The Earths Layers
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
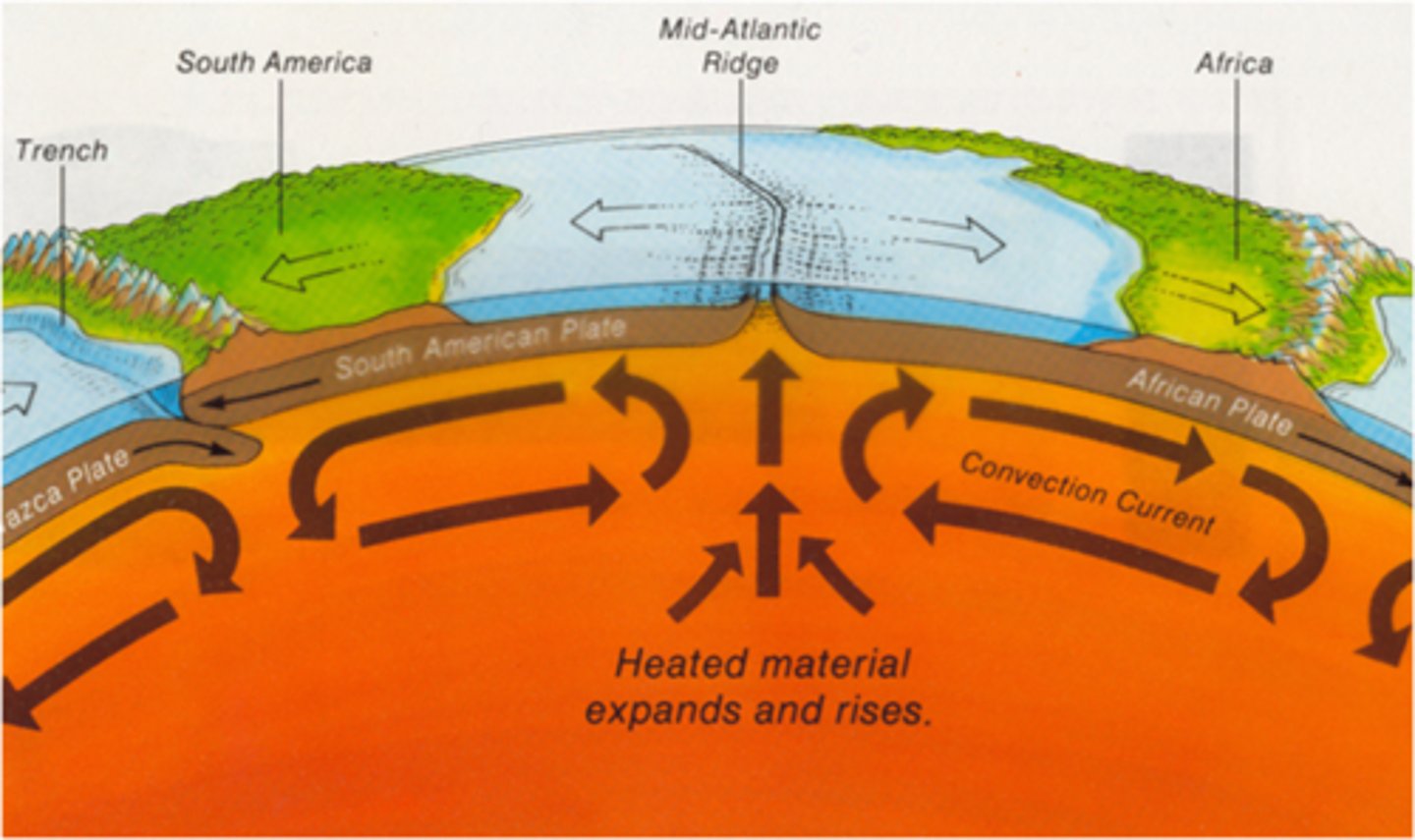
seafloor spreading
The formation of new oceanic crust at a mid-ocean ridge
earthquakes and volcanoes relate to plate boundaries.
Volcanos and earthquakes happen when the plate boundaries are moving. Earth quakes are due to the subduction zone under the crust, and where there is a weak spot magma is pushed up there. Causing a volcano to form. In addition, an earth quake is where the the plate move, and the earthquake is an after affect.
