rivers
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
What are the three fluvial processes?
Erosion
Transportation
Deposition
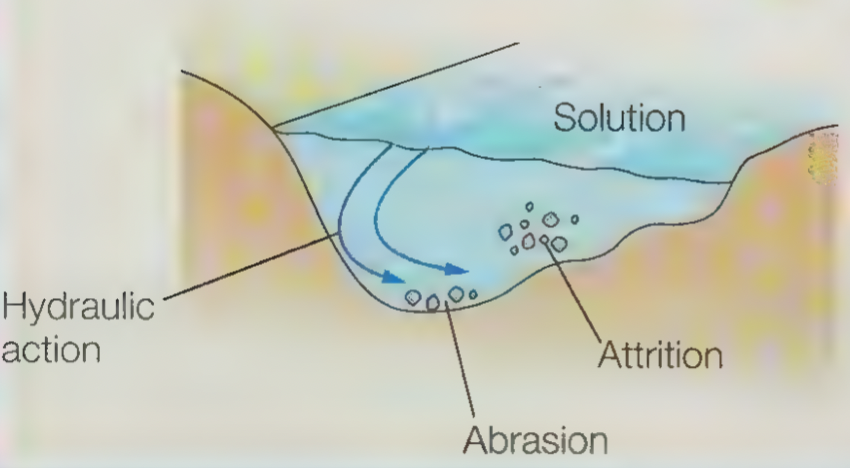
What are the four main types of erosion?
Hydraulic action
Abrasion/Corrasion
Attrition
Solution/Corrosion
What is hydraulic action?
The force of the water hitting rock which traps air into its cracks, causing the rock to weaken and break away from the river bed and banks.
What is abrasion/corrasion?
When the load of the river hits and scrapes against the river bed and banks causing it to wear away.
What is attrition?
When the stones and rocks carried by the river knock into each other, causing them to break into smaller fragments and become rounder.
What is solution?
When water from the river reacts with rock, causing it to weaken and dissolve.
What is the difference between lateral and vertical erosion?
Lateral erosion is erosion that causes the river channel to become wider whereas vertical erosions causes the river channel to become deeper.
What are the 4 types of transportation?
Traction
Saltation
Suspension
Solution
What is traction?
Large boulders and rocks are rolled along the river bed.
What is saltation?
Small stones and pebbles are bounced along the river bed.
What is suspension?
Small particles are carried along by the water.
What is solution?
Soluble, fine sediment is dissolved in the water and carried along.
How does water reach the river channel?
surface runoff (fastest)
throughflow
groundwater flow (slowest)
When does deposition occur?
When the speed and energy of the water decreases because:
a) discharge decreases
b) the amount of load being carried increases
c) the gradient becomes less steep
d) the river flows into the sea
How does the size of the river’s load affect when it is deposited?
Heavier, larger material (bedload) isn’t transported far and the first to be deposited, in the upper course.
Smaller sediment is transported further and deposited later, in the lower courses, closer to the river’s mouth.
What fluvial landforms are formed from erosion?
Gorges + waterfalls
Interlocking spurs
How is a gorge and waterfall formed?
Waterfalls form where a river flows over a layer of hard rock followed by a band of soft rock beneath.
The soft rock is (vertically) eroded faster than the hard rock by hydraulic action and abrasion, forming a step.
The river continues to erode the soft rock beneath and undercuts the hard rock, forming an overhang and plunge pool - a waterfall.
Eventually the overhang becomes unstable and collapses, its fragments used to erode and deepen the plunge pool via abrasion.
This causes the waterfall to retreat over time and results in the formation of a gorge.
How are interlocking spurs formed?
In the upper course, there is more vertical erosion than lateral erosion.
The river doesn’t have enough energy to erode laterally, so is forced to flow around the spurs.
This forms interlocking spurs.
What fluvial landforms are formed from deposition?
Levees
Floodplains
Estuaries
What is a levee?
Natural raised river banks found along the edges of a river channel.
How are levees formed?
