history of our planet week 4.1
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
extinction. triggers of snowball earths and mass extinction events
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
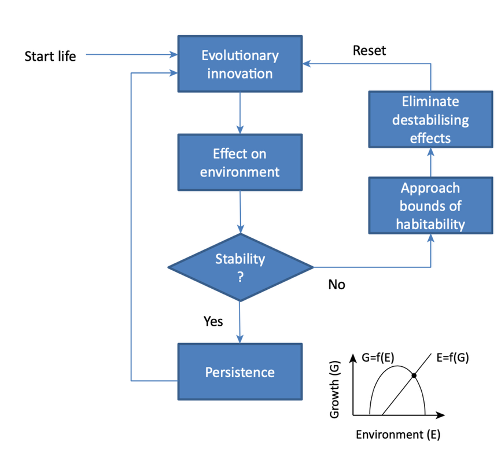
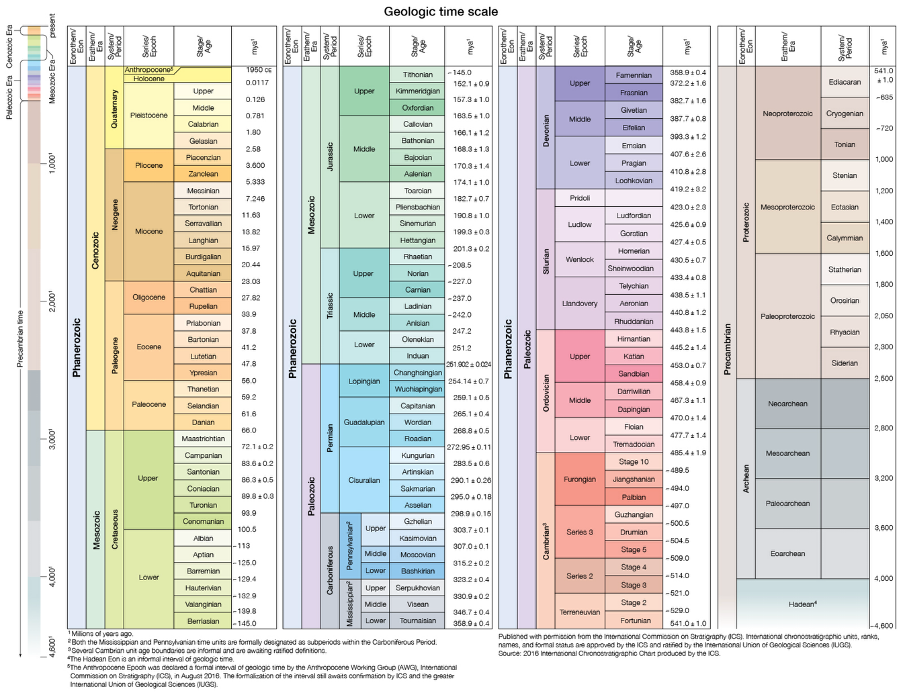
organisation of time
hadean at start, quaternary currently
time segments
eon, era, period, epoch, age
causes of mass extinctions - external triggers
extraterrestrial impact, massive volcanism
causes of mass extinctions - internal feedbacks
global climate change, ocean anoxia and acidification
mass extinctions defined for marine animal genera
genera = class of species
can seen marine better due to fossils
big 5 extinction
End Ordovician (O-S)
Late Devonian
End Permian (P-Tr)
End Triassic (Tr-J)
End cretaceous (K-P)
+ present day
late permian model
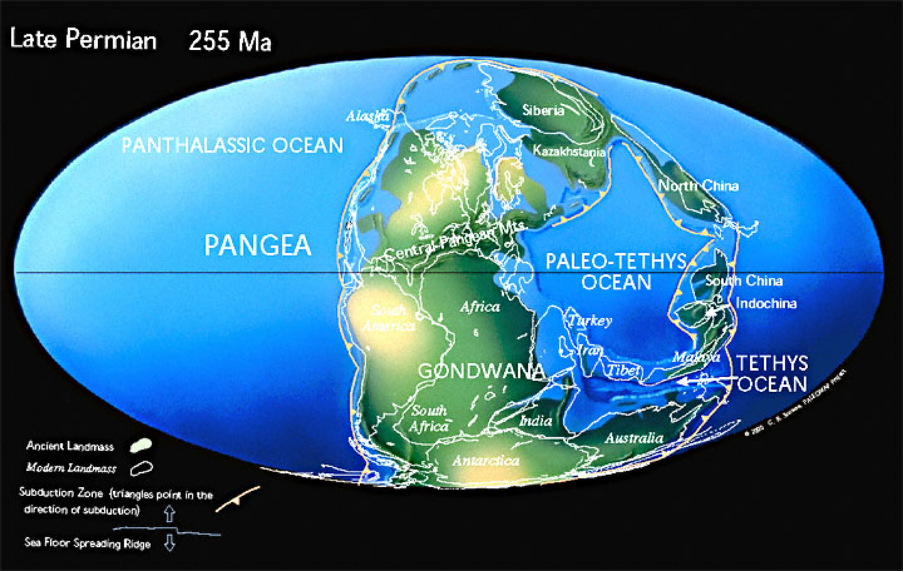
end permian mass extinction
Extinction of families:
63% land (over 75% species)
Only things living for a number of years were ferns (tall – pleuromeia fossils)
49% marine (over 90% species lost)
61% total
end permian mass extinction on land
The lystrosaurus mammal- like shovel lizard – nearly the only 4 legged creature living through this period
o Mutagenesis of plants
o Forests lost for 5 Myr
§ Replaced by the lycopsids including ferns
§ Extensive erosion
end permian mass extinction Volcanic event:
End Permian saw massive volcanic eruptions of the Siberian traps – a large igneous province
Spewed our 2million km^3 of lava covering 1.6 million^2 to a depth of us to 3000m
volume was erupted in less than 1 million years
Recent study says 60,000 yr (a geological instant)
Believe lava was being pushed into vast beds of coal, setting coal on fire – releasing more co2 as the coal beds are being ignited and making its way to the atmosphere
end permian mass extinction- Carbon cycle perturbation:
Volcanic eruptions release co2 and lava intruded into coal beds igniting them and releasing more co2
Carbon isotope record shows the release of large amounts of isotopically light (^13C-depleted) material
Either organic carbon or methane
Evidence for extreme global warming of ~10*C
end permian mass extinction- Ocean acidification:
When large amounts of CO2 are added to the atmosphere and dissolve in the ocean this acidifies it