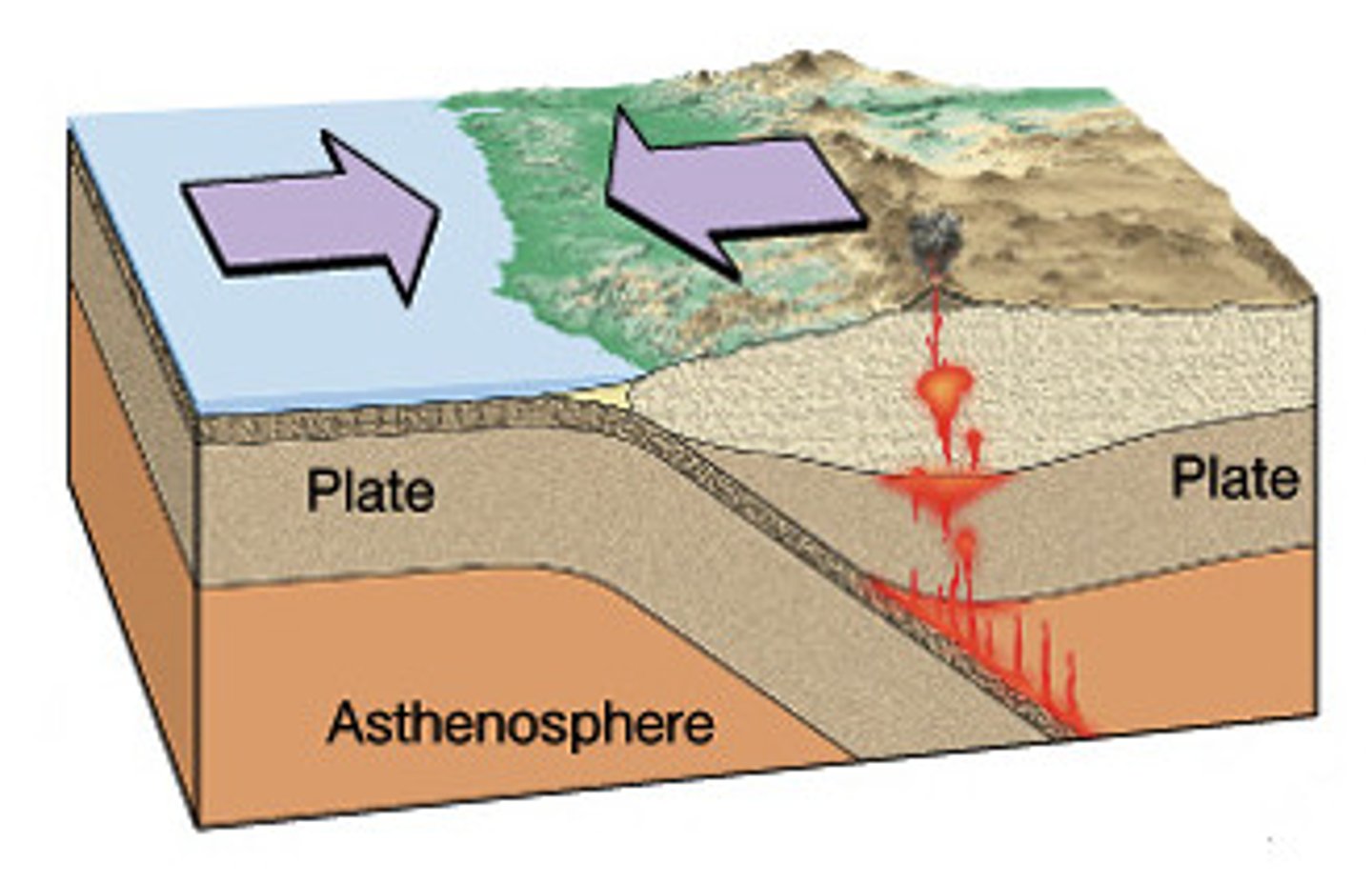
Oceanic-continental convergent - land forms
trench, earthquakes, volcanos
Curst made out of?
consist of solid rocks and minerals
how temperature changes with depth below the Earth's surface.
The temperature changes with depth below the Earth's surface. The tempture slowly rises as the depth increases.