During a flood, the river transports and deposits its load on the floodplain.
The largest and heaviest sediment is deposited first and closest to the river channel (because it lacks the energy to transport it further).
This process repeats, causing the heavy deposited sediment to build up along the river channel and forming levees.
What is a floodplain?
A flat area of land alongside a river which is prone to flooding.
How is a floodplain formed?
When a river floods, the water loses its energy and deposits the load it’s carrying, building up the floodplain.
As meanders widen due to lateral erosion, they migrate across the floodplain and eventually erode part of the valley side (bluff) causing the floodplain to become wider.
What is an estuary?
The tidal mouth of a river.
How is an estuary formed?
At high tide, the water has little energy so deposits the sediment it is carrying.
At low tide, the fine sediment forms mudflats which eventually develop into salt marshes.
What fluvial landforms are formed from erosion and deposition?
Meanders
Ox-bow lakes
What is a meander?
A bend in the river channel.
How is a meander formed?
In the outside of a bend in a river, the water moves the fastest and has the most energy.
This means sediment is eroded on the outside of the bend, forming a river cliff.
In the inside of the bend, the water moves the slowest and has the least energy.
This means the sediment it is carrying is deposited, forming a river beach (or slip-off slope).
This causes the meander to become wider.
How is an ox-bow lake formed?
Continual erosion and deposition in a meander causes the outside bends to come closer to form a swan’s neck.
Eventually, they meet during a flood, causing the river to the shortest course through the swan’s neck.
Deposition causes the meander to be cut off, forming an ox-bow lake.
What is surface runoff?
The flow of water over the surface of the ground.
What causes surface runoff?
saturated soil (soil that has reached its infiltration capacity)
very dry soil
impermeable surfaces (concrete)
What is throughflow?
The flow of water through the soil, parallel to the surface
What is groundwater flow?
The flow of water through permeable rock, parallel to the surface
How is water absorbed into the ground?
infiltration
percolation
What is infiltration?
The absorption of water into the soil.
What is percolation?
The absorption of water into permeable rock.
How is water stopped from reaching the river channel?
interception
evaporation
vegetation storage
transpiration
What is interception?
The storage of water on plant leaves.
What is evaporation?
The heating of liquid water via the sun into water vapour.
What is vegetation storage?
The storage of water in a plant.
What is transpiration?
The loss of water stored in plants through their pores.
What is river discharge?
The volume of water flowing through the river channel.
What is river discharge measured in?
Cumecs (cubic metres per second)
When does flooding occur?
When the water levels exceeds bankfull discharge.
What is bankfull discharge?
The maximum discharge that a particular river channel can carry without flooding.
What physical factors affect flood risk?
Heavy/prolonged rainfall
Geology
Relief
How does heavy rainfall affect flood risk?
Heavy rainfall causes water to arrive too quickly to infiltrate the soil, resulting in more surface runoff. This means the water reaches the river channel faster and so the risk of flooding is greater.
How does prolonged rainfall affect flood risk?
Prolonged rain can cause the soil to become saturated which increases surface runoff because no more rain can infiltrate the soil. As a result, more water reaches the river channel faster and so the risk of flooding is greater.
How does geology affect flood risk?
Water cannot infiltrate impermeable soils/rocks (i.e. granite) so surface runoff is increased. Thus, the flood risk is greater because water reaches the river channel faster.
How does relief affect flood risk?
In areas with steep relief, water reaches the river channel faster because it can flow down steep slopes faster. This consequentially increases flood risk.
What human factors affect flood risk?
Land use:
Urbanisation
Deforestation
How does urbanisation affect flood risk?
In urban areas, there are more impermeable surfaces like concrete which water cannot infiltrate. This results in more surface runoff and increases the speed at which the water reaches the river channel - therefore, flood risk is greater.
Man-made drainage systems also causes water to reach the river channel faster by transporting runoff directly to the river.
How does deforestation increase flood risk?
