ib economics chapter 3
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/14
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
1
New cards
Elastic: when changes in price is greater than changes in quantity
Inelastic: when changes in price is smaller than changes in quantity
Inelastic: when changes in price is smaller than changes in quantity
Explain elastic and inelastic
2
New cards
a numerical measure of responsiveness of quantity demanded following a change in price
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
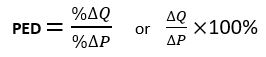
3
New cards
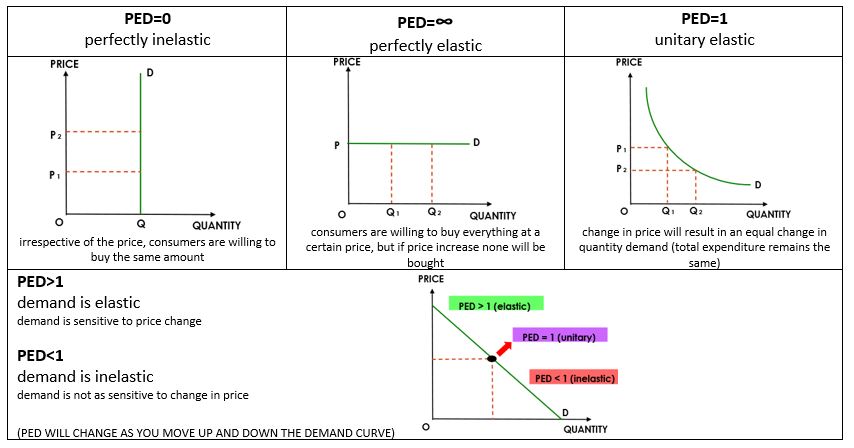
1. PED is always negative- because of law of demand ‘inverse relationship between p & q’
2. PED is always measured as a percentage- for easier comparison
2. PED is always measured as a percentage- for easier comparison
PED Rules
4
New cards
Factors Affecting PED:
1. Range and attractiveness of substitutes: increase in attractive substitutes= increase in willingness to switch
2. Necessities vs luxuries:
o Necessities- things that are essential for survival (PED
1. Range and attractiveness of substitutes: increase in attractive substitutes= increase in willingness to switch
2. Necessities vs luxuries:
o Necessities- things that are essential for survival (PED
Factors Affecting PED
5
New cards
1. Pricing decisions of a firm
2. Relevance to primary and manufactured products
3. Indirect taxes
2. Relevance to primary and manufactured products
3. Indirect taxes
Applications of PED:
6
New cards
3 Different PED Graphs
7
New cards
a numerical measure of responsiveness of one demand following a change in income
Income Elasticity of Demand (YED)
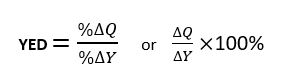
8
New cards
1. Relationship between income and demand may not always be positive
2. YED is always measured as a percentage- for easier comparison
3. When YED= positive (normal goods):
• income increases, leads to increase in quantity demand
• income decreases, leads to decrease in quantity demand
4. When YED= negative (inferior goods):
• income increases, leads to decrease in quantity demand
• income decreases, leads to increase in quantity demand
2. YED is always measured as a percentage- for easier comparison
3. When YED= positive (normal goods):
• income increases, leads to increase in quantity demand
• income decreases, leads to decrease in quantity demand
4. When YED= negative (inferior goods):
• income increases, leads to decrease in quantity demand
• income decreases, leads to increase in quantity demand
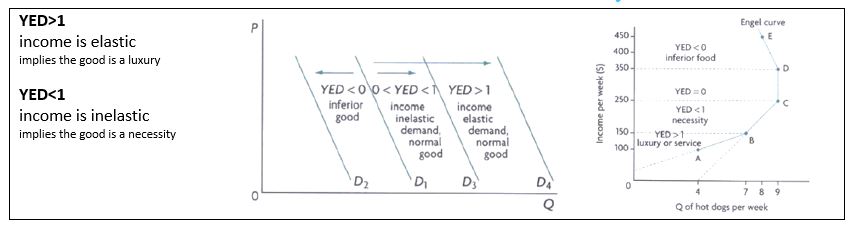
Rules for YED
9
New cards
YED Graphs
10
New cards
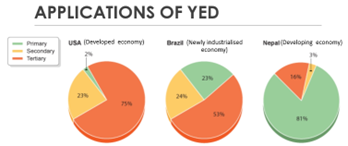
1. YED and Producers- as economic growth increases, income increases, thus demand for goods and services (expansion of a market of a particular good depends on its YED, the more expansion the higher profit for producers)
• During Economic Growth: demand for normal luxury goods will increase by a larger proportion where YED>1
o Y⇧- the demand for inferior goods and necessities will increase by a smaller proportion (YED
• During Economic Growth: demand for normal luxury goods will increase by a larger proportion where YED>1
