6. Cell Injury: Postmortem Changes
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What are postmortem changes the result of?
autolysis (decomposition)
When do antemortem changes occur? How long do they take to develop?
prior to deaht; take minutes to hours to weeks to develop
True or false: Postmortem changes are not a pathologic process, therefore they are not lesions.
true
decomposition of cells which occurs due to loss of cellular integrity or breakdown of cells which occurs after death
autolysis
How can autolysis be minimized?
by performing a post mortem evaluation and collection of tissues as close to the time of death possible
What can halt autolysis? Why?
fixing tissues in a fixative such as formalin at the time of collection; fixatives cross link proteins, providing cell stability
What are the variables in post mortem decomposition?
T
T
C
E
B
M
tissue
type of animal
cause of death
environmental temperature
body temperature
microbial flora
How do the microbial flora contribute to postmortem changes?
produce gas causing bloat of tissues and organs which can result in post mortem prolapse of the rectum, uterus, or proptosis of the eyes and even the diaphragm can rupture
What is significant about autolysis in further febrile animals?
they will autolyze faster due to higher body temperatures
What is the effect of hot external or environmental temperatures on the rate of autolysis?
will increase it
What can cooling of the carcass do to autolysis? Should you freeze it? Why or why not?
slow it down; no, because it destroy tissue architecture and cellular integrity due to ice crystal formation
What will abundant adipose tissue or thick wool do to the rate of autolysis?
will retain heat within the body for longer and thus autolysis progresses more rapidly
Which tissues tend to autolyze quickly?
I
B
S
intestinal mucosa
brain
spinal cord
What type of tissue will maintain their integrity for much longer?
skeletal muscle
What is significant about the actions of striated muscle after death?
has the ability to contract which can lead to artifacts
When will rigor mortis commence? How long will it persist for?
1-6 hours after death; 1-2 days
How soon does autolysis begin?
immediately
gravitational pooling of blood after death, which results in discoloration of tissues
liver mortis or hypostatic congestion
Where else can liver mortis be present? What does it indicate?
organs including the lung; the animal died on the side of the pooling
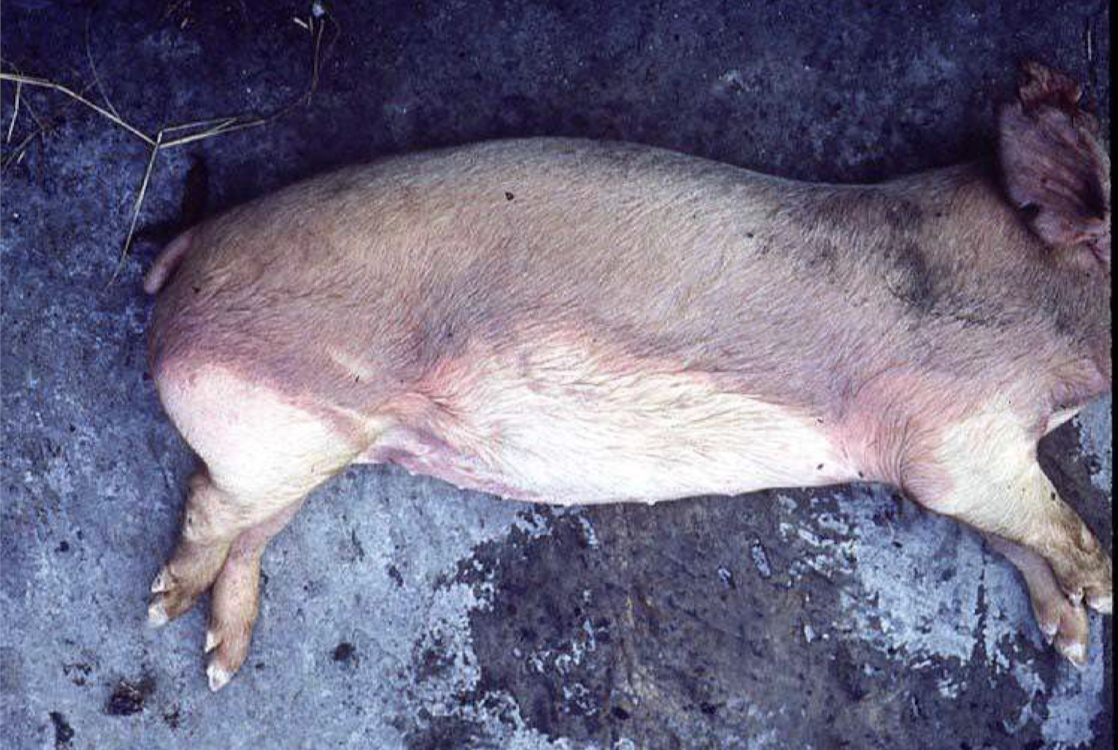
What postmortem change is this?