Deforestations means there are less trees to intercept rainwater and allow it to evaporate from their leaves. There are also less trees to absorb and store water from the soil which reduces infiltration capacity and increases surface runoff. This increases the volume and speed of the water that reaches the river channel, increasing flood risk.
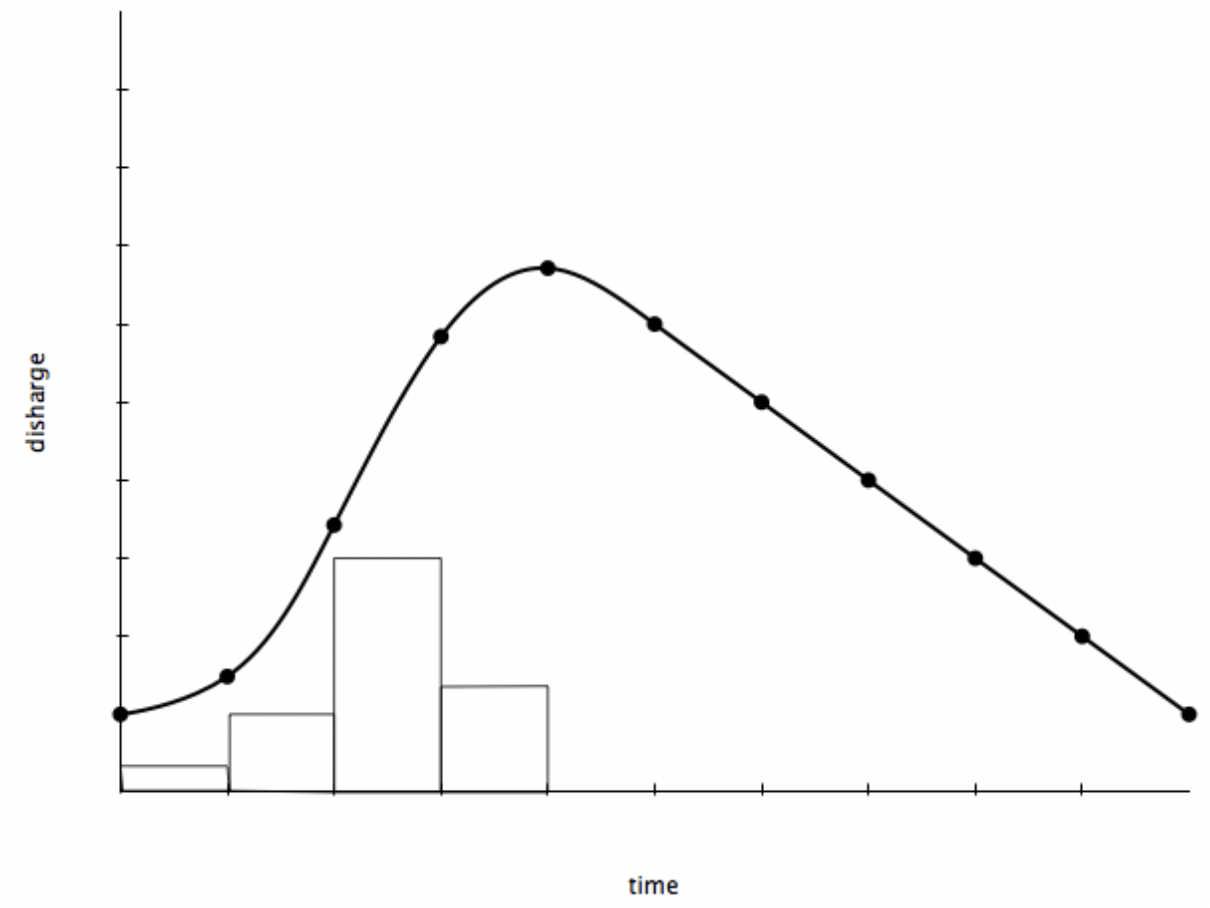
What is a hydrograph?
A graph that shows how discharge in a particular point in a river changes over time relative to rainfall.
