Clinical Correlations/Opioid Epidemic
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What are the five causes of the current opioid epidemic?
1. Pain as the fifth vital sign
2. Unrealistic patient expectations regarding chronic pain management
3. Very bad statistics (0.03%)
4. Marketing of oxycontin and duragesic in the 1990s
5. Neuroexcitatory effects of oxycodone, oxymorphone, and hydromorphone
Past research said that __% of opioid users developed dependency.
0.03% (not true!)
What is misuse?
use of a medication (prescribed for a medical purpose) other than as directed or as indicated, whether willfully or unintentionally and whether or not harm results
What is physical dependence?
a state of adaptation that is manifested by a drug-class-specific withdrawal syndrome that can be produced by abrupt cessation, rapid dose reduction, decreasing blood level of the drug or administration of an antagonist
What is tolerance?
a state of adaptation in which exposure to a drug induces changes that result in the diminished effects of one or more drugs in the body over time
What is abuse?
any use of an illegal drug or the intentional self-administration of a medication for a nonmedical purpose such as altering one's state of consciousness (for example, "getting high")
What is addiction?
a primary, chronic, neurobiological disease, with genetic, psychosocial and environmental factors influencing its development and manifestations; it is characterized by behaviors that include impaired control over drug use, compulsive use, continued use despite harm and craving or a combination of these
How did COVID cause a significant rise opioid use?
disruptions in treatment and support systems
isolation
social determinants of health cause greater vulnerability
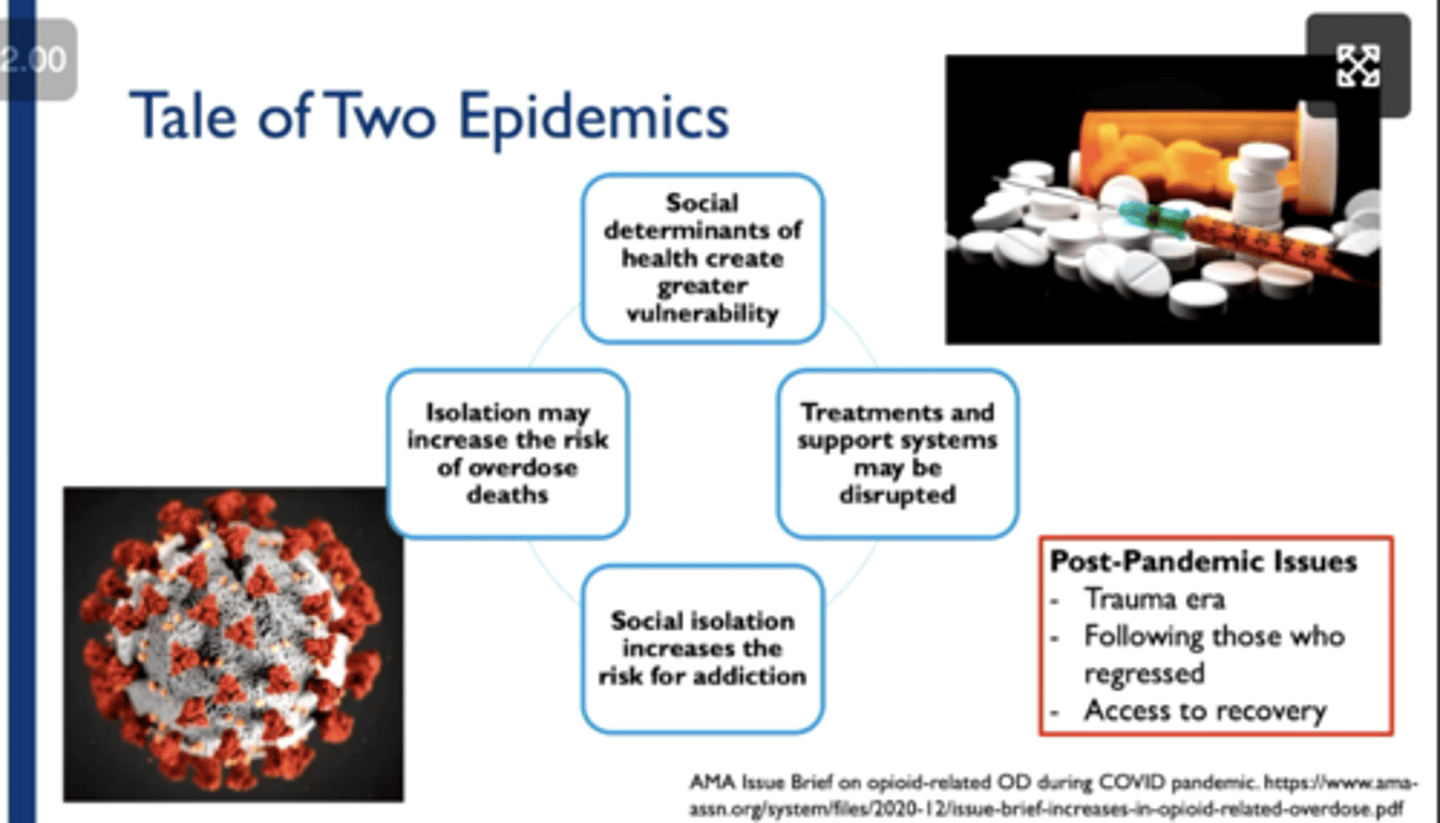
Post-pandemic opioid use issues include
trauma era
follow up with those who regressed
access to recovery
In NC in 2022, there were ____ overdose deaths per 100,000 residents.
38.5
Post-surgical patients receiving opiates for pain control are particularly vulnerable to dependence due to
Excessive post-procedural prescribing of opioids
Gaps in follow-up
Inadequate disposal of unused excess suppl
___% of opioid naive patients develop dependence.
5-15%
What groups are at higher risk of overdose?
Diagnosed mental health condition
Substance use disorder
Which procedures account for the highest proportions of US dental opioid prescriptions?
extractions (65.2%)
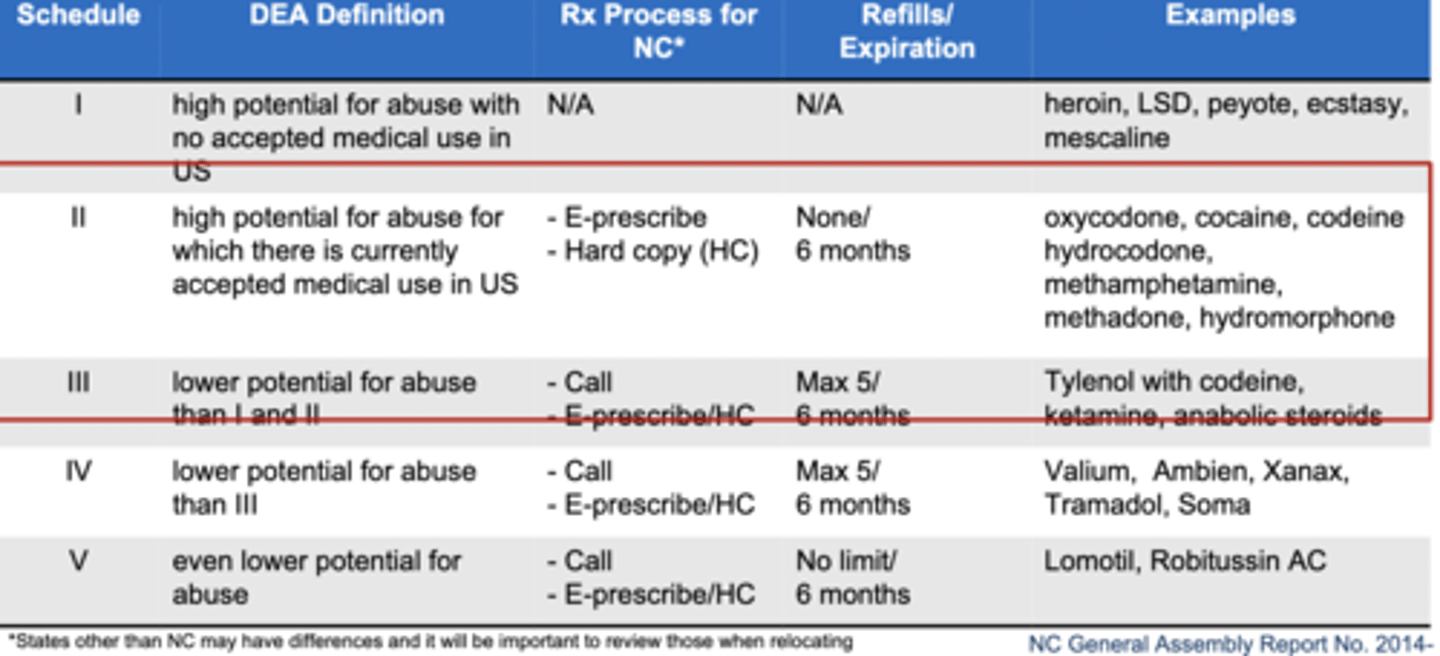
What are the classifications for the controlled substance drug schedules?
