UDP
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
How does phase 2 metabolism detoxify drugs
Adds a water solubilising agent to allow for excretion of the drug/metabolites
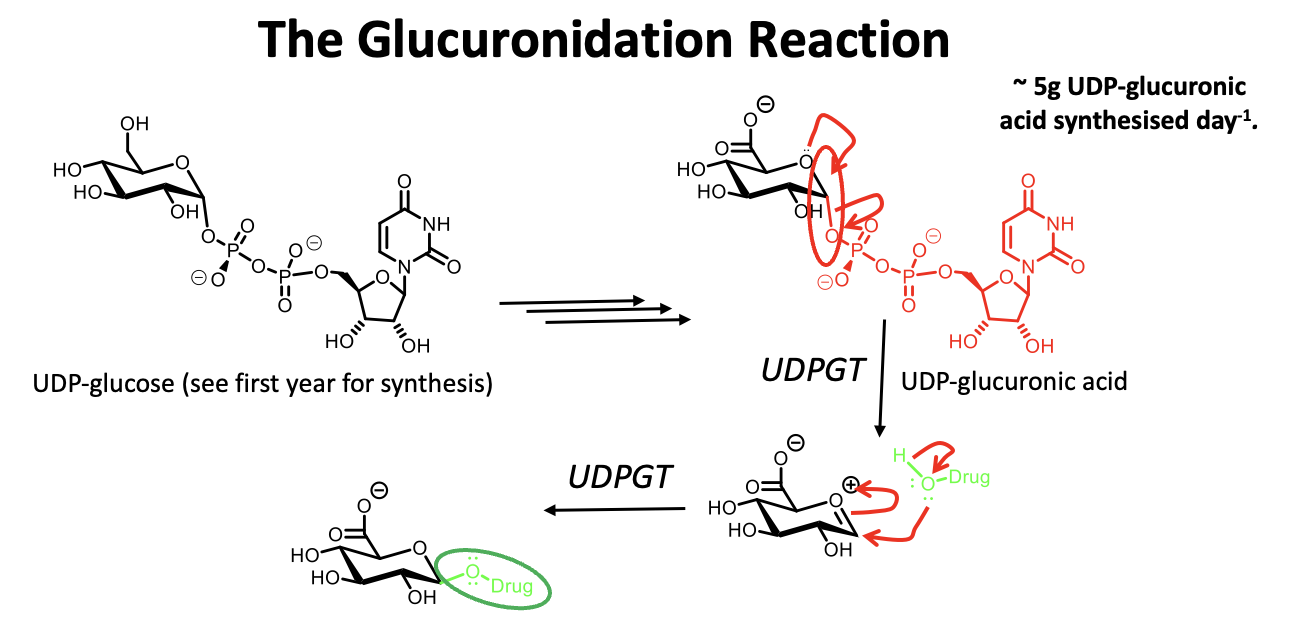
Glucouronidation
Addition of glucuronic acid( an electrophile) to nucleophile
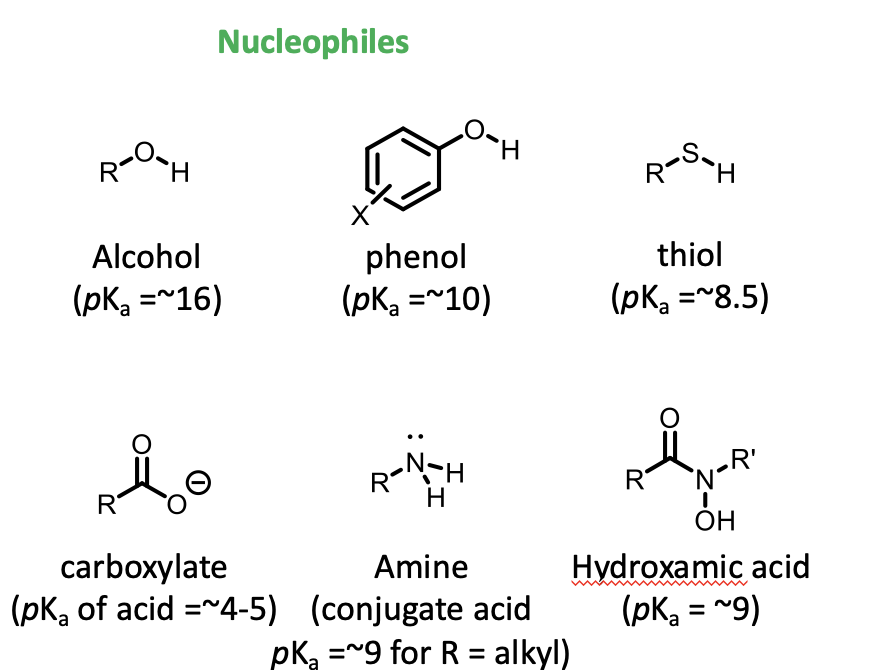
examples of nucleophiles
OH
phenols
SH groups
carboxylate groups
amines
hydroxamates
Has a lone pair of electrons and negative charge
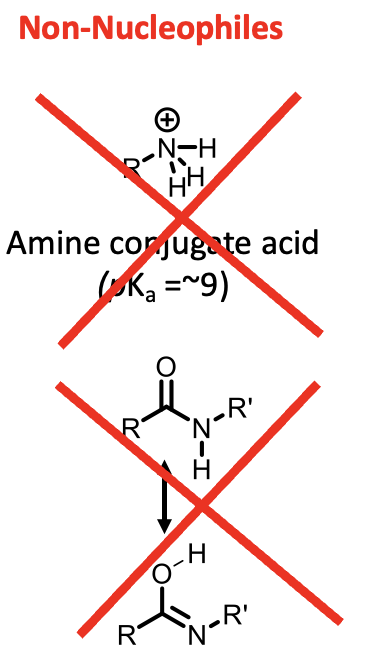
Examples of non-nucelophiles
Protonated amines: lone pair is not available
Amides: their lone pair of electrons is resonance stabilised with the carbonyl group
Explain the glucuronidation reaction
ØMost common reaction in phase 2 metabolism.
ØReactions goes with inversion of configuration (α to β) at anomeric position.
ØVariable amounts of drug can be glucuronidated (~11 to 90%).

Describe the structure of UDP
a-helix
irregular coil
UDP-glucuronic acid and drug
Where are UDPGTs found
in membrane of ER
In many tissues especially liver, skin, intestine, kidney, lungs, adrenals and spleen
Effect of MW on drugs
ØDrugs Mw <200 Da. excreted in urine.
ØDrugs Mw >200 Da. excreted in the bile (via GI system).

Expression of UDPGTS in younger patients
Low expression
Low enzyme activity in babies and neonates
which means the half life of the drug is longer in children
extended time to eliminate the drug
May need lower dose
Metabolism in elderly
Decreased first pass metabolism of drugs
e.g. cytotoxic drugs, codeine
May need lower dose
Enterohepatic circulation