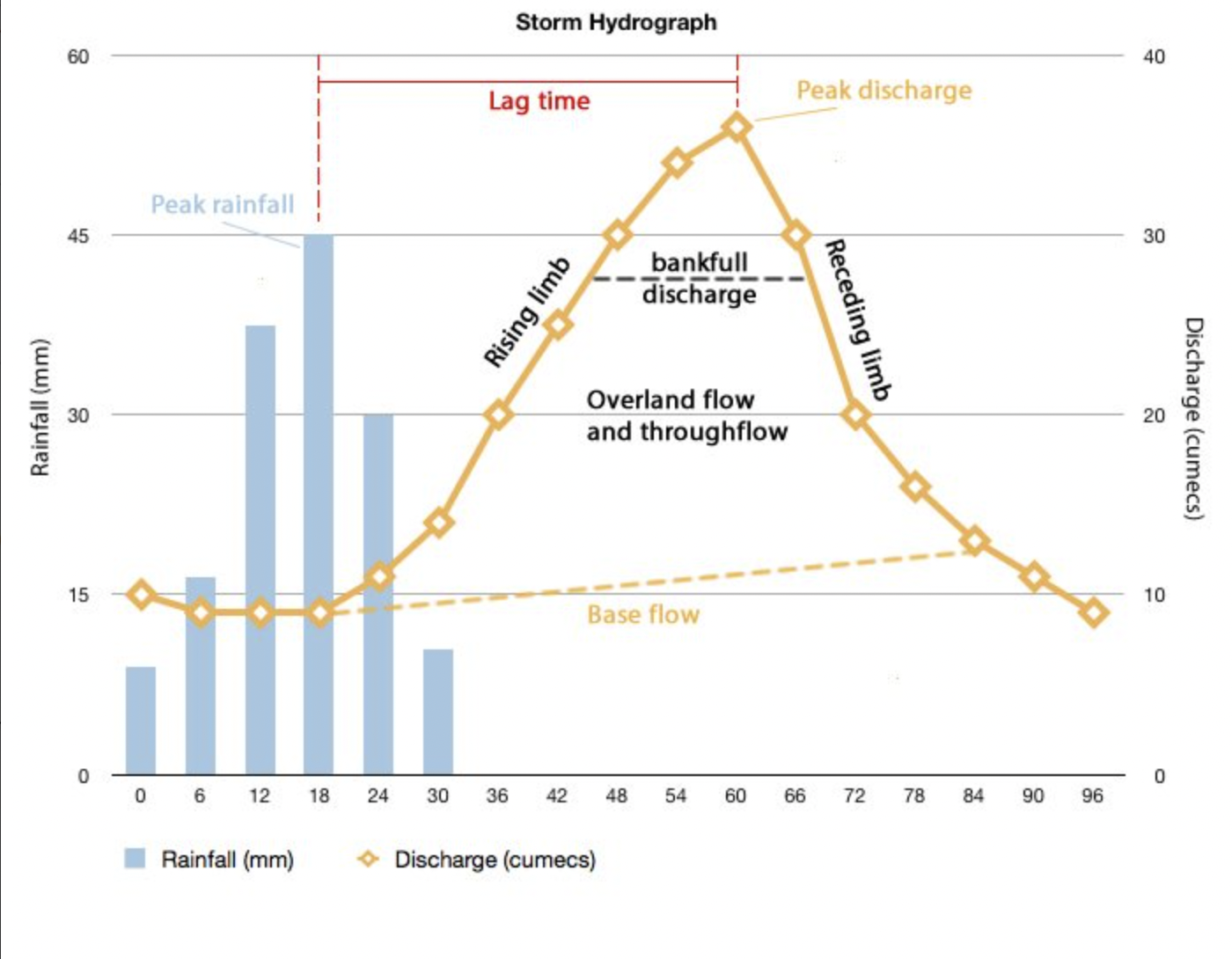
What is peak discharge?
The point on a hydrograph where river discharge is at its greatest.
What is peak rainfall?