Schedule I = highest potential for abuse with no accepted medical use
Schedule II = high potential for abuse with some accepted medical use
↓
Schedule V = lowest potential for abuse
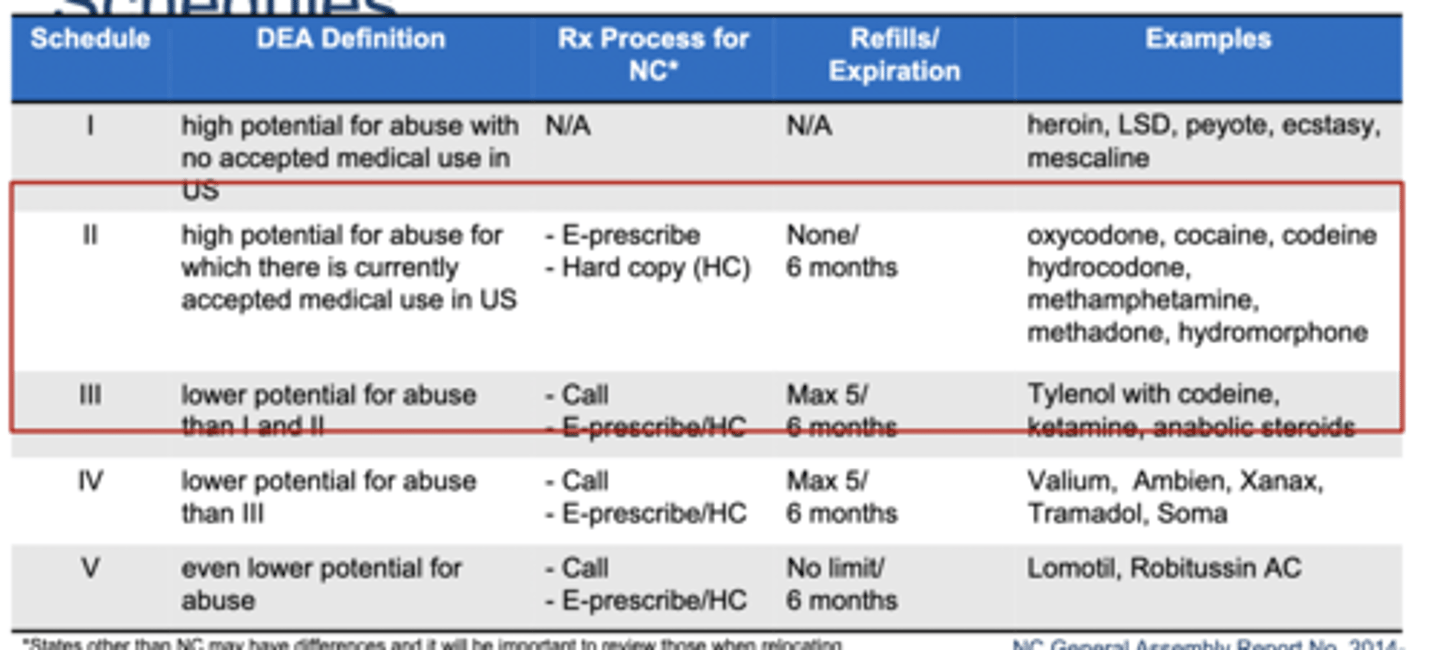
Most opioids are schedule
II - III
What is the NC STOP Act 2017?