What proof did Wegene used to support his theroy
plants and fossils
tectonic plates
A section of the crust and upper mantle
convergent
Plates moving towards one another
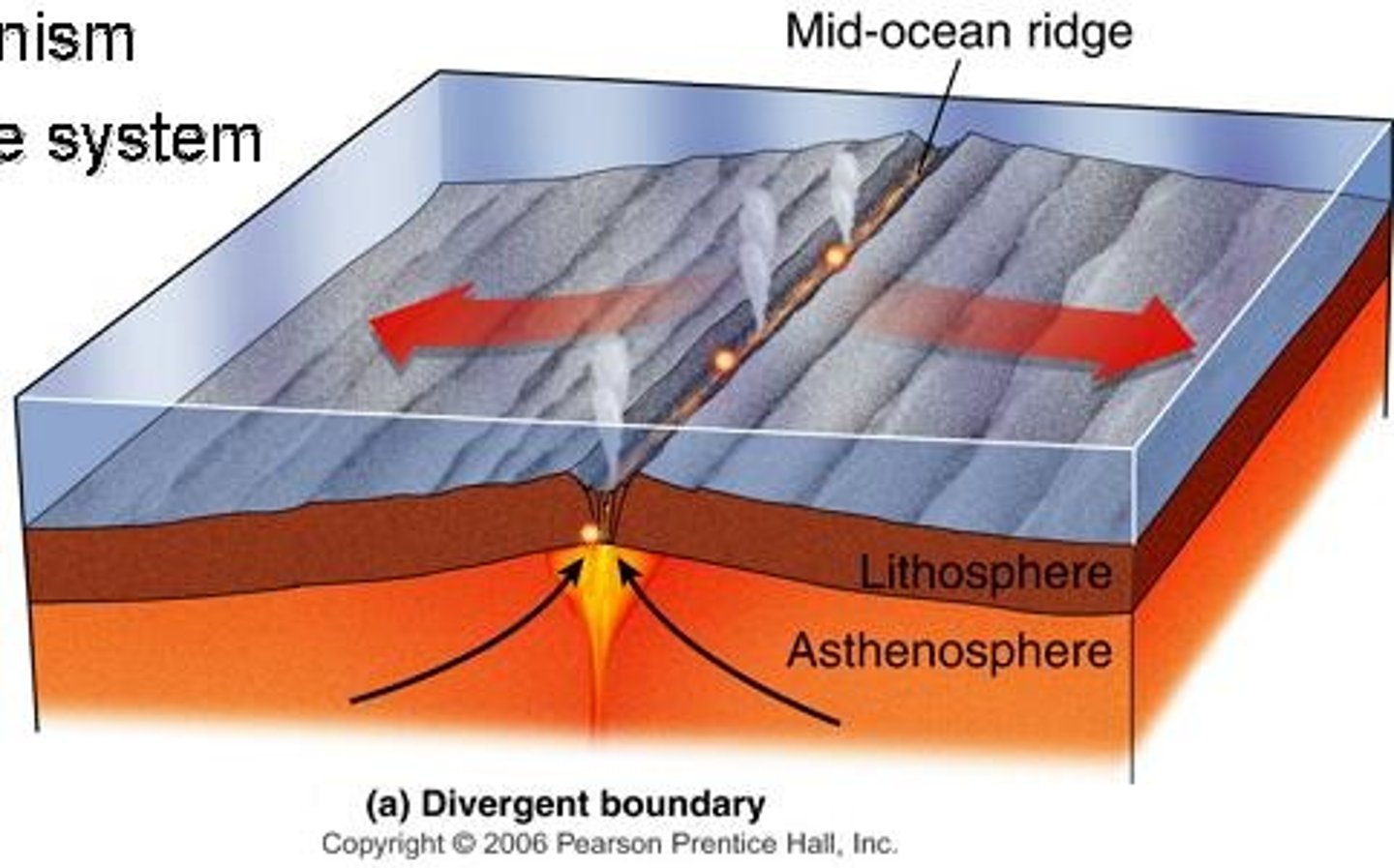
divergent
Plates moving away from one another
Oceanic-continental dirvergent
Subduction also occurs in this case. The much denser oceanic crust always sinks beneath the continental crust. This produces a trench along the subduction zone and volcanoes on the continental crust.
Continental-continental
convergent
Continental crust is too light to sink into the mantle. So when two continents collide, the crust is pushed up to form high mountain ranges.
Oceanic-oceanic
divergent
When two plates with oceanic crust pull apart, a mid-ocean ridge forms. Cracks in the thin crust allow magma to rise from the mantle. Eruptions from deep-sea volcanoes produce new oceanic crust. This causes slow seafloor spreading.
Continental-continental
divergent
A divergent plate boundary in continental crust creates a long depression. This is known as a rift valley. Magma rises through the thinned continental crust and creates volcanoes.