The point on a hydrograph where rainfall is at its greatest.
What is lag time?
The delay between peak rainfall and peak discharge.
What is the rising limb?
The increase in river discharge as the rainfall flows into the river channel.
What is the falling limb?
The decrease in river discharge as the river levels return to base level.
What are the characteristics of a gentle hydrograph?
It has a gentle rising limb and long lag time - the rainfall takes longer to reach the river channel and so the river discharge slowly increases, meaning the river is less likely to flood.
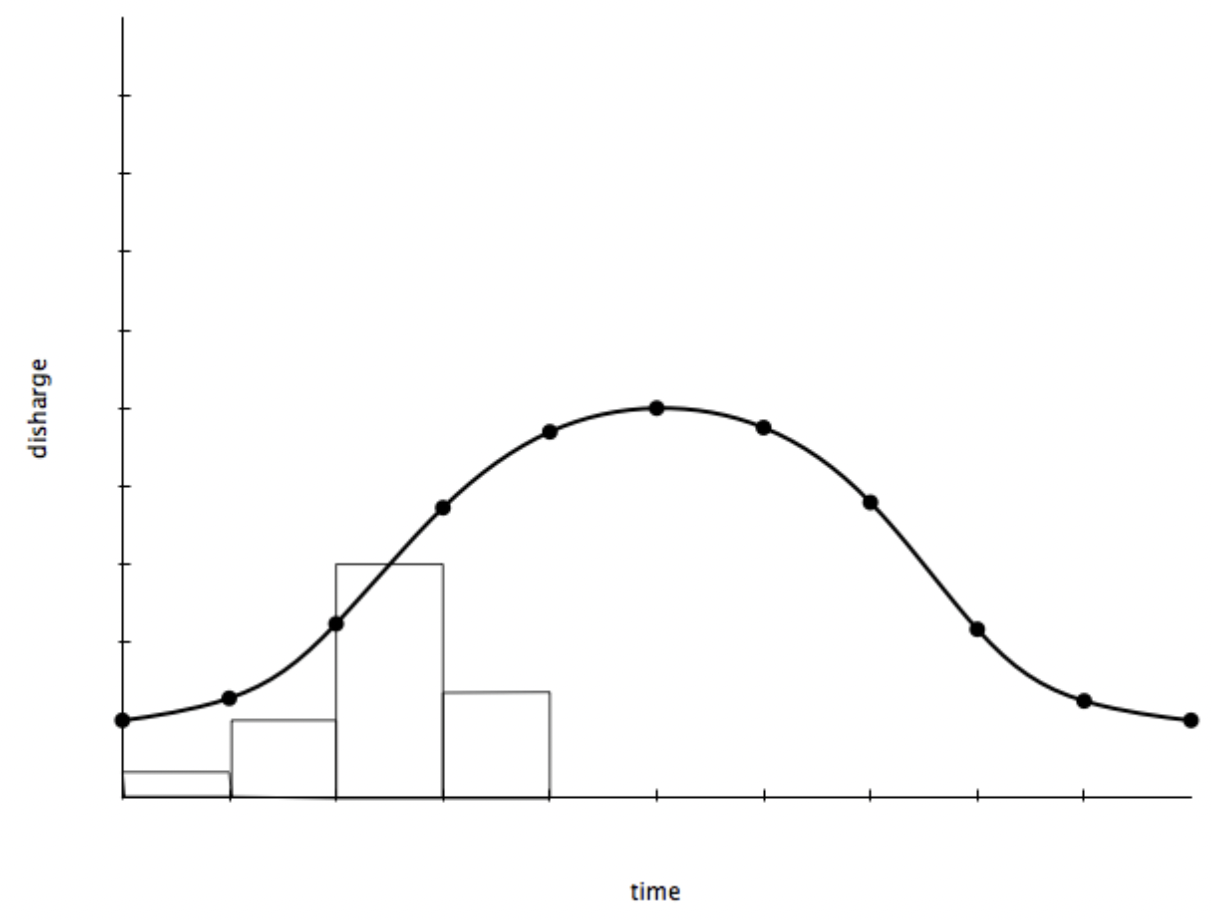
What are the characteristics of a flashy hydrograph?
