Introduction
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 3: Monday, September 8th
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
the number off chromosome sets an organism has is _______
ploidy
true or false: polyploidy is common among plants
True
one set of chromsomes in a cell/organism (n) is called _______
haploid
two sets of chromosomes in a cell/organism (2n) is called _______
diploid
one chromosome from each parent and a copy of each, all of which have the samee genes by may have different alleles, is called _______
homologous chromosomes
true or false: homolgous chromosmes are only present tin sexually reproducing animals
true
The study of haploid genome is called _______
Genomics
Haploid genome is mostly in the _______, but some is _______
nucleus, extranuclear
True or false: in bacteria, mitochondria and chloroplast have additional genomes
False. in eukaryotes, mitochondria and chloroplast have additional genomes
True or false: in bacteria, plasmids carry extra DNA exclusive of the nucleoid
true
DNA is in a coiled state in the cell, referred to as _______
chromatin
DNA wrapped around histones is referred to as _______
Chromatin
True or false: histones are structural eukaryotic proteins
True
True or false: condensing helps with DNA coiling
true
The compressed area of DNA holding sister chromatids together that separates the p-arm from q-arm refer to as the _______
centromere
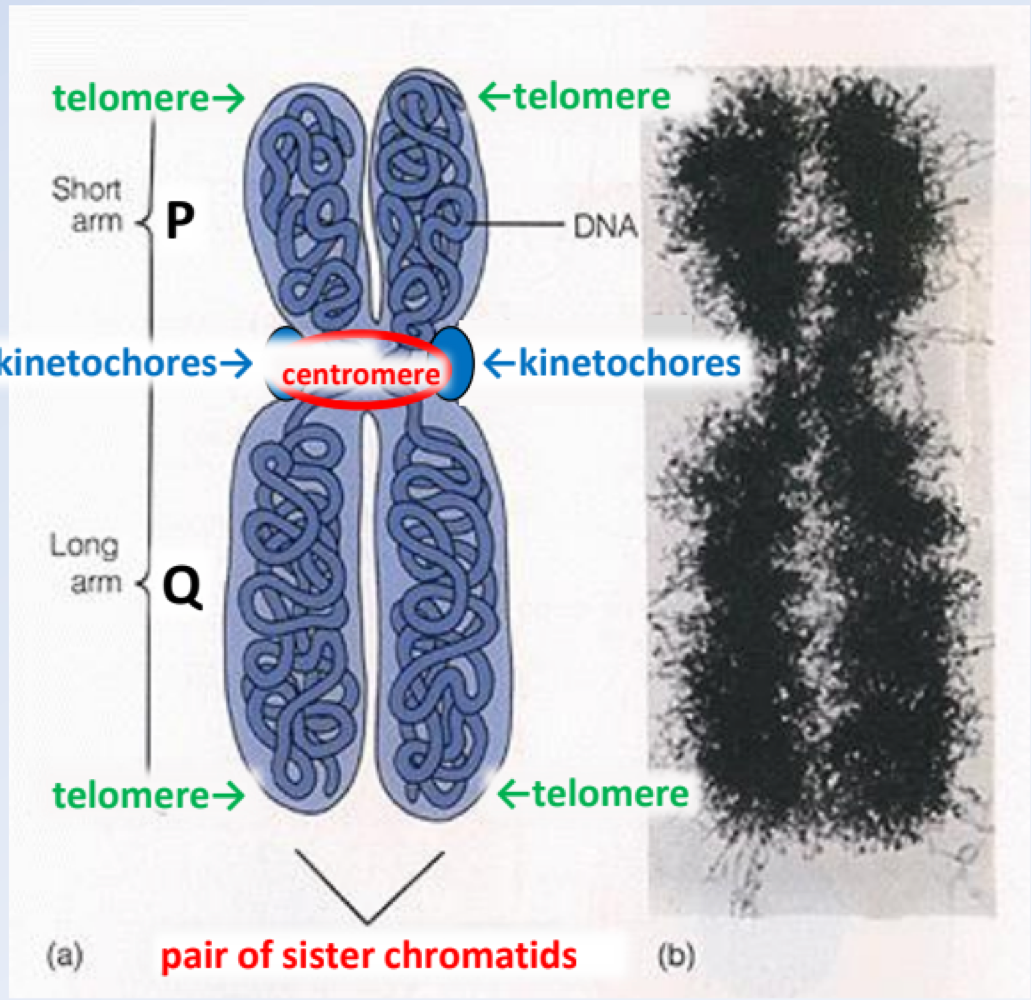
true or false: cell division can occur even if DNA is replicated at the centromere
false: cells must replicate DNA at centromere before division
The protein clumps were spindle fibers attached for cell division are referred to as _______