Oceanic-oceanic convergent - land forms
trench
Continental-continental convergent - land forms
volcanic eruptions and earthquakes
eg. Himalaya Mountains
Oceanic-oceanic divergent - landforms
underwater volcanoes, mid-ocean ridges
Continental-continental divergent - landforms
ridge and valleys
Transform - land forms
faults
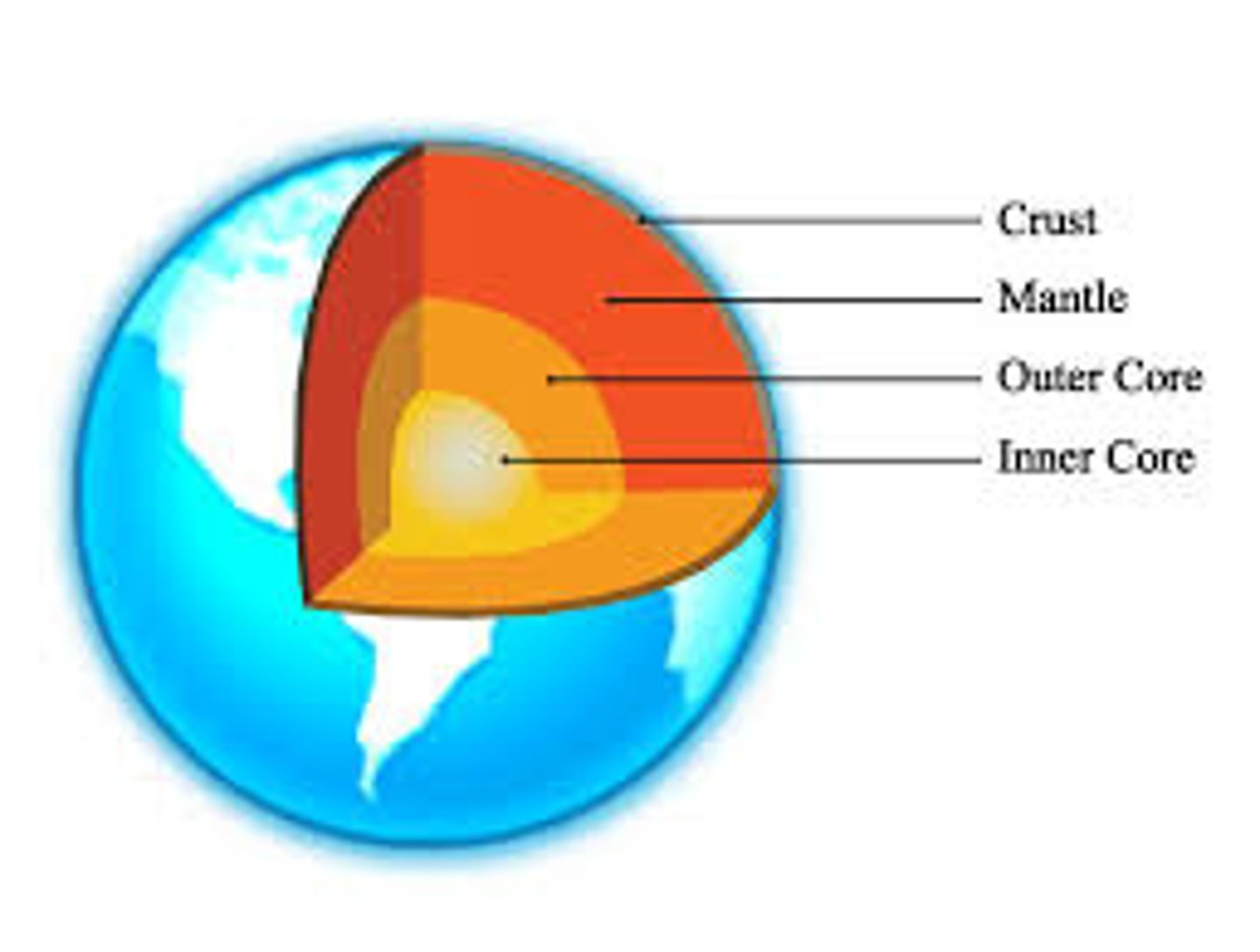
The layers of the earth
crust, mantle, outer core, inner core
What is the mantle made out of?
The mantle consisiting primarily of magnesuim.
Solid / liquid
What is the outer core made out of?
liquid iron - nickel mixutre
What is the inner core made of?
Iron and nickel
how pressure changes with depth below the Earth's surface.
Pressure in the Earth increases with depth due to the weight of the overlying rock layers.