It has steep rising limb and short lag time - the rainfall quickly reaches the river channel and so river discharge rapidly increases, meaning the river is more likely to flood.
What physical factors affect hydrographs?
size of drainage basin
relief of drainage basin
drainage density
geology of drainage basin
amount of vegetation in drainage basin
rainfall in drainage basin
How does the size of a river’s drainage basin affect its hydrograph?
Water takes longer to reach the river channel when it has a large drainage basin because it has to travel further, which increases lag time. However, larger drainage basins catch more precipitation, increasing peak discharge as well.
Water reaches river channels with small drainage basins faster as it doesn’t have to travel as far, causing a shorter lag time. They also catch less precipitation, decreasing peak discharge.
How does the relief of a river’s drainage basin affect its hydrograph
In a drainage basin with steep relief, water will reach the river channel faster because it flows faster over steep slopes. This shortens the lag time.
In a drainage basin with gentler relief, water will reach the river channel slower given that it doesn’t flow as fast over gentle slopes. This increases the lag time.
How does drainage density affect a river’s hydrograph?
Basins with a high drainage density have a shorter lag time because water reaches the river channel more quickly.
Basins with a low drainage density have a longer lag time because water reaches the river channel more slowly.
How does the geology of a river’s drainage basin affect its hydrograph?
If the rock within the drainage basin is impermeable, rainwater cannot infiltrate and therefore travels as surface runoff. This shortens the lag time and increases peak discharge because more water reaches the river channel faster.
If the rock within the drainage basin is permeable, rainwater can infiltrate and therefore there is less surface runoff. This increases the lag time and reduces peak discharge as less water reaches the river channel slower.
How does the amount of vegetation in a river’s drainage basin affect its hydrograph?
A drainage basin with plenty of vegetation has a longer lag time and smaller peak discharge because more plants intercept or absorb and store the water, which is eventually lost to the atmosphere either by evaporation or transpiration. Therefore, the infiltration capacity of the soil is greater, decreasing surface runoff and the volum and speed at which the water reaches the river channel.
A drainage basin with few pieces of vegetation has a shorter lag time and greater peak discharge because less plants intercept or absorb and store the water so that it can be returned to the atmosphere via evaporation/transpiration. As a result, the infiltration capacity of the soil is smaller, increasing surface runoff and the volume and speed at which the water reaches the river channel.
How does rainfall in the river’s drainage basin affect its hydrograph?
Heavy rainfall in its drainage basin causes more water to reach the river channel, increasing peak discharge.
Gentle rain in its drainage basin causes less water to reach the river channel, decreasing peak discharge.
What human factors affect a river’s hydrograph?
urbanisation + deforestation in its drainage basin
How does urbanisation affect a river’s hydrograph?
In urban areas, there are more impermeable surfaces which increase surface runoff because rainwater is unable to infiltrate. There are also drainage systems which directly transport the water to the river channel, preventing infiltration. This increases both the volume and speed at which water reaches the river channel, decreasing lag time and increasing peak discharge.
Rural areas have more permeable surfaces which allow the infiltration of water and reduce surface runoff. This reduces the volume and speed at which the water reaches the river channel and so causes a longer lag time and smaller peak discharge.
How does deforestation affect a river’s hydrograph?
Deforestation reduces the number of trees that intercept or absorb and store rainwater which eventually is returned to the atmosphere. This reduces the soil’s infiltration capacity and increases surface runoff. Thus more water reaches the river channel faster which shortens the lag time and increases peak discharge.
Afforestation increases the number of trees that intercept or absorb and store rainwater which eventually is returned to the atmosphere. This increases the soil’s infiltration capacity and reduces surface runoff. Therefore less water reaches the river channel slower which increases the lag time and decreases peak discharge.
What is hard engineering?