kinetochores
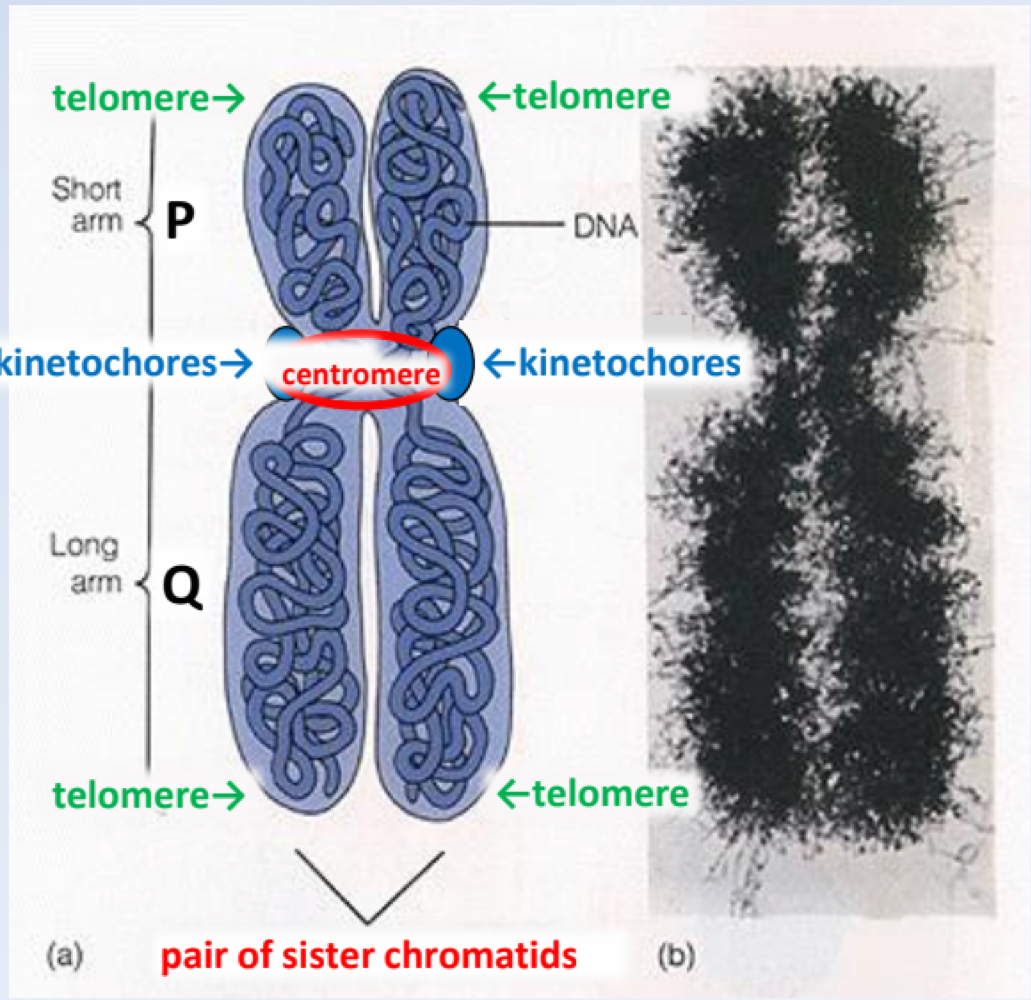
The ends of chromosomes kept with compressed triple-stranded DNA (p-ter & p-ter) are referred to as _______
telomeres
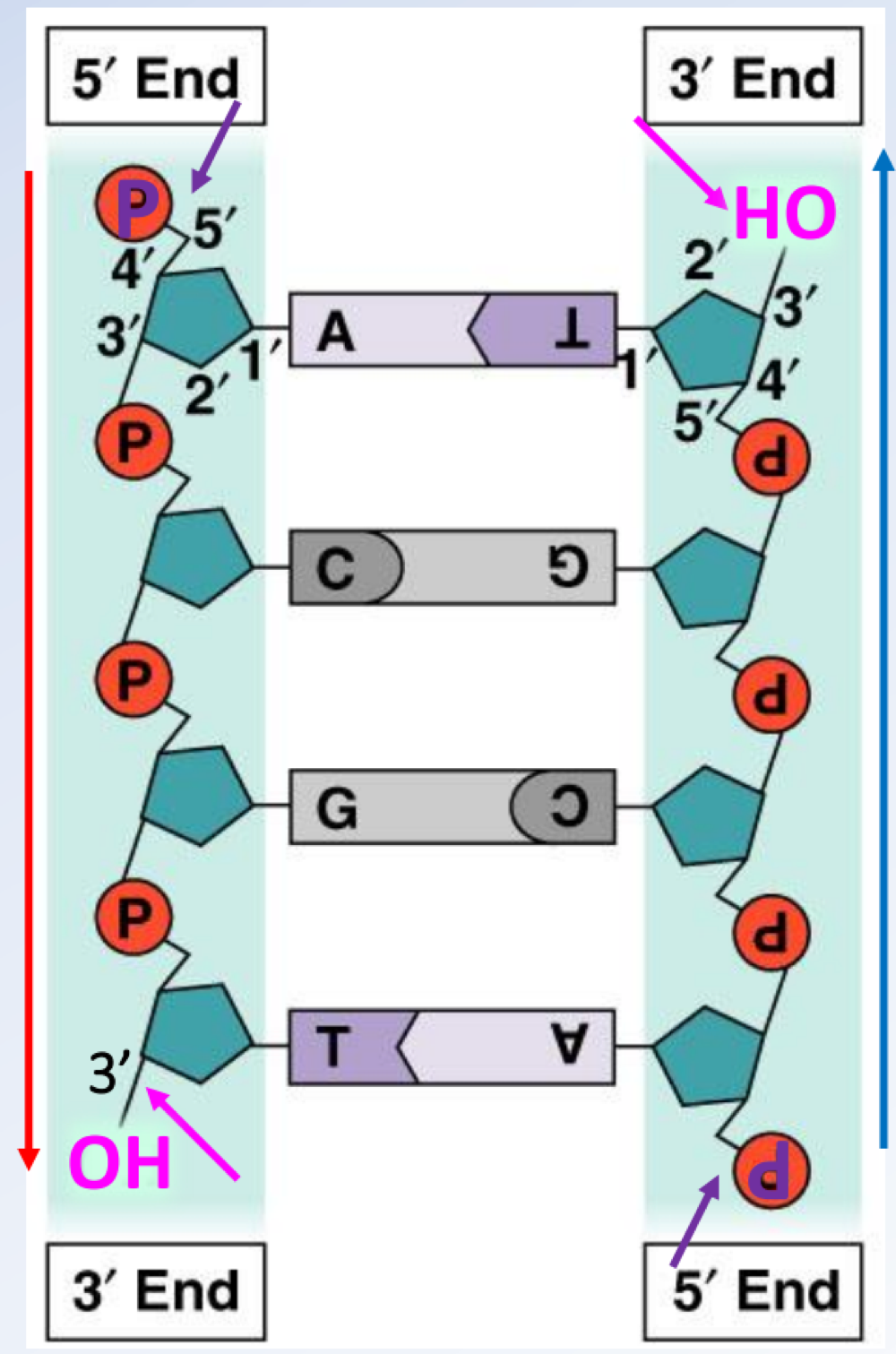
DNA structure is double stranded—strands are held by complementary binding of _______ and _______, which have 2 hydrogen bonds, and _______ and _______ we have 3 hydrogen bonds
Adenine and thymine, and cytosine and guanine
True or false: purines are adenine and thymine
False. Are adenine and guanine
True or false: prymidines are cytosine and thymine
true
DNA structure is antiparallel—five-carbon sugar has five attachment points: 5"‘ ( PO4- group, which is _______) and 3’ (-OH group, which is _______)
upstream, downstream
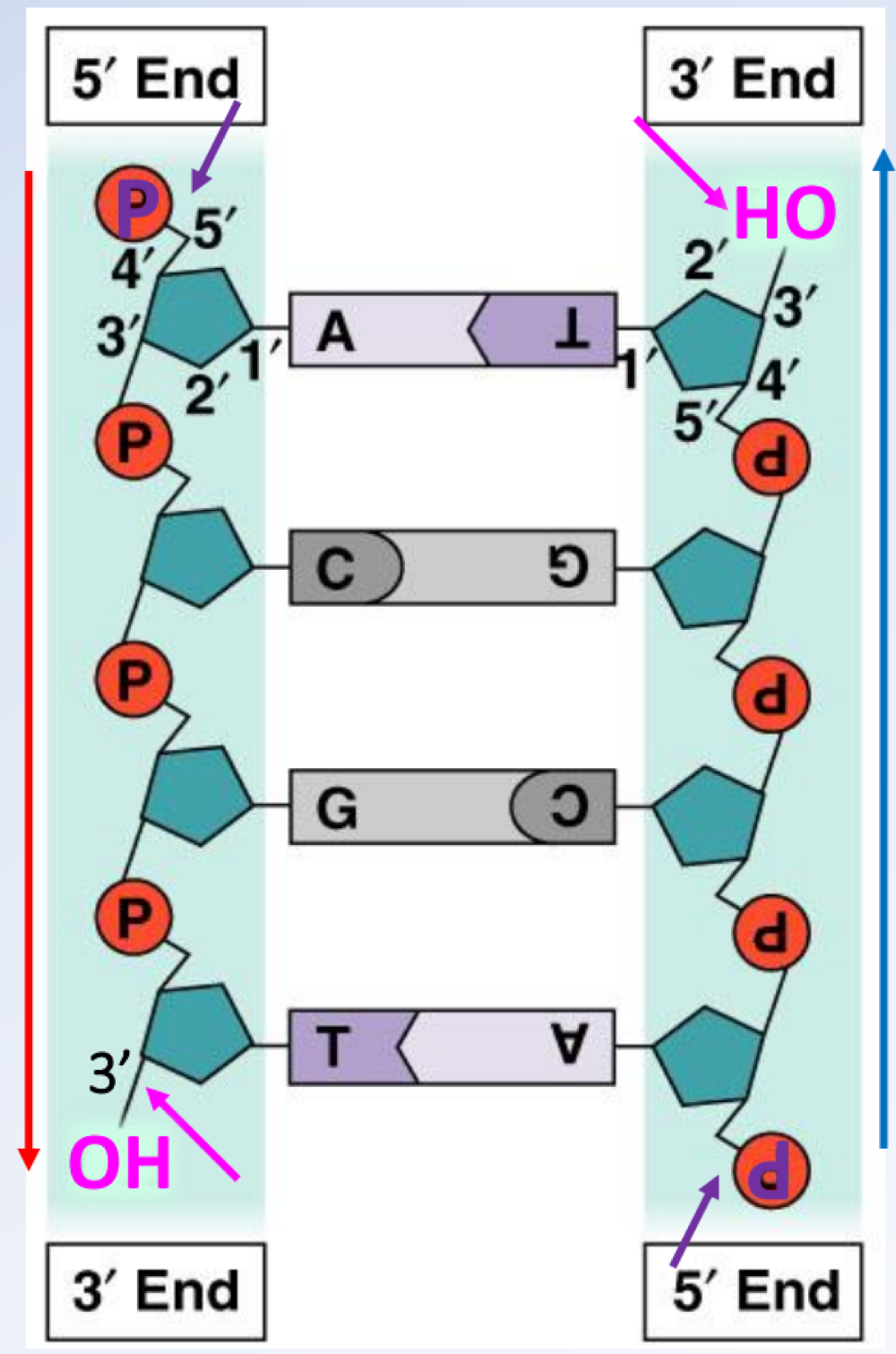
In 1869, _______ discovered DNA and named nuclein