This inhibits the formation of calcium carbonate shells (calcium carbonate shells required for calcifying organisms which are important for photosynthesis)
Key for carbon cycle and marine food chains
The second phase pf extinction was particularly bad for calcifying organisms
end permian mass extinction- Ocean anoxia:
Extinctions suggest that mush of the pecan became anoxic (dissolved oxygen)
E.g. loss of shelf bottom dwelling communities
Anoxic and euxinic – toxic H(2)S
Euxinic - Lots of hydrogen sulphide
What generate anoxia?
Increase in oxygen demand due to increases phosphorus input from land
Decrease in oxygen supply due to warming reducing oxygen solubility
In the sediments there are lots of different elements locked up in mud. One of these in sulphur (can be stable), but with very low oxygen conditions at the bottom of the sea, that water sediment interface has a chemical reaction and sulphur starts to leak out. Means there was a reltively narrow range of depth at which any animal could have lived bc too high = too hot and too low = no oxygen or too much hydrogen sulphide
end cretaceous world
Lump of rock size of Manhattan ~10km radius impacted earth
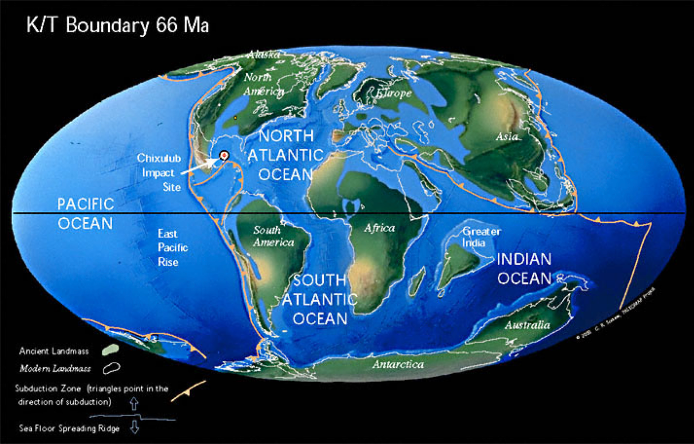
end cretaceous mass extinction
60% of all genera became extinct
Extinctions occurred very rapidly
Unusual in its selectivity:
Large land animals suffered extinction, most famously the (non-avian) dinosaurs
But those who could shelter in water/soil/burrows or who had larvae/eggs underground (e.g. crocodiles) survived
Evergreen vegetation suffered more than higher-latitude deciduous vegetation
end cretaceous world - impact event
Hypothesised 1980 by walter alvarez based on global iridium (Ir) anomaly (only could have happened from a large meteor)
1991- alan hildebrand published evidence of a 180km wide impact crater at Chicxulub dated at 65Million years ago
Estimated to be caused by a 10km diameter asteroid
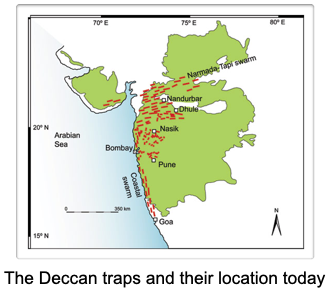
end cretaceous world - volcanic event
End cretaceous saw massive volcanic eruptions of the deccan traps
A large igneous province
800 Kyr basalt outpouring emplaced 365,000km^3 of lava
Eruptions were underway before the impact event, warming the climate – putting the earth in a more vulnerable state
end cretaceous world -The ‘Strangelove’ ocean