How do we classify UDPGT
in super-families and sub-families
each enzymes has a distinct profile but this can overlap with others and regioselectvity
has great homology
important for metabolism of steroids
1A10 UDPGT enzyme
Broad substrate selectivity
What can cause variations in UDPGTs
Exons (coding regions: shares 2-5 exons but has a variable exon 1
results in polymorphisms which affect drug metabolism
Can also affect rate of transcription, translation, enzyme stability, catalytic activity
What causes this variable rate of drug metabolism between populations
Polymorphism
What is Gilbert’s syndrome
A UDPGT deficiency
Haem→ Bilirubin → UDPGT defence prevents conversion to glucyronic acid conjugate
Increased levels in bilirubin the blood
Common mutation in Caucasians, affects enzyme expression
Missense in asian population, reduces enzyme activity
Gilberts’ Syndrome: Consequences
cyclical, can be affected by stress, heavy exercise, dehydration
Symptoms: jaundice, fatigue
Affect on medicines: atazanavir, irinotecan (anticancer), paracetamol metabolism reduced
So medication and dose needs to be tailored
Drug Interactions with UDPGTs
occurs when two drugs have been metabolised by the same CYP enzyme
What can cause reduced metabolism
depletion of UDP-glucuronic acid by drug
e.g., paracetamol causes toxicity in neonates and babies due to accumulation of bilirubin (degradation product of haem)

What can caused increased metabolism
Can get increased metabolism due to enzyme induction from drugs, cigarette smoke, pollutants etc. (Same reason as for CYP enzymes).