Miescher
In 1910, _______ knew the DNA chemicals A/T/C/G
Levene
in 1950, _______ was developed, and showed that adenine = thymine, and cytosine = guanine
Chargaff’s Rule
True or false: DNA is 60% pruines and 40% pyrimidines
false. DNA is 50% purines and 50% pyrimidines
True or false: Chargaff also discovered that the quantities of nucleotides differ between or organisms
true
in 1953, _______ were shown the work of Frankel, and found the DNA structure but gave her zero credit
Watson & Crick
True or false: RNA → DNA because of RNA viruses and telomeres, and they’re nucleotide-derived, but Protein ↛ RNA because their precursors are different
true
The process of _______ occurs in nucleus/nucleoid, where a single strand of DNA transcribed (copied) into single strand of mRNA (transcript)
Transcription
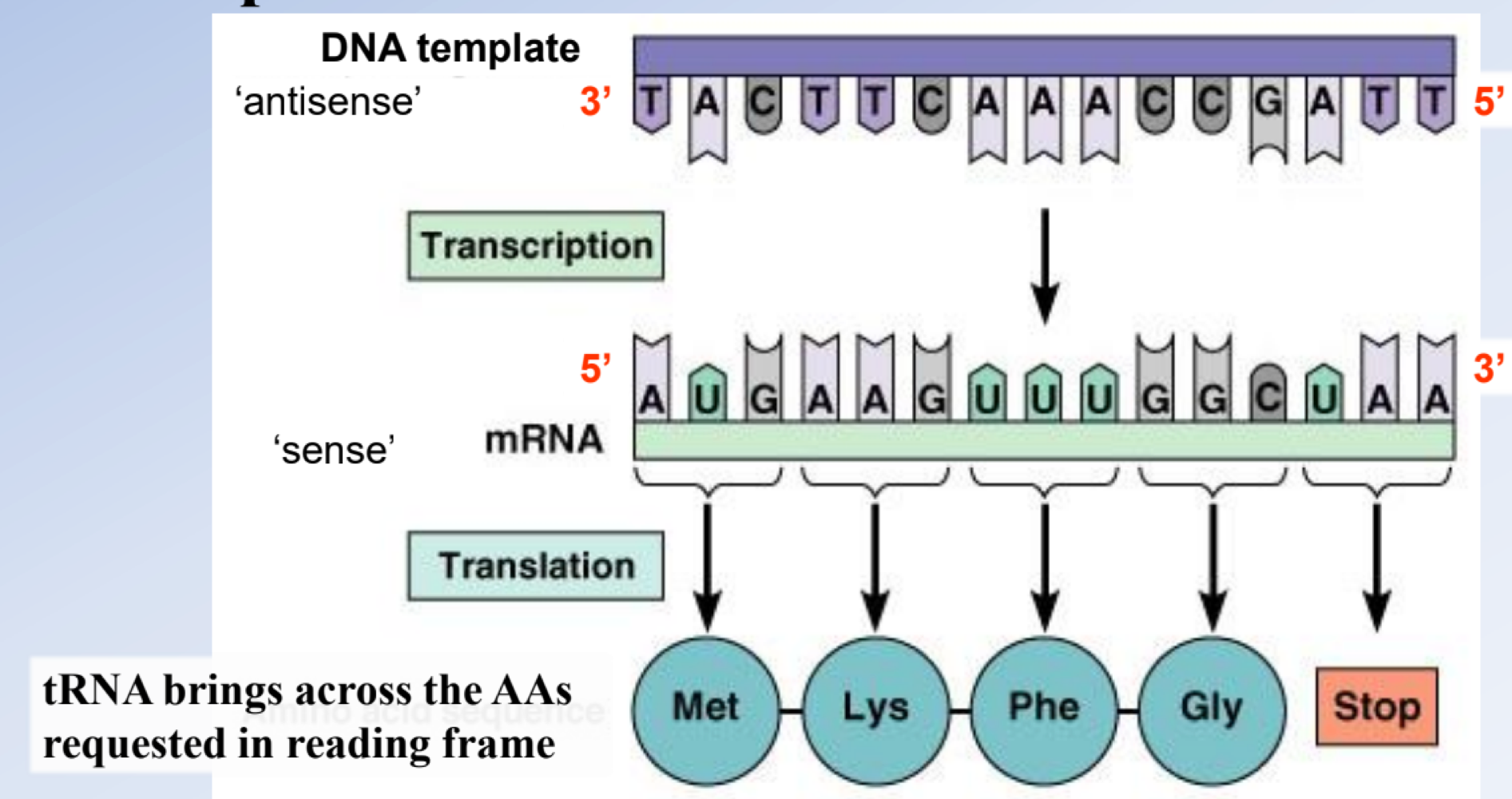