Ocean photosynthesis (primary production) was wiped out
Calcareous nanoplankton (marine phytoplankton) suffered 90% species loss only 12 species survived
Globally synchronous extinction
Supports ‘impact winter’ hypothesis of dark, cold conditions with long periods without sunlight
Photosynthetic activity largely stops working
end cretaceous world -Effects on the carbon cycle:
The biological pump takes up CO2 from the atmosphere and transfers it to the deep
Shutting this down caused a 2-3x increase in atmospheric CO2
This added to CO2 from deccan traps eruptions causing global warming
end cretaceous world - Oxygen catastrophe:
Oxygen was toxic to most microbial life at the time
Anaerobic habitats on land and in the surface ocean largely disappeared
But the formation if the ozone layer offered new protection from the UV radiation
Methane was removed from the atmosphere contributing to the glaciations including the first ‘snowball earth’ 2.2 Ga
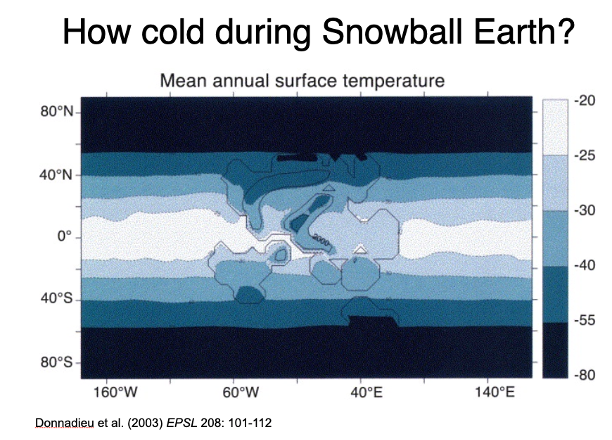
how cold during snowball earth?
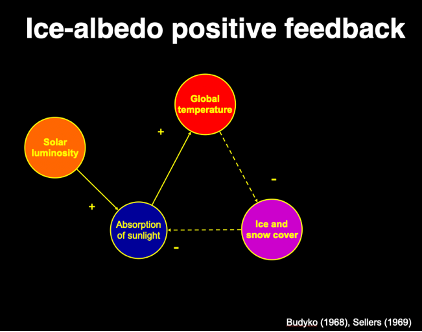
end cretaceous world - runaway feedback
Cooling leads to ice advance
More ice reflects more sunlight
Less sunlight absorbed
More cooling…more ice advance…
Once ice crosses a critical latitude (~30 degrees)
Runaway - snowball earth
end cretaceous world? snowball earth- when did it happen
~2220 Ma (makganyene)
Long gap then:
~710 Ma (sturtian)
~ 640 Ma (marinoan)
end cretaceous world? exit from snowball earth
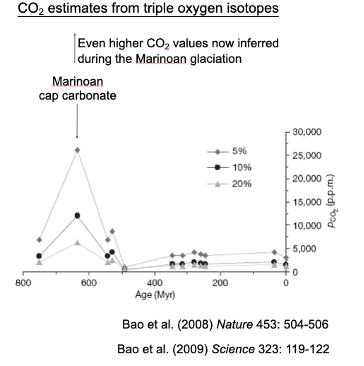
Trigger: co2 build up
Amplifier: reverse ice-albedo feedback
Should produce a very hot, high CO2 world in the aftermath
end cretaceous world? snowball earth- Cap carbonates:
These occur right after the glaciations (i.e above them in the geological strata)
They are explained in terms of mixing a high CO2 atmosphere with an ocean full of alkaline ions (e.g. Ca^2+) to form carbonates
they are enormous, consistent with a huge amount of CO2 being removed
end cretaceous world? snowball earth- What triggered the events:
Geologists link snowballs to the break up of supercontinents (e.g. redinia)
Basalt outpouring produced a highly weatherable surface
Increased runoff promoted high weathering rates and co2 drawdown
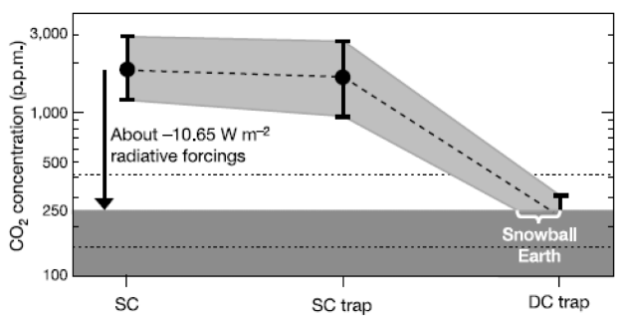
is this how Gaia works?