What happens with chiral drugs
Can get complex behaviour with chiral drugs, and drugs with more than one glucuronidation site (see following slides). Because of chiral selectivity which can form diastereoisomers and epimers which react different with UDPGTs

Chiral selectivity
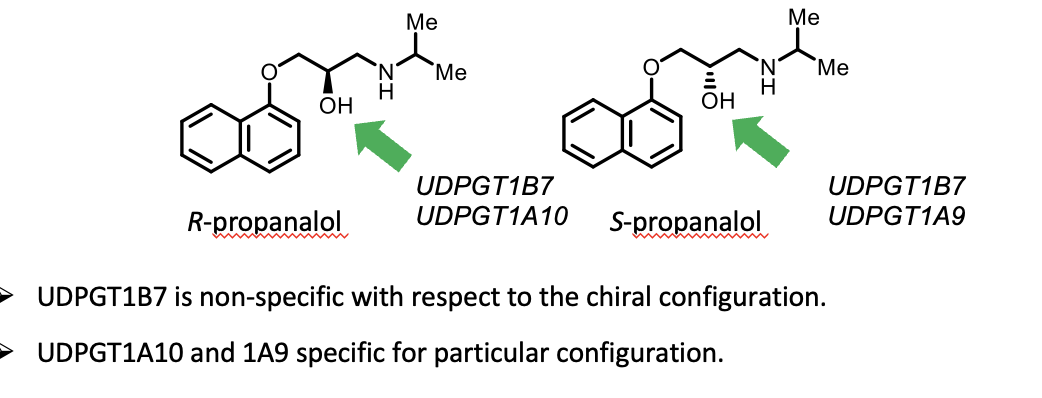
What happens if a compound has multiple nucleophilic groups
Multiple products can result
