Preparation of Serum and Plasma for Testing
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
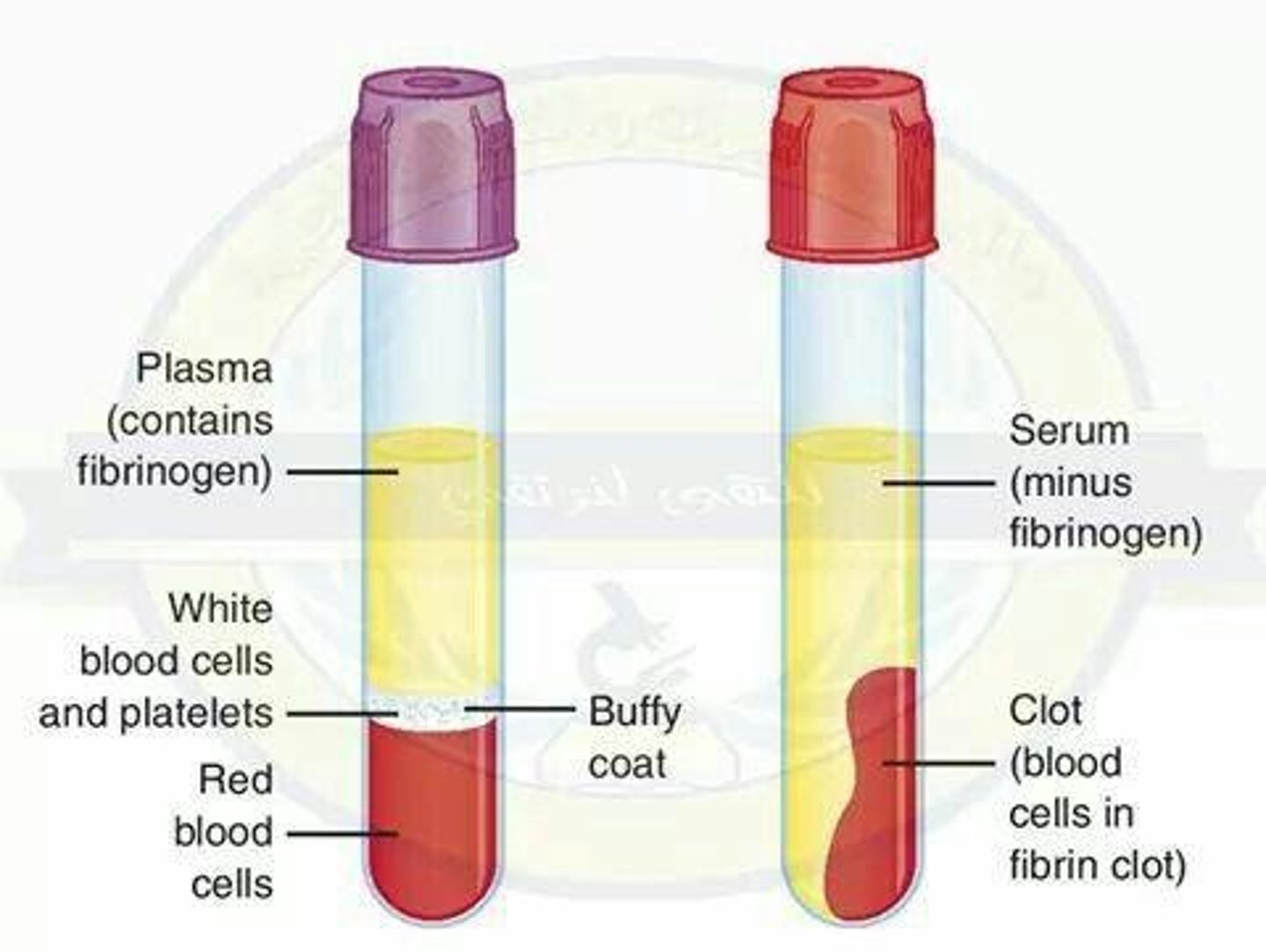
Serum
Clear liquid from clotted blood, without clotting factors.
Plasma
Straw-colored liquid, transports blood cells and substances.
Hematopoiesis
Process of blood cell formation in the body.
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells responsible for oxygen transport.
Leukocytes
White blood cells involved in immune response.
Platelets
Cell fragments aiding in blood clotting.
