TRAFFIC ENGINEERING AND FLOW CHARACTERISTICS
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
It is important to realize that the primary function of a highway is to provide [BLANK]
Mobility
[BLANK] can be characterized by a number of different operational performance measures.
Traffic Streams
[BLANK] is usually expressed in units of minutes per mile.
Travel Time
A traffic stream that operates free from the influence of such traffic control devices as signals and stop signs is classified as [BLANK]
Uninterrupted Flow.
Traffic streams that operate under the influence of signals and stop signs are classified as [BLANK]
Interrupted Flow
[BLANK] is a simple and widely used measure of the quality of traffic flow
Speed of Travel
[BLANK] is commonly expressed in miles per hour or feet per second. Its reciprocal,
Speed
[BLANK] is the "instantaneous" speed of a vehicle as it passes a specified point along a street or highway.
Spot Speed
Formula for Time mean Speed
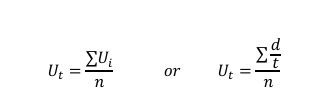
Formula for Space mean Speed
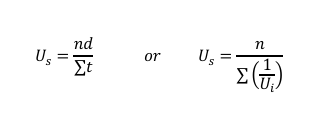
[BLANK] is defined as the number of vehicles that pass a point along a roadway or traffic lane per unit of time.
Traffic volume
[BLANK] is a fundamental traffic measurement needed for the determination of vehicle-miles of travel on the various categories of rural and urban highway systems.
ADT
[BLANK] is often measured over the course of an hour, in which case the resulting value is typically referred to as volume.
Flow
Formula for Rate of Flow (𝒒)
Where:
q = rate of flow per unit time
n = number of vehicles
t = duration of time interval
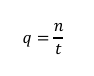
[BLANK], also referred to as traffic concentration, is defined as the average number of vehicles occupying a unit length of roadway at a given instant.
Traffic density
Formula for Traffic Density
Where:
k = Traffic Density
n = number of vehicles
d = distance travelled by vehicle
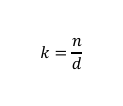
The [BLANK]is simply the distance between successive vehicles typically measured from front bumper to front bumper.
Spacing
[BLANK] is the time between the arrival of successive vehicles at a specified point, and it is the reciprocal of volume.
Time-headway
Formula for spacing of vehicles
Where:
k = traffic density (vehicle per unit distance)
n = number of vehicles
d = distance travelled by the vehicle
t = time
q = traffic volume/rate of flow
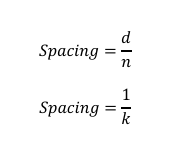
Formula for Minimum Time Headway (hrs)
Where:
k = traffic density (vehicle per unit distance)
n = number of vehicles
d = distance travelled by the vehicle
t = time
q = traffic volume/rate of flow
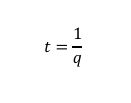
Formula for Speed, Volume, Density
Where:
q = rate of flow per unit time
k = traffic density
U𝑠 = space mean speed
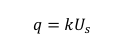
The analysis of vehicle traffic provides the basis for measuring [BLANK]
the operating performance of highways
This is where traffic flow is likely to continue without breakdown and serious compositions. It follows that at capacity, the quality of level of service is far from ideal.
Maximum Volume
The Capacity is stated in passenger cars per hour. Trucks and buses in the traffic stream can decrease the road capacity substantially.
Number of Vehicles
Values for capacity cannot be determined exactly due to the many variables that affect traffic flows, particularly at high volumes. Assigned values for capacity are more of probability rather than certainties.
Reasonable Expectations
Traffic is one direction flows independently from that of the other. On the other hand, on two and three lane roads there are interactions between traffic in the two directions and these affect traffic flow and capacity.
One Direction Against Two Directions
Traffic volume and capacity are stated in vehicles per hour, but traffic flow does not vary uniformly with time, volume and capacities. This variation within an how is expressed by a peak hour factor (PHF) This factor which is less or equal to one in the quotient of the hourly volume divided by the shorter period volume multiplied by the number of periods in an hour.
A Given Time Period
Formula for Peak Hour Factor
Where:
q = rate of flow in veh/hr
q𝑚𝑎𝑥 = rate of flow at the peak hour factors
q𝑚𝑎𝑥 = 𝑚𝑎𝑥 𝑛𝑜. 𝑜𝑓 𝑣𝑒ℎ𝑖𝑐𝑙𝑒𝑠 (𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒)
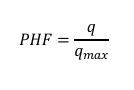
This includes physical features that affect capacity like lane and shoulder width, sight distance and grades. It also reflects changes in the character of the traffic stream.
Prevailing Roadway and Traffic Conditions
is weather related conditions that affect capacity such as rain, fog, smog or wind.
Ambient Condition
Standard motor vehicle traffic accident classification is according to the types listed below. If more than one of these events occurs in the same accident, preference is given to the first event that occurs on the roadway.
Classification of Accidents
[BLANK] are often used to compare traffic hazard (a) in different areas for the same periods of time, or (b) in the same areas or at the same locations for different periods of time.
Accident records
The traffic hazard to life in a community is commonly expressed as the number of traffic fatalities per 100,000 populations.
Death Rate on Population Basis.
Another measure of exposure to accidents lies in the motor vehicle registration in a state or community; hence death rate is often expressed as deaths per 10,000 vehicles registered.
Death Rate on a Registration Basis.
The true exposure to accidents is probably more nearly approximated by the miles of travel by motor vehicles than by either the population or the registration. The mileage rate is usually expressed as deaths per 100 million vehicle miles or as accidents per million vehicle miles.
Death Rate on a Mileage Basis.
Formula for Accident rate for 100 million vehicles per miles of travel in a segment of highway.
Where:
A = number of accidents during period of analysis
ADT = average daily traffic
N = time period in years
L = length of segment in mile
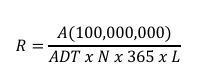
Formula for Accident rate per million entering vehicles in an intersection.
Where:
A = number of accidents during period of analysis
ADT = average daily traffic
N = time period in years
L = length of segment in mile
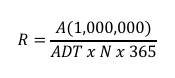
Formula for Severity Ratio

These are the three basic classes or measures of speed of travel
Spot Speed, Overall Speed and Running Speed.