Pangaea
continents once joined together as a supercontinent
why scientists didn't accept Wegener's theory of continental drift.
1. They believed land bridges allowed land animals to spread between continents
2. There was no way to explain how the continents could move
Describe the theory of continental drift.
Alfred Wegene who thought of this, proposed a new theory, where continents once joined together as a supercontinent called Pangaea. The theory of continental drift, is the idea that the continents move by the tectoic plates.
mantle
The thickest layer of Earth, between the core and the crust
lithosphere
The lithosphere sits on a layer of the mantle that is partially melted.
The lithosphere is the solid, outer part of Earth. The lithosphere includes the brittle upper portion of the mantle and the crust, the outermost layers of Earth's structure.
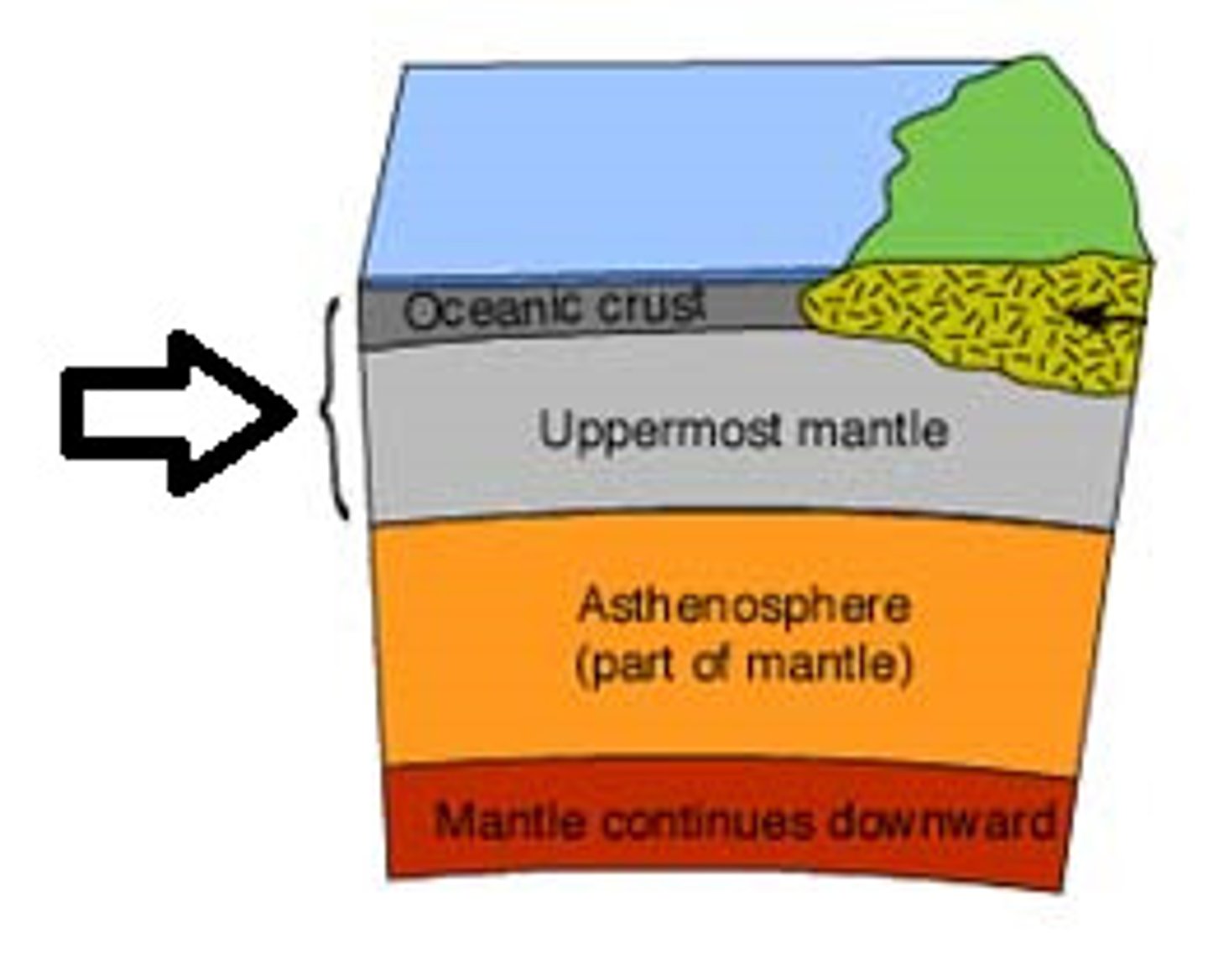
plate boundary.