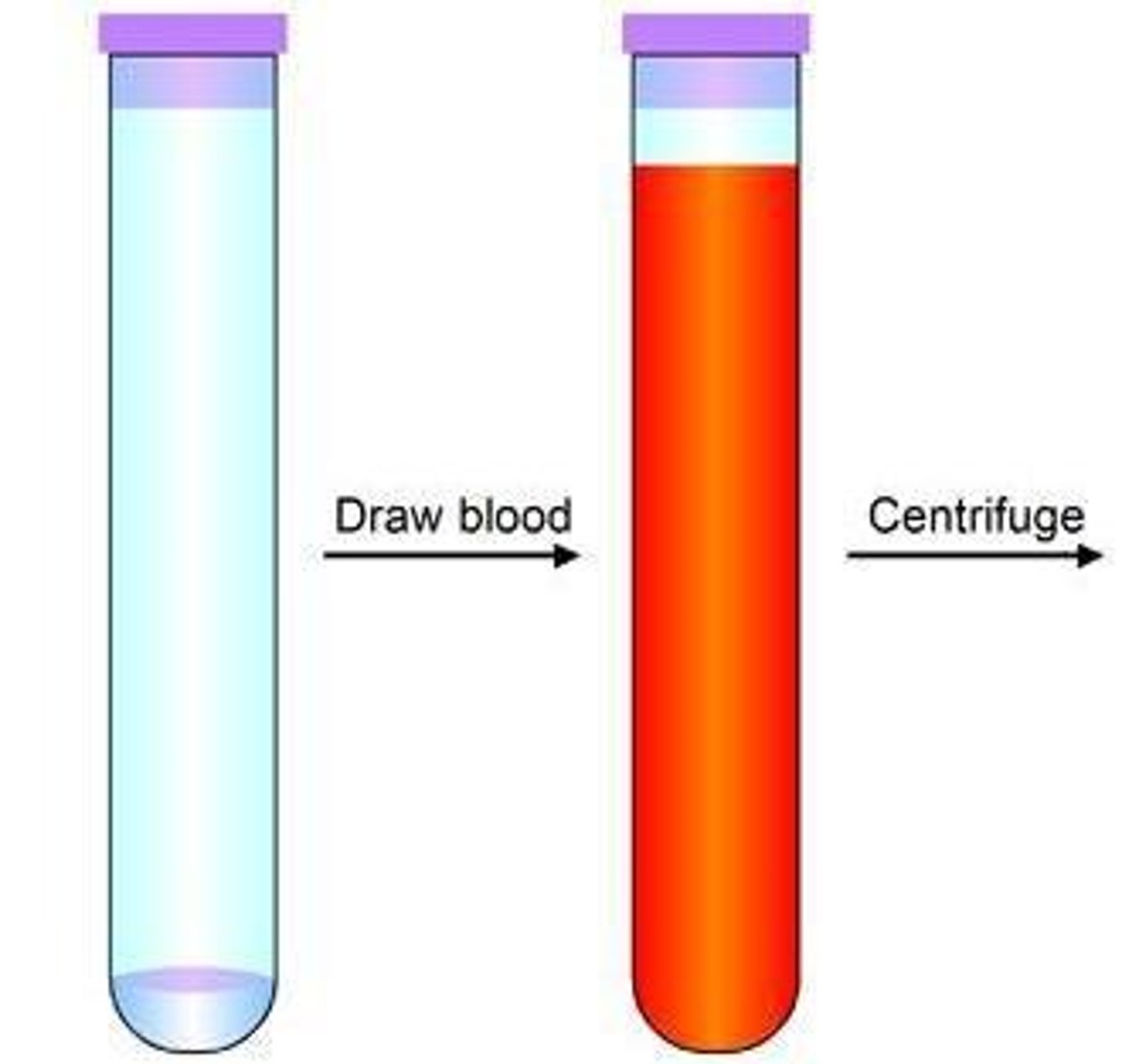
Centrifugation
Process to separate components by density.
Icteric Serum
Yellow serum due to elevated bilirubin levels.
Bilirubin
Substance that can interfere with laboratory tests.
Hemolyzed Serum
Serum with leaked intracellular substances from cells.
Lysis of Cells
Breakdown of cells leading to hemolysis.
Lactescence
Milky serum due to elevated chylomicrons post-meal.
TAG Level
Triglyceride level indicating lipemic serum condition.
Plasma Proteins
Proteins in plasma, including albumin and globulin.

Albumin
Most abundant plasma protein, 60% of total proteins.
Globulin
Plasma protein, 35% of total proteins, includes antibodies.
Fibrinogen
Plasma protein, 4% of total proteins, essential for clotting.
Electrolytes
Minerals dissolved in serum, vital for body functions.
Closed Circulatory System
Blood circulates within vessels, not open to environment.
Short Life Span
Blood cells are continuously replaced in the body.
Common Interferences
Factors causing unacceptable serum or plasma specimens.
Clinical Chemistry
Field studying chemical processes in the body.