The use of man-made structures to control the flow of rivers and reduce flood risk.
What are examples of hard engineering?
Dams + reservoirs
Channel straightening
Embankments
Flood relief channels
What are dams + reservoirs?
Dams are barriers built across rivers, particularly in the upper course, which form reservoirs behind them.
What are the advantages of dams + reservoirs?
The reservoir can store immense amounts of water, preventing flooding in periods of prolonged/heavy rainfall
The water flowing through the dam can be used to generate hydroelectric power.
The reservoir can be used for leisure activities, attracting tourists to the area.
What are the disdvantages to dams + reservoirs?
Its construction requires many people to be displaced so that land can be flooded to make the reservoir.
The flooding of land also destroys many animal habitats
They are costly to build
Sediment is deposited in the reservoir which reduces the amount deposited downstream, causing the soil in floodplains (often used as farmland) to become less fertile.
What is channel straightening?
The removal of meanders to make the river channel straighter and increase the speed of the river’s flow.
What is the advantage of channel straightening?
Because the river’s flow is faster, the water leaves vulnerable areas quickly rather than building up which reduces flood risk in that particular area.
What are the disadvantages of channel straightening?
Given that the water is travelling faster, there is an increase risk of flooding downstream.
The faster-moving water may also cause more erosion downstream.
What are embankments?
Raised river banks built to increase the volume of water that the river can hold.
What is the advantage of embankments?
Because the river channel can hold more water, flood risk is reduced.
What are the disadvantages of embankments?
They are expensive to build.
If the embankments burst or break, there is a risk of severe flooding.
What are flood relief channels?
An artificial channel built to divert:
water from urban areas
excess water if the river levels get too high.
What is the advantage of flood relief channels?
Gates on the channel can control river discharge through the release of water, which consequently reduces flood risk.
What are the disadvantages of flood relief channels?
There is increased discharge where the relief channel rejoins the river, increasing flood risk in that area.
They are expensive to build.
What is soft engineering?
Schemes that work with the natural processes along the river to reduce the risk of flooding and do not involve the building of man-made structures.
What are examples of soft engineering?
Flood warnings + preparation
Flood plain zoning
Afforestation
River restoration
What is flood warning + preparation?
The use of various forms of media (TV, radio, newspaper, the internet e.t.c.) to alert people when river is likely to flood. In the UK, the Environment Agency is responsible for issuing these warnings when floods are likely.
What is the advantage of flood warnings + preparation?
They give people time to move possessions upstairs, put sandbags or other flood defences and evacuate, reducing the impact of the flood.
What are the disadvantages of flood warnings + preparation?
Warnings do not stop flooding from happening.
Some people may not be aware of the flood warnings
What is flood plain zoning?
Placing restrictions to prevent building in areas of the flood plain that are likely to be affected by a flood.
What are the advantages of flood plain zoning?
Flood risk is reduced as fewer impermeable surfaces (e.g. roads) are constructed on the floodplain.
It reduces the impact of flooding because there are no buildings to damage.
What are the disadvantages of floodplain zoning?
Flood risk in parts of the floodplain have already built on is not reduced.
The growth of urban areas is limited if there aren’t any other suitable building sites besides the restricted areas.
What is afforestation?
The planting of trees.
What are the advantages of afforestation?
River discharge and flood risk are reduced given that more rainwater can be intercepted - this also increases the lag time.
The trees act as habitats for wildlife and prevent soil erosion
What is a disadvantage of afforestation?
It requires a lot of land, meaning less is available for farming, and time.
What is river restoration?
The return of a river to its original course by recreating natural fluvial features and removing artificial structures.
What are the advantages of river restoration?
It reduces discharge and therefore flood risk downstream.
Little to no maintenance is required, making it a cheaper solution.
There is an improvement of wildlife habitats.
What is a disadvantage of river restoration?
Local flood risk can increase, particularly if nothing is done to prevent major flooding.