The process of _______ occurs in the cytoplasm, where mRNA binds to a ribsome and is translated into a protein using amino acids delivered by tRNA
Translation
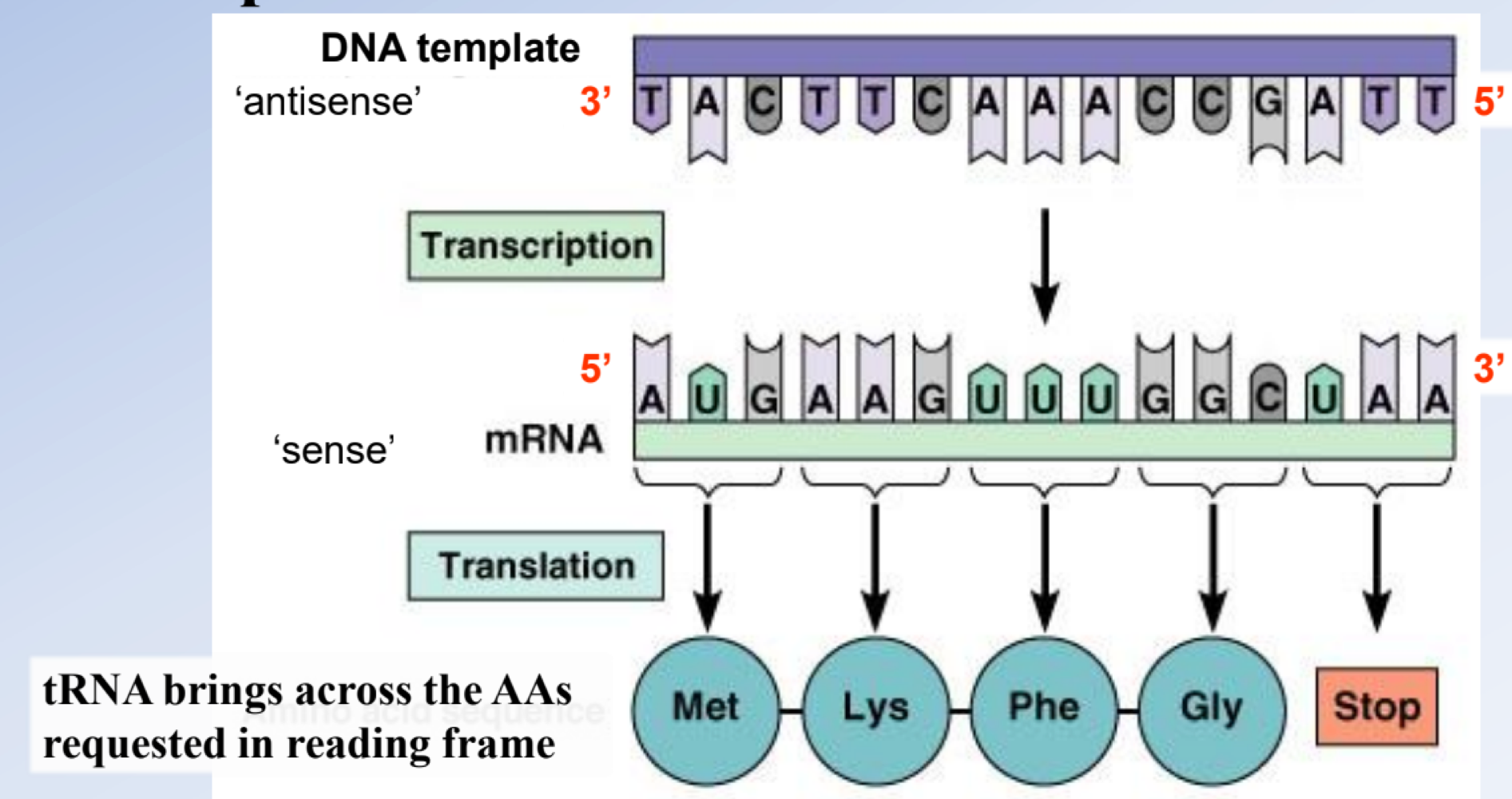
genetic code is made up of triplet nucleotides, _______, in mRNA that encodes for amino acids hooked together by the ribosome
condons
there are 20 common amino acids, but 64 codon possibilities (4³), which created _______ in the codons, or _______, which lessens the chance a mutation is harmful
redundancy, degeneracy
_______ are the coding regions of genes (codons), which make up < 2% of a human’s genome
exons
_______ are any change in ≤ 1 DNA bases
variations (alleles)
True or false: the genotype is biallelic (one set from each parent)
true
true or false: a phenotype can result from only one gene