liver mortis or hypostatic congestion
True or false: Postmortem lesions can mask antemortem lesions.
true
bile leached out into the surrounding tissues
bile imbibition
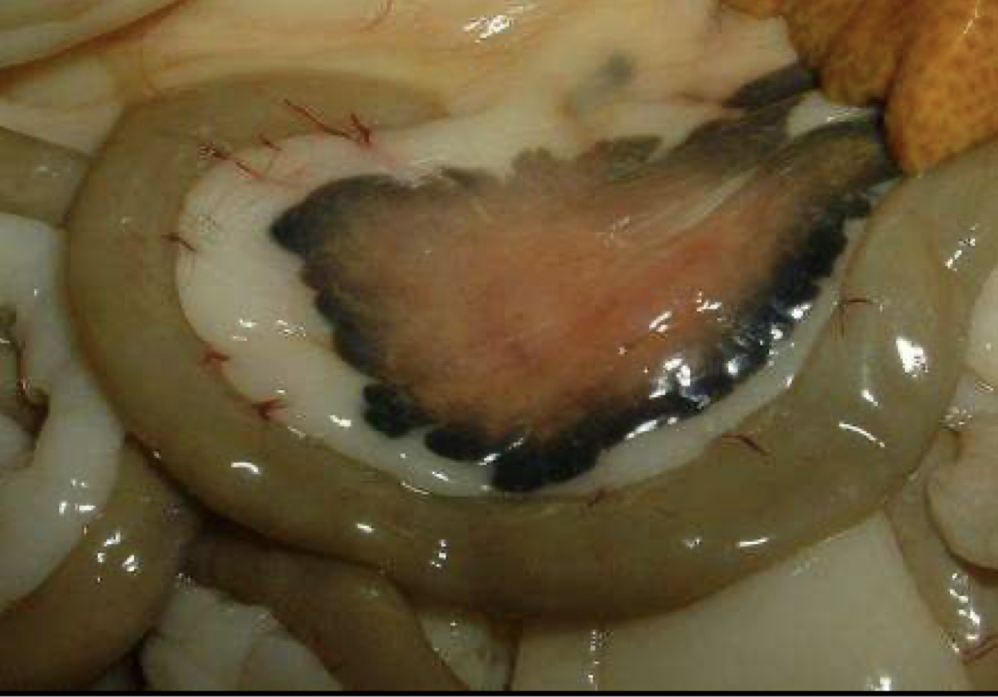
What is this showing?
bile imbibition