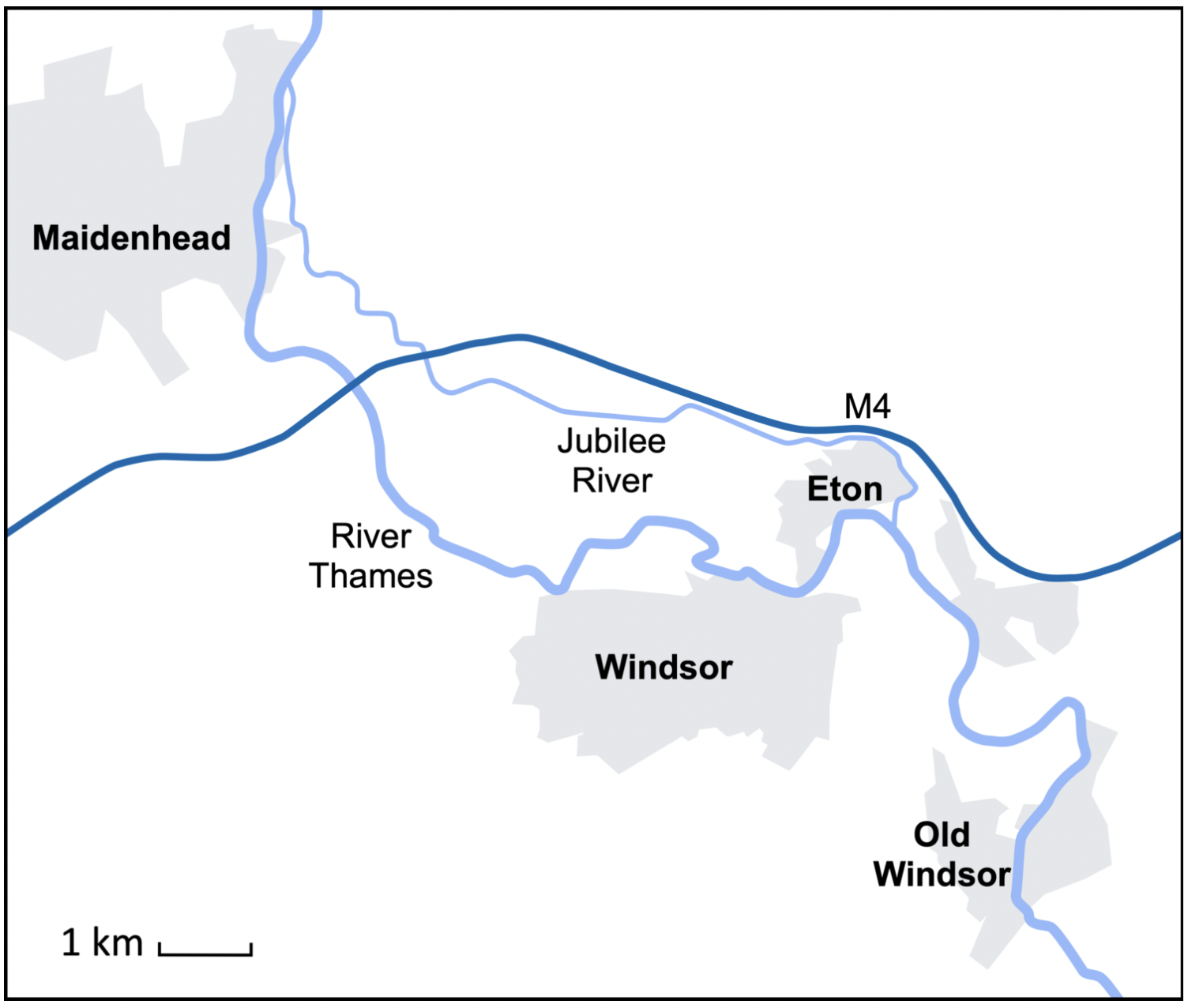
What is the Jubilee River?
A flood relief channel funded by the Environmental Agency which was constructed to reduce flooding in Windsor and Eton by diverting water from the River Thames.