The group that is glucuronidated depends on the nuceleophilicity of the group and availability and activity of the enzyme
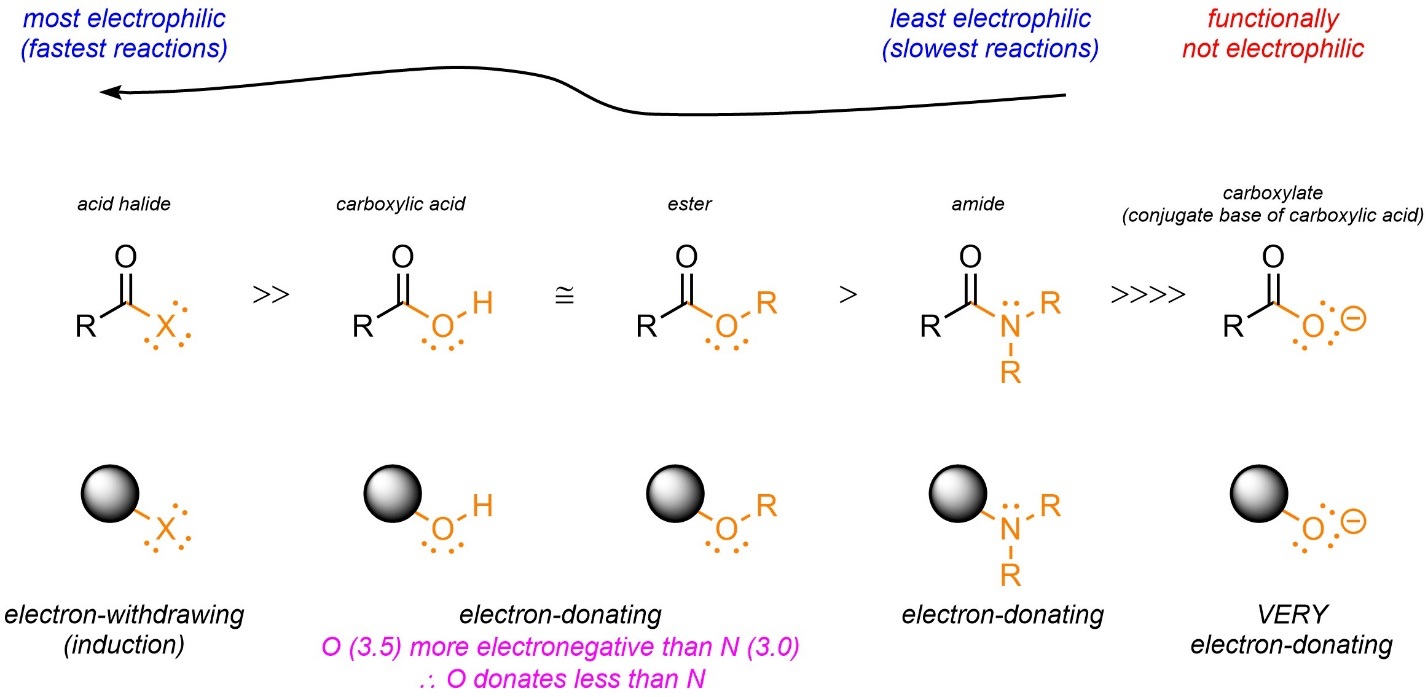
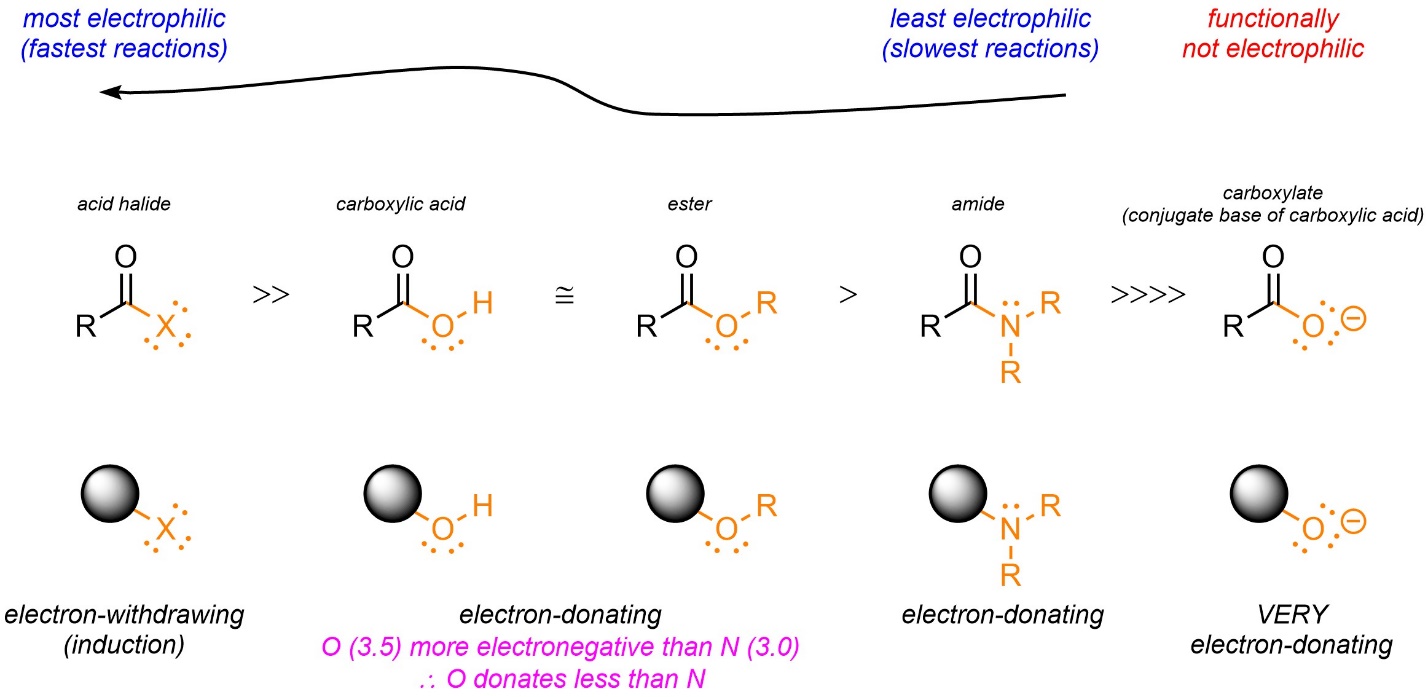
What is the impact of major and minor products of UDPGT
Can have different pharmacological activities
for example:
Major product of O3-glucuronide is inactive
Minor product: O6-glucuronide is active on u-opiod receptor