o Y⇧- the demand for inferior goods and necessities will increase by a smaller proportion (YED
Applications of YED
11
New cards
a numerical measure of responsiveness of supply for a product following a change in price of that product
Price Elasticity of Supply (PES)
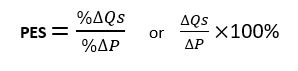
12
New cards
1. Length of time- firms can increase their productive capacity over time by investing in capital equipment and taking advantage of technological advances
2. Mobility of factors of production- factor mobility= increase in PES, as there is more of an ability to move factors of production out of one production process to another
3. Spare capacity of firms- firms need to accommodate to demand with output changes rather than change in price, spare capacity = ⇧ in PED and output , maximum capacity= ⇩ in PES and output
4. Ability to store stocks- if firms posses unused raw materials, components of finished products, they can quickly increase their production in response to an increase in price. Some products are easier to store e.g. books vs fresh produce
2. Mobility of factors of production- factor mobility= increase in PES, as there is more of an ability to move factors of production out of one production process to another
3. Spare capacity of firms- firms need to accommodate to demand with output changes rather than change in price, spare capacity = ⇧ in PED and output , maximum capacity= ⇩ in PES and output
4. Ability to store stocks- if firms posses unused raw materials, components of finished products, they can quickly increase their production in response to an increase in price. Some products are easier to store e.g. books vs fresh produce
Factors Affecting PES
13
New cards
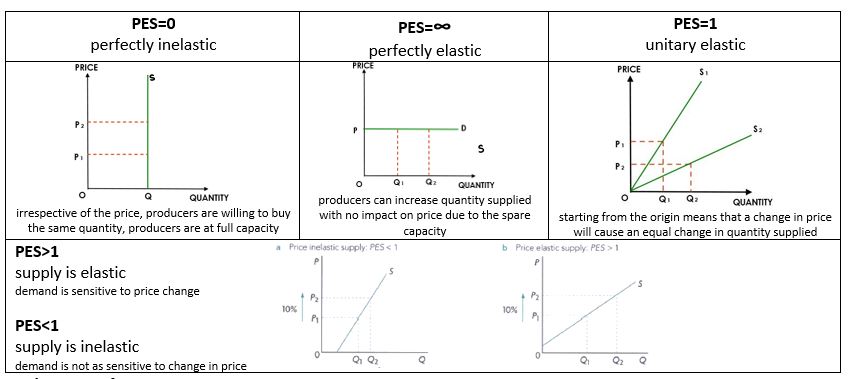
PES Graphs
14
New cards
1. PES in relation to primary and manufactured products:
• primary products are goods that are available from cultivating raw materials without a manufacturing process, PES=inelastic as time taken to respond to price changes is too long, PED=inelastic, thus causes fluctuations in price and producer’s revenue
• manufactured products are the making of goods or wares by manual labour or by machinery, PES = elastic because it is easier to adapt to price change, PED= elastic, thus demand and supply will not create volatile price changes and unstable revenue
• primary products are goods that are available from cultivating raw materials without a manufacturing process, PES=inelastic as time taken to respond to price changes is too long, PED=inelastic, thus causes fluctuations in price and producer’s revenue
• manufactured products are the making of goods or wares by manual labour or by machinery, PES = elastic because it is easier to adapt to price change, PED= elastic, thus demand and supply will not create volatile price changes and unstable revenue
Applications of PES
15
New cards
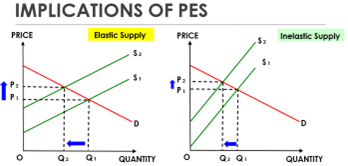
A change in price and quantity is greater for elastic supply than inelastic supply. PES will influence the nature of a change in the equilibrium following a shift in supply curve
Implications of PES