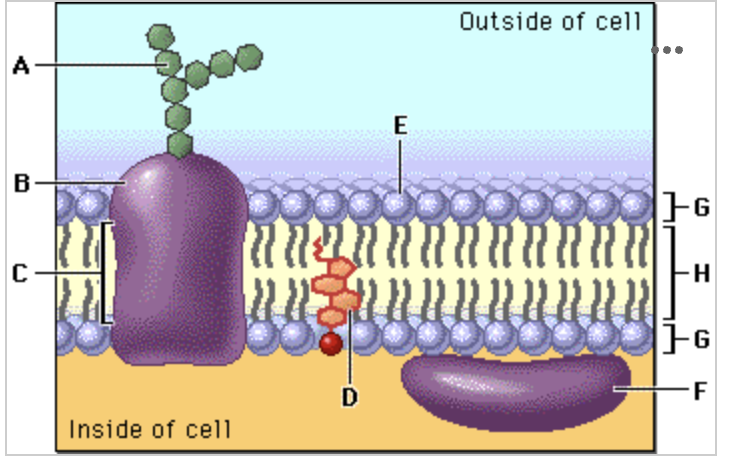
In the diagram, structure G,H and G all together corresponds to:
a phospholipid bilayer
Nonpolar molecules that cluster away from water are called _____ molecules.
Hydrophobic
Which of the following is the first step in a scientific investigation?
Observation
It is the polarity of water that gives water its unique properties. The ability of water molecules to
form hydrogen bonds with other water molecules is critical to
The milder temperatures of coastal regions compared to inland areas.
The movement of water from the roots of a tree to its leaves via cohesion and adhesion.
The ability of certain insects to walk on the surface of water.
Evaporative cooling of skin surfaces.
Which of the following processes can move a solute against its concentration gradient (low to high)?
active transport
What is the basic difference between exergonic and endergonic reactions?
Exogonic reactions release energy; endergonic reactions absorb it.
Which transport mechanism can bring whole cells into a cell?
phagocytosis
Which is the correct term for compounds that do not mix with water?
hydrophobic
Saturated fats have all of the following characteristics except:
they tend to dissolve in water easily
The principal force driving movement in diffusion is
concentration gradient
Simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion are related in that both
depend on a concentration gradient
Water moves via osmosis _________
from an area with a high concentration of water to one of lower concentration
The part of the cell that directly regulates what enters and leaves the cell is the ___________.
cell membrane
Homeostasis is the _____.
maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment
Which is an organic molecule?
CH4
Which of the following is/are properties of life?
A complex organization
The ability to reproduce
the ability to take in energy and use it
The ability to respond to the environment
Facilitated diffusion across a biological membrane requires ________ and moves a substance ________ its concentration gradient.
transport proteins . . . down (high to low)
Which of the following sequences correctly lists in order the steps for proteinaceous protein synthesis
synthesis of the protein on the ribosome, modification in the endoplasmic reticulum, tagging in the Golgi, distribution via the vesicle
Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins?
Long term energy storage
The following chemical reactants produce the ester ethyl ethanoate (C4H8O2):
C2H6O + CH3COOH-> C4H8O2
What type of reaction occurs to make ethyl ethanoate?
condensation
You are adrift in the Atlantic Ocean, and, being thirsty, drink the surrounding seawater. As a result,
you dehydrate yourself.
The type of logical thinking that uses related observations to arrive at a general conclusion is called ________.
inductive reasoning
When viewing a specimen through a light microscope, scientists use ________ to distinguish the individual components of cells.
special stains
An important class of proteins are called enzymes.
What is the primary function of enzymes?
act as catalysts in biological reactions
The smallest unit of biological structure that meets the functional requirements of “living” is the ________.
cell
What is the process by which cells link monomers together to form polymers?
dehydration (or condensation) synthesis
Starches are polymers of _____.
monosaccharides
Atoms that vary in the number of neutrons found in their nuclei are called ________.
isotopes
When acids are added to a solution, the pH should ________.
decrease
The presence of a membrane-enclosed nucleus is a characteristic of ________.
eukaryotic cells
Insulin is a protein that is produced by pancreatic cells and secreted into the bloodstream. Which of the following options correctly lists the order of the structures through which insulin passes from its production to its exit from the cell?
rough ER, transport vesicles, cell membrane
What are the 4 classes of macromolecules needed for life?
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
What is the primary function of carbohydrates attached to the exterior of cell membranes (Glycoprotine or Glycolipid)?
identification of the cell
Which of the following sequences represents the hierarchy of biological organization from the most inclusive to the least complex level?
atom, molecule, macromolecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ
Chemiosmosis involves
the movement of hydrogen atoms across a mitochondrial membrane
Which respiration process yields more energy?
aerobic; it makes about 38 ATPs
The energy that is produced from the breakdown of glucose comes in the form of _____. When this energy is used it turns into ______
ATP; ADP
Which of the following is an important difference between light-dependent and light independent reactions of photosynthesis?
The light-dependent reactions produce ATP and NADPH; the light-independent reactions use energy stored in ATP and NADPH.
Through respiration, humans breathe in O2 and breathe out CO2. However, what would happen if we did not breathe in O2?
We would not make enough ATP to meet our energy requirements
Which of the following does NOT perform cellular respiration?
viruses
Which statement correctly describes carbon fixation?
the conversion of CO2 into an organic compound
Which process yields more energy per molecule of glucose?
aerobic; it makes about 38 ATPs
Coupling occurs when the energy released by an exergonic reaction is
Used to drive an endergonic reaction.
