Chapters 17-18 Vocab
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
1
New cards
Equilibrium constant (K)
The value obtained when equilibrium concentrations are substituted into the reaction quotient.
2
New cards
Haber Process
An industrial process used to form ammonia from its elements.
3
New cards
Law of chemical equilibrium (law of mass action)
The law stating that, when a system reaches equilibrium at a given temperature, the ratio of quantities that make up the reaction quotient has a constant numerical value.
4
New cards
**Le Châtelier’s principle**
A principle stating that, if a system in a state of equilibrium is disturbed, it will undergo a change that shifts its equilibrium position in a direction that reduces the effect of the disturbance.
5
New cards
Metabolic pathway
A biochemical reaction sequence that flows in one direction, with each reaction catalyzed by an enzyme.
6
New cards
Reaction quotient (Q) or mass action expression
A ratio of terms for a given reaction consisting of product concentrations multiplied together and divided by reactant concentrations multiplied together, with each concentration raised to the power of its balancing coefficient. The value of *Q* changes until the system reaches equilibrium, at which point it equals *K.*
7
New cards
Van’t Hoff equation
An equation for calculating the change in equilibrium constant that occurs with a change in temperature
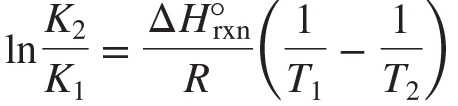
8
New cards
acid-dissociation (acid-ionization) constant (Ka)
An equilibrium constant for the dissociation of an acid (HA) in H2O to yield the conjugate base (A−) and H3O+
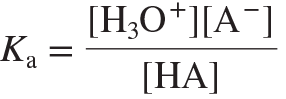
9
New cards
Adduct
The product of a Lewis acid-base reaction, a species that contains a new covalent bond.
10
New cards
Amphiprotic
A substance that can either donate or accept a proton (H+).
11
New cards
Arrhenius acid-base definition
A model of acid-base behaviour in which an acid is a substance that yields H3O+ when dissolved in water, and a base is a substance that yields OH− when dissolved in water.
12
New cards
Autoionization (self-ionization)
A reaction in which two molecules of a substance react to give ions. The most important example is for water
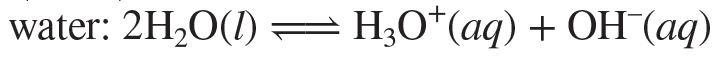
13
New cards
base-dissociation (base-ionization) constant (Kb)
An equilibrium constant for the reaction of a base (B) with H2O to yield the conjugate acid (BH+ and OH−)
14
New cards
**Brønsted-Lowry acid-base definition**
A model of acid-base behavior based on proton transfer, in which an acid and a base are defined, respectively, as a species that donates a proton and one that accepts a proton.
15
New cards
Conjugate acid-base pair
Two species related to each other through the gain or loss of a proton; the acid has one more proton than its conjugate base.
16
New cards
**hydronium ion (H3O+)**
A proton covalently bonded to a water molecule.
17
New cards
ion-product constant for water (Kw)
The equilibrium constant for the autoionization of water; equal to 1.0 × 10−14 at 298 K (Kw = \[H3O+\]\[OH-\]
18
New cards
Leveling effect
The inability of a solvent to distinguish the strength of an acid (or base) that is stronger than the conjugate acid (or conjugate base) of the solvent.
19
New cards
Lewis acid-base definition
A model of acid-base behaviour in which acids and bases are defined, respectively, as species that accept and donate an electron pair.
20
New cards
Neutralization
The process that occurs when an H+ ion from an acid combines with an OH− ion from a base to form H2O.
21
New cards
pH
The negative of the common logarithm of \[H3O+\]
22
New cards
polyprotic acid
An acid with more than one ionizable proton.
23
New cards
Bronsted-Lowry base
A species that accepts an H+ ion (a proton acceptor)
24
New cards
Bronsted-Lowry acid
A species that donates an H+ ion (a proton donor)