Transporters, Enzymes and Ion Channels
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What is a transporter?
Transmembrane protein that undergoes a conformational change and facilitates the transport of a "packet" of substrate across the membrane.
How can drugs inhibit transporters?
Inhibitor:
-Molecule binds to the transporter and prevents further transport
False substrate:
-Usually has higher affinity than the substrate, competitively inhibits the substrate but when absorbed has NO effect on the target cell
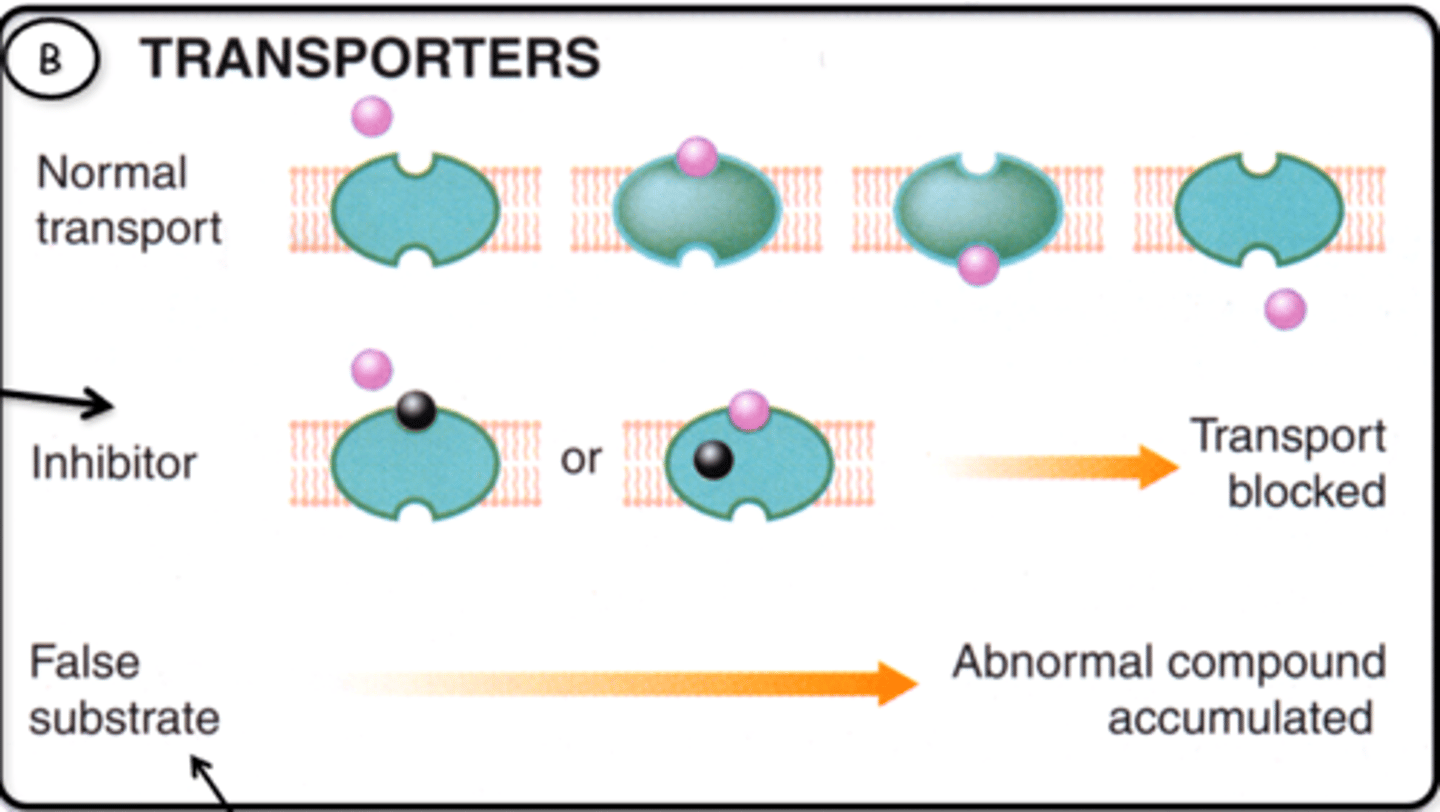
Give an example of a drug that blocks transporters
Inhibitors:
-Cocaine
-Fluoxetine
-Digoxin
False substrates:
-Reserpine
What are the main ways drugs can effect ion channels?