The electron transport system is a series of electron carrier molecules. In eukaryotes, where can this structure be found?
mitochondria
Explain the anabolic reaction and catabolic reaction which are the chemical reactions happening in your body and give me a example of each reaction.
anabolic reactions build larger molecules from smaller ones, requiring energy,(Protein synthesis: Amino acids are linked together to create proteins). while catabolic reactions break down larger molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy.(Digestion: Food molecules are broken down into smaller, absorbable components.)
Most of the carbon dioxide normally present in human blood comes from
the Krebs cycle
Energy is _____.
the capacity to perform work
Cramps in human during exercise are caused by:
lactic acid fermentation
Which kinds of organisms perform cellular respiration?
anything living performs cellular respiration
Oxygen consumption can be used as a measure of metabolic rate because oxygen is
necessary for ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation
The most ATP is produced during the cellular respiration from a glucose by __________________.
Oxidative phosphorylation
The electron transport system is a series of electron carrier molecules. In eukaryotes, where can this structure be found?
mitochondria
Which of the following would occur next if oxygen is present in the cell?
Krebs Cycle
What is the basic difference between exergonic and endergonic reactions?
Exogonic reactions release energy; endergonic reactions absorb it.
Which of the following is NOT involved in the direct production of energy through chemiosmosis?
the production of ethyl alcohol in anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic respiration (fermentation) occurs under which of the following conditions?
no oxygen is present
Where is the potential energy in the molecule stored?
in the bond
The energy currency used by cells is ________.
ATP
Through respiration, humans breathe in O2 and breathe out CO2. However, what would happen if we did not breathe in O2?
We would not make enough ATP to meet our energy requirements
What role does NADH & FADH2 play in aerobic respiration?
it is a carrier molecule for hydrogens & electrons
Which of the following occurs in both photosynthesis and respiration?
chemiosmosis
Which of the following statements regarding enzyme function is false?
Enzymes are used up in chemical reactions.
The mechanism of enzyme action is to __________.
Lower the energy of the activation of a reaction
Which of the following comparisons or contrasts between endergonic and exergonic reactions is false?
Endergonic reactions take place slowly and exergonic reactions take place quickly
What is the basic difference between exergonic and endergonic reactions?
Exogonic reactions release energy; endergonic reactions absorb it.
What is the name of the process in which glucose is converted to pyruvate?
glycolysis
What is removed from pyruvate during its conversion into an acetyl group?
carbon dioxide
In what part of the cell does the krebs/citric acid cycle occur?
mitochondria
What role does ATP play in aerobic respiration?
it is a molecule used for energy
During respiration, most ATP is formed as a direct result of the movement of
protons(H+) down a concentration gradient
Which of the following does NOT perform cellular respiration?
viruses
An allosteric inhibitor does which of the following?
Binds to an enzyme away from the active site and changes the conformation of the active site, decreasing its affinity for the substrate
In which compartment of the plant cell do the light independent reactions of photosynthesis take place?
stroma
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
glycolysis occurs in the mitochondria
An important class of proteins are called enzymes.
What is the primary function of enzymes?
act as catalysts in biological reactions
Three of the same species of plant are each grown under a different colored light for the same
amount of time. Plant A is grown under blue light, Plant B is grown under green light, and Plant C is grown under orange light. Assuming the plants use only chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b for photosynthesis, what would be the predicted order of the plants from most growth to least growth?
A, C, B
What is the purpose of cellular respiration? (What’s the POINT?!)
to break down glucose to make ATP
Which of the following is the FIRST process to happen when food molecules enter into a cell?
Glycolysis
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a toxic by-product of cellular metabolism in aerobic organisms. The reaction shown occurs within the cells to prevent the accumulation of hydrogen peroxide.
Calalase
H2O2---------------------> H2O +O2
In this reaction, catalase functions as an
Enzyme in the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide.
The end products of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis are
ATP, NADPH, O2
What are the products of anaerobic respiration (fermentation) if the organism is a plant?
ethyl alcohol, CO2 & ATP
Explain why I recommended you to run during the daytime rather than night time in ch8 photosynthesis lecture?
by running during the day, you benefit from the oxygen released by plants during photosynthesis, potentially making your run more efficient and enjoyable
In incomplete dominance, there are no
Dominant or recessive alleles
Meiosis differs from mitosis in that ____________only occurs in meiosis
crossing over
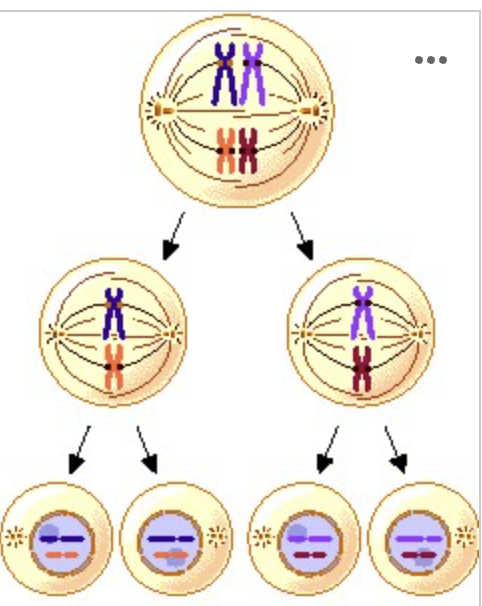
What process is illustrated?
Meiosis
A dominant allele masks the effects of a recessive allele