The border between two tectonic plates
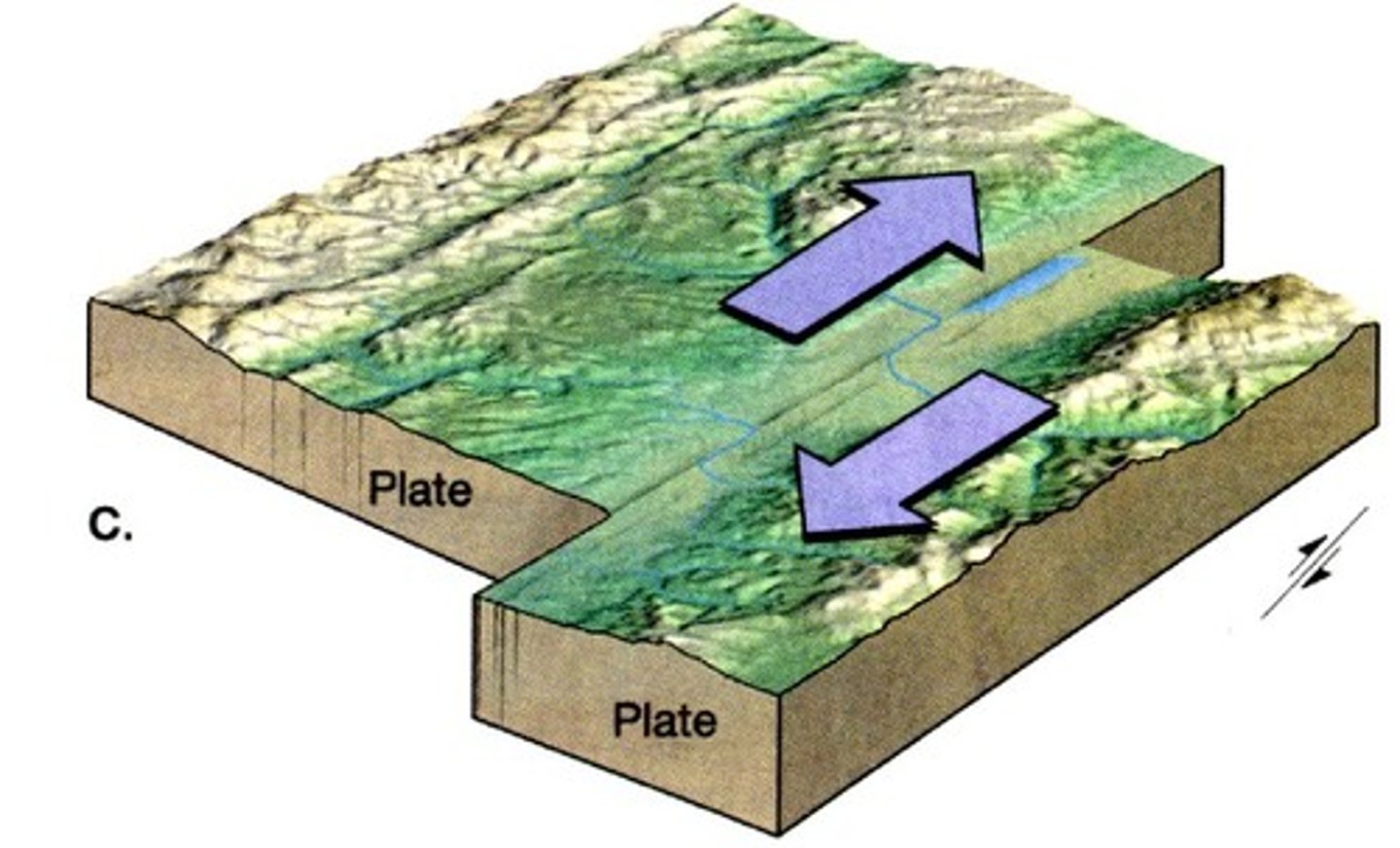
transform
Plates sliding past one another
Oceanic crust
thinner, more dense, younger crust making ocean floor
Continental crust
the relatively thick part of the earth's crust that forms the large landmasses. It is generally older and more complex than the oceanic crust.
transform
Two plates sliding past each other form a transform boundary. The two plates slide past each other along a large fault.
Explain why earthquakes can occur on every type of plate boundary.
Due to the plate moving, the earthquake is at every plate boundary.They occur where plates are subducting , spreading, slipping or colliding.