Blockers:
-Permeation block the ion channels by sitting inside the channel pore
Modulators:
-Allosterically bind to the ion channel to increase or decrease opening permeability
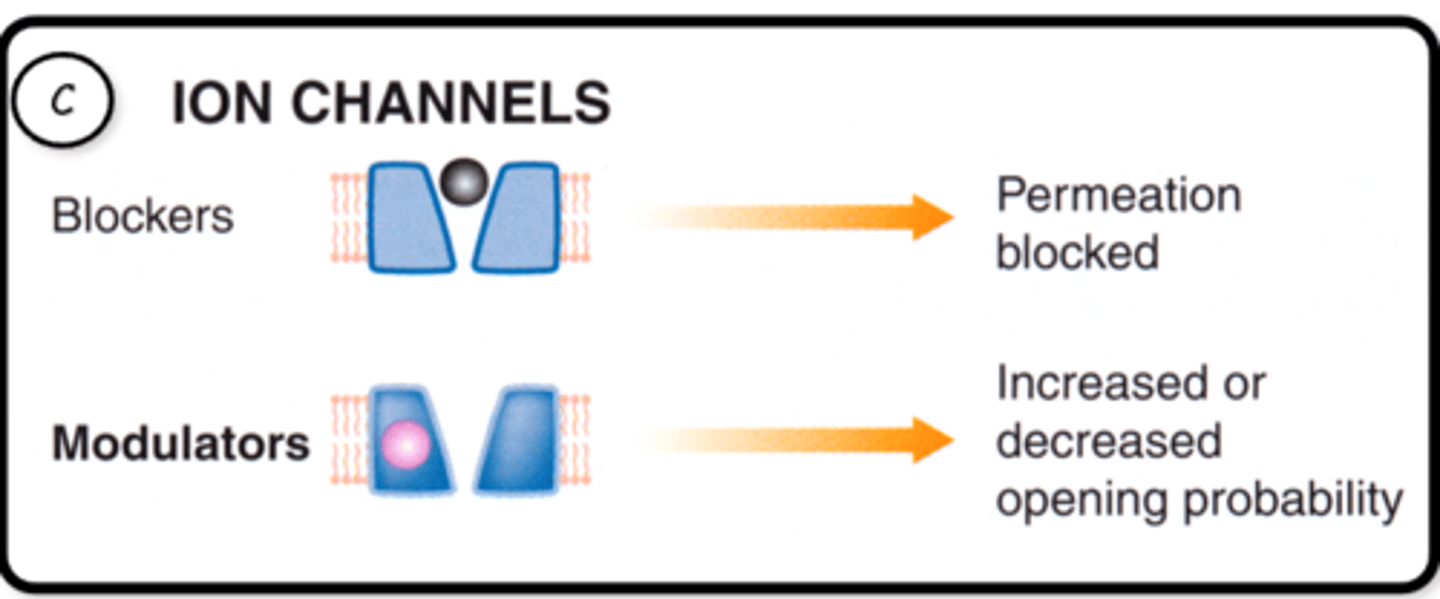
Give some examples of ion channel blockers and what channels they block
-Verapamil = Calcium
-Lidocaine = Sodium
-Sulphonylureas = Potassium
How are local anaesthetics thought to work?
-A ion channel-blocker (e.g. lidocaine) is administered
-They block voltage-gated Na channels in the post-synaptic axon
-This means that action potential can no longer be generated
-This means that pain impulses are impossible to be generated and hence no pain is felt
What is a pro-drug?
A biologically inactive compound that can be metabolised in the body to produce a drug.
What are the mechanisms that drugs use to effect enzymes?