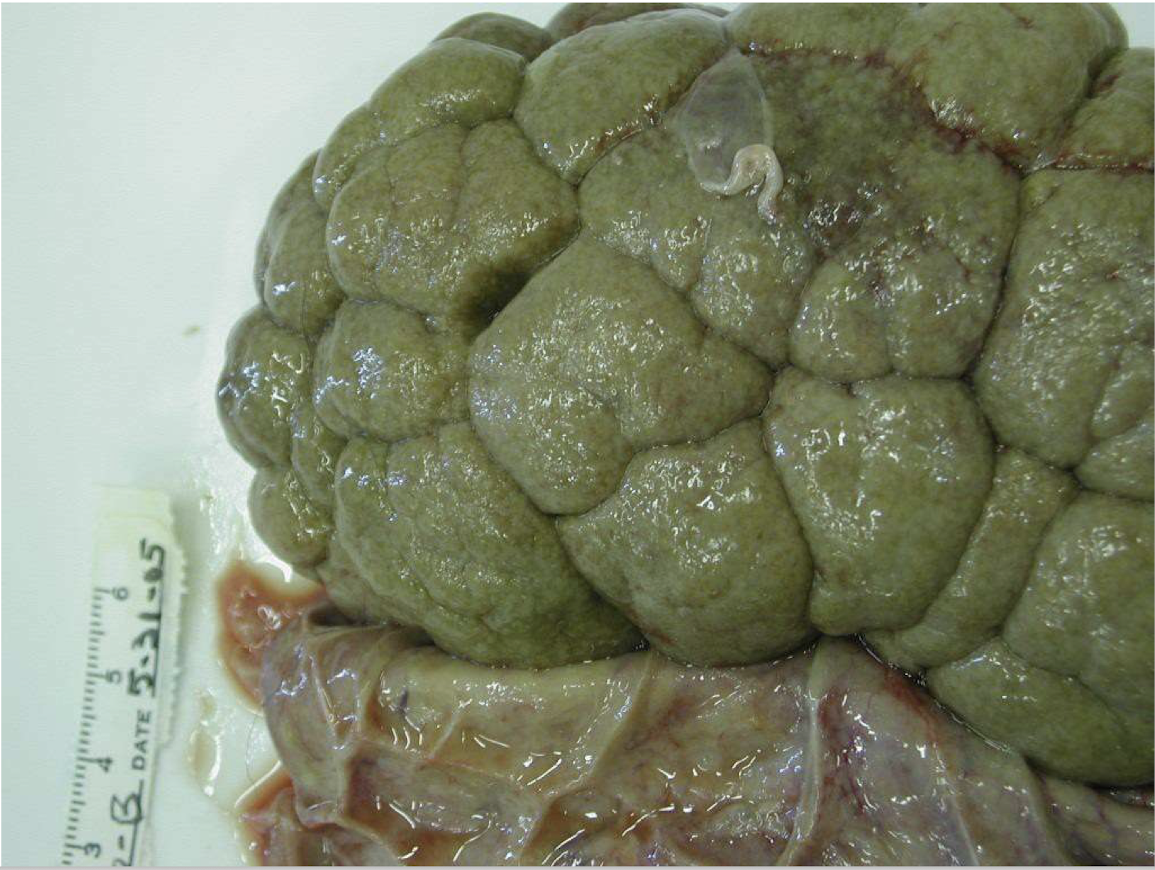
What is this showing?
rotten bovine kidney
breakdown of RBCs and hemoglobin leaking that stained the surrounding tissues
hemoglobin imbibition
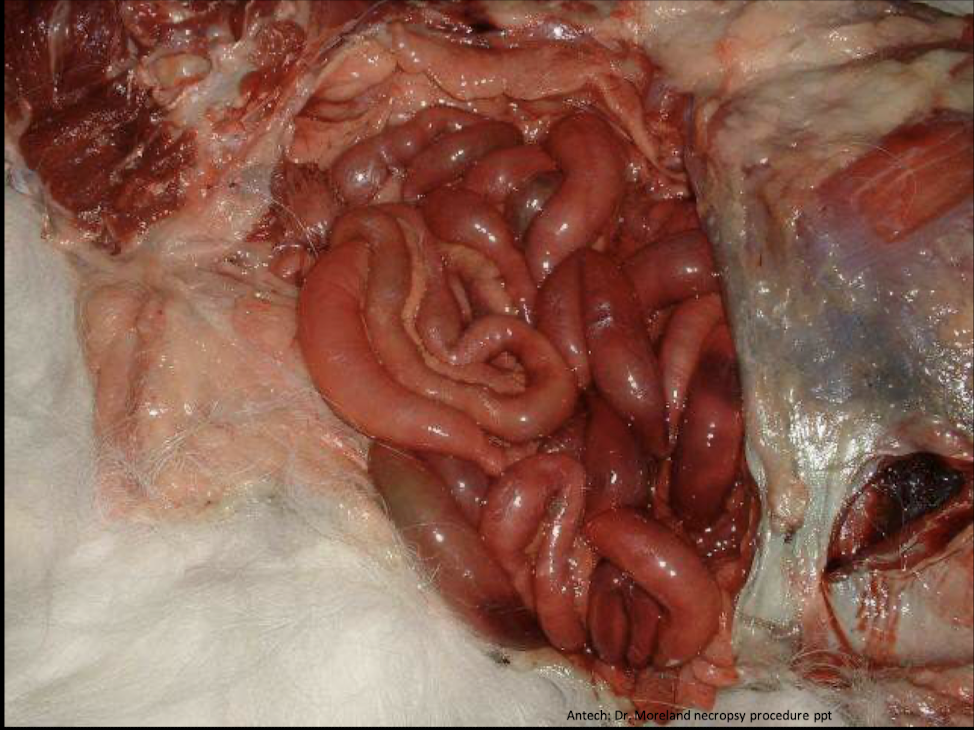
What is this showing?
