BIOL 2440 unit 1: chapter 1, 2, & 3
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cell Bio Exam #1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
what are the factors of cell diversity?
size
shape
chemical requirements
specialization
what are the factors of cell unity?
composed of the same molecules
same type of chemical reactions
same genetic components
same basic biochemical machinery
What is created by the central dogma?
DNA—-> RNA—-> protein
what process is used to create RNA from DNA?
transcription
what process is used to create Proteins from RNA?
translation
what are proteins made of?
amino acids
what are DNA and RNA made of?
nucleotides
how do we study cells?
cell fractionation, cell homogenate, pellet, supernatant
microscopy (17th century)
what is the cell theory that is universally accepted by all biologists ?
everything Is made up of cells
all cells come from other pre-existing cells
what are the two types of basic cells?
prokaryotes
eukaryotes
what is a way to distinguish between the prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
eukaryotes have a nucleus, prokaryotes do not
what process does prokaryotic cells go through for cell