Inhibitor:
-Bind to the active site or allosteric site (competitive and non-competitive inhibition) to inhibit normal action
False substrate:
-Competitively inhibit the enzyme and result in a false substrate being produced
Pro-drug:
-Drug has similar shape to the active site of target enzyme, so once the enzyme binds and acts on it, an active drug is produced
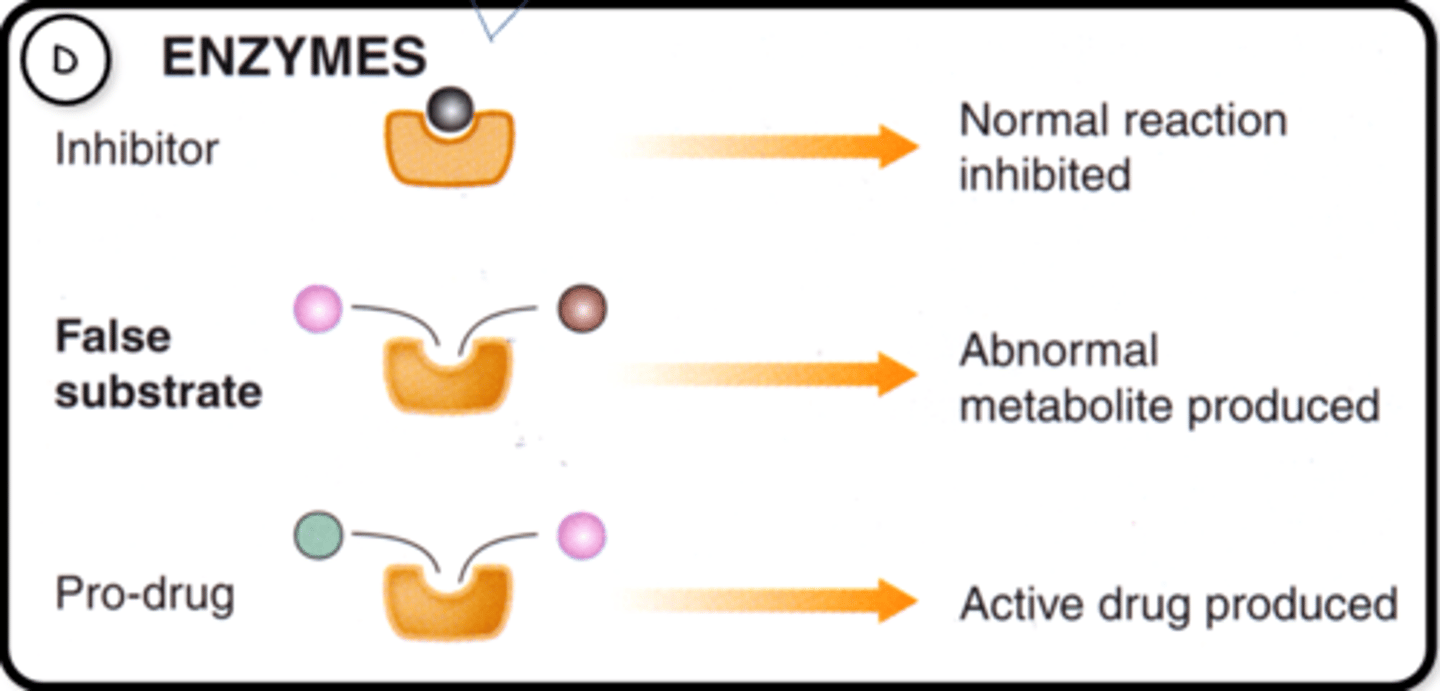
Give an example of an enzyme inhibitor drug and the type of inhibition they cause
-Captopril = Competitive and reversible
-Aspirin = Non-competitive and irreversible
How does aspirin work to treat pain and inflammation?
-It inhibits cyclooxygenases to prevent inflammation and pain impulses from being generated
-Also prevents them from aiding in the regeneration of the stomach lining (hence causing occasional GI symptoms)
How do anti-cholinesterases treat myasthenia gravis?
-E.g. anticholinesterases such as neostigmine are given
-This binds to the enzyme and prevents it from functioning
-This boosts ACh levels meaning that signal transduction can work properly