hemoglobin imbibition
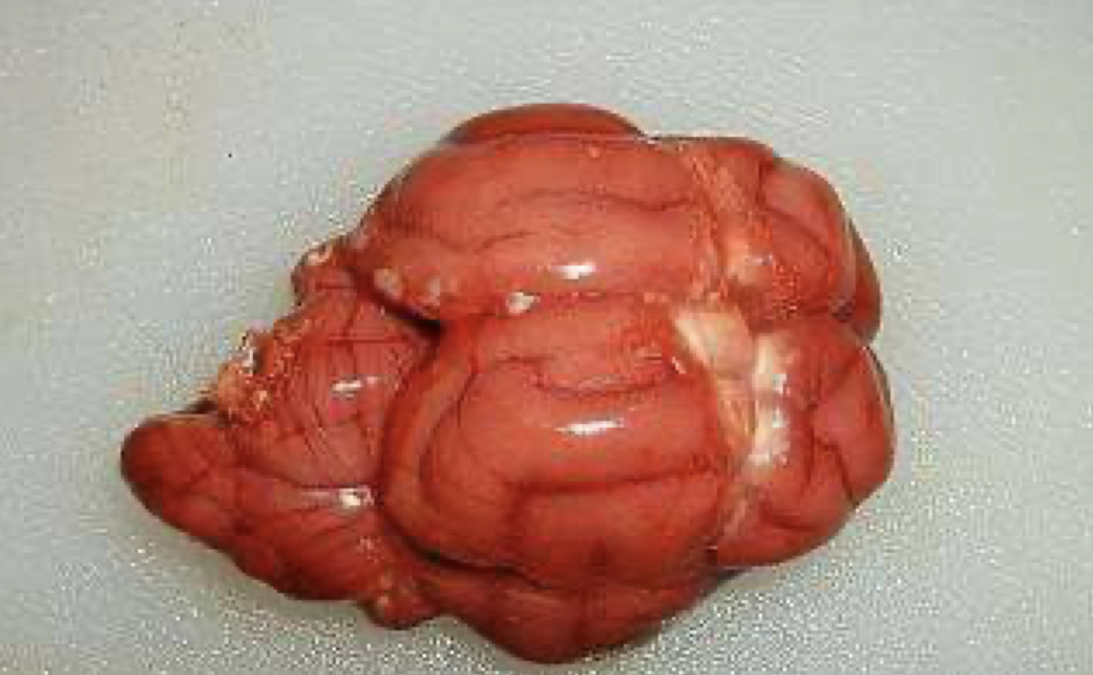
What is this showing?
hemoglobin imbibition
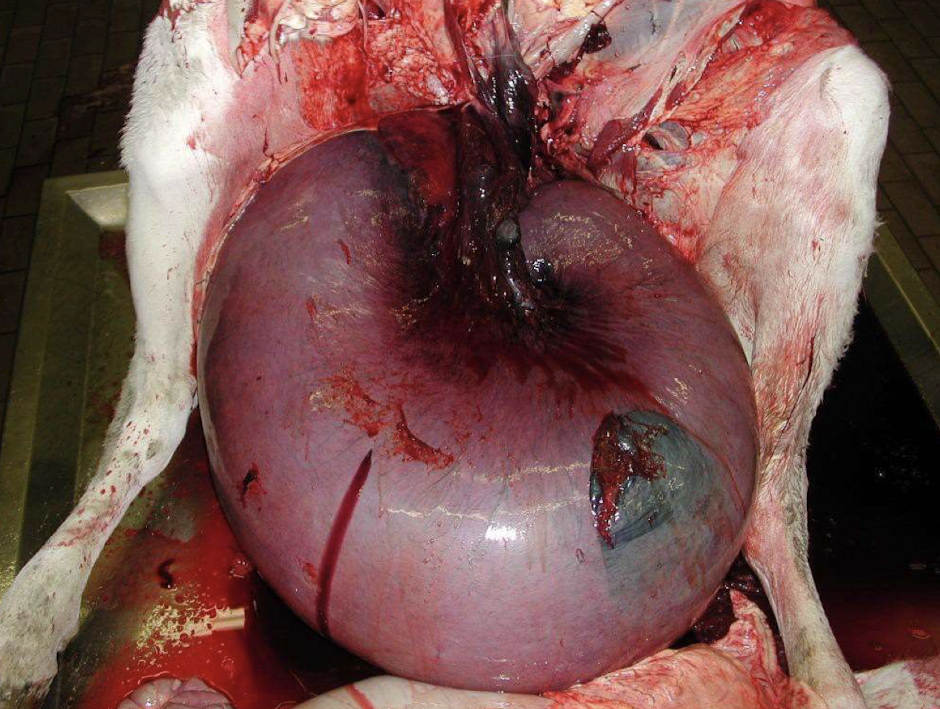
Is this antemortem or postmortem? How do you know?
O
R
O
antemortem;
observance of uterine torsion
root of uterus is extremely dark
other intestines are the colors they should be