false. a phenotype can result from one or multiple genes
true or false: separate, non-coding regions of DNA that make up 35% of the human genome are pseudogenes
false. separate, non-coding regions of DNA that make up 35% of the human genome are introns
introns are involved in the mix-matching of exons once introns are cut, a process known as _______
alternative splicing
introns are involved in coding for small pieces of rna that mess up mRNA so it can’t be translated, a substance known as _______
RNA interference (RNAi)
true or false: the promoter is a motif that occurs downstream of START (where RNA polymerase binds to promote transcription [TATA])
false. the promoter is a motif that occurs upstream of START (where RNA polymerase binds to promote transcription [TATA])
the process that produces a mutation is called _______
mutagenesis
true or false: during a point mutation, a two bases are changed, and theres a 1/3 chance its unharmful
false. During a point mutation, a single base is changed, and there’s a 1/3 chance its unharmful
a point mutation is also _______ if multiple codons code for the same amino acid (degeneracy)
silent
during a _______ mutation, a new amino acid is coded for
missense
during a _______ mutation, everything is affected downstream, which is sually caused by insertion/deletion (indels) events
frameshift
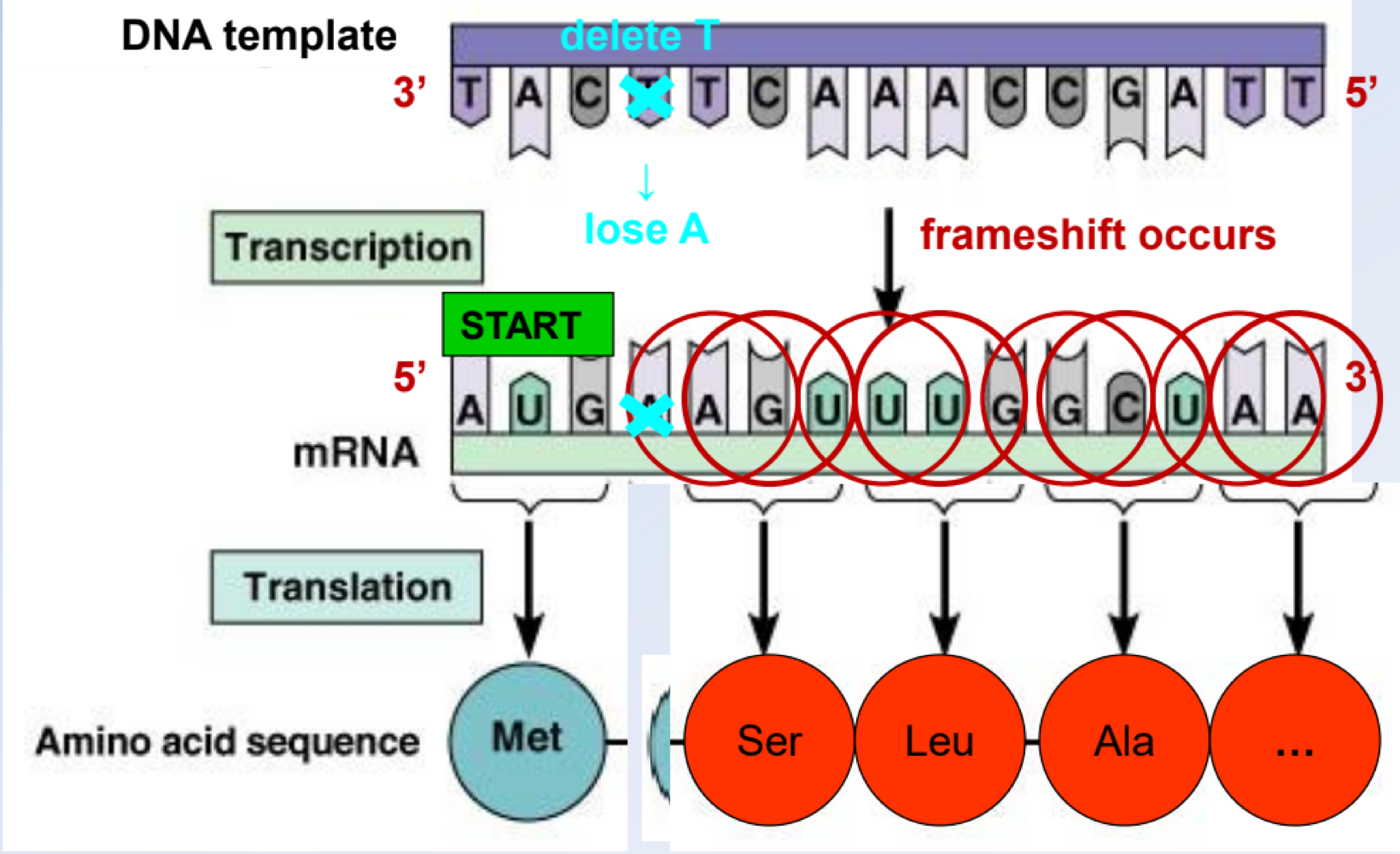
true or false: a frameshift mutation is harmful because it results in a new amino acid coding frame
true
true or false: lab model organisms should mature slowly
false. lab model organisms should mature rapidly
true or false: lab model organisms should be available cheap
true
true or false: lab model organisms should be easily manipulated
true
true or false: lab model organisms should have a long life span
false. lab model organisms should have a short life span
true or false: lab model organisms should produce many offspring
true
true or false: lab model organisms should have a readily available genome sequence
true
true or false: lab model organisms should be easy to keep in a lab regardless of their size
false: lab model organisms should be easy to keep in a lab since small
true or false: lab model organisms should be pathogen or non-pathogenic
false. lab model organisms should be non pathogenic
true or false: lab model organisms should have a different physiology/biology to humans
false. lab model organisms should have a similar physiology/biology to humans
true or false: lab model organisms should have synteny with human chromosomes
true