limits supply of opioids doctors can prescribe to 5-7 day supply, with follow up necessary for refills
required E-prescriptions
mandatory use of PDMP and document

What is the NC HOPE Act 2018?
increase penalties for healthcare workers who steal patient drugs
increase law enforcement on drug distribution in communities

What are the types of orofacial pain?
nociceptive (tissue injury, inflammation)
neuropathic (lesion or nervous system dysfunction)
nociplastic (hypersensitivity, altered nociceptive pain with MSK involvement)
What are some pharmacological approaches to acute dental pain and patient considerations?
pre-conditioning (focus on function)
appropriateness and individualization of prescribing
non-narcotic alternatives and efficacy
develop a practice policy/protocol addressing risk mitigation measures
What is the DIPM?
Dental Impaction Pain Model
post surgicaldental pain generally may be moderate to severe but typically resolves in 1-2 days after the extraction
How does presurgical NSAID use delay the onset of postoperative pain?
Reach therapeutic blood levels of the NSAID before the surgical trauma generates various prostaglandins
NSAIDs inhibit prostaglandin synthesis but do not attenuate the response to prostaglandins once they have been formed
Mild acute orofacial pain can be treated with
ibuprofen 200-400 mg PO every 4-6hours PRN
Mild to moderate acute orofacial pain can be treated with
ibuprofen 400-600 mg PO every 6hours x 24 hours, then every 4-6hours PRN
Moderate to severe acute orofacial pain can be treated with
Ibuprofen 600 mg + APAP 650 mg every 6 hours x 24 hours, then every 4-6 hours PRN
"2-4-24 Regimen"
Severe acute orofacial pain can be treated with
opioids
What is the maximum daily dose of ibuprofen?
1200 mg/day (OTC)
3200 mg/day (prescription)
What is the max acetaminophen in tablets now?
325 mg
What is NNT?
number of patients that need to be treated in order to have an impact on one person
you want the number as close to 1 as possible
What is the benefit of acetaminophen in combo with NSAIDs?
avoid dose ceiling effect
What is the acetaminophen max daily dose?
4000 mg
Which opioid receptor is associated with dependence?
delta
Which opioid receptor is associated with respiratory depression and euphoria?
mu
Which opioid receptor is associated with dysphoria?
kappa
What is the drug of choice for nociceptive pain?
anti-inflammatories
NOT opioids
What are the cons of tramadol?
Limited therapeutic advantage alone
increased risk of serotonin syndrome
can cause seizures at 300 mg
300 mg of tramadol can cause
seizures
What is cold/heat therapy? What is the benefit?
first 1-2 days, ice packs 15 mins on, 10 mins off
next 2-3 days, heat packs 20 minute cycles for swelling
rotation reduces skin irritation and expands blood vessels
True or False: NSAIDs increase risk of GI bleeding in the presence of SSRIs.
TRUE!
True or False: Avoid prescribing opioids and benzodiazepines concurrently whenever possible.
TRUE!
The goal of risk mitigation is
make opioid prescribing safer while maintaining access to opioid analgesics for those patients who are benefitting from them
What are some key risk mitigation strategies?
1. assess patient history
2. use PDMP
3. optimal patient communication practices and expectations
4. appropriate storage and disposal
5. consideration for naloxone co-prescribing when appropriate
What is the PDMP?
Prescription Drug Monitoring Program
Used to effectively track patient's controlled substance uses across different health facilities (in the same state)
What is the difference between acute, subacute, and chronic pain?
acute < 1 month
subacute 1 - 3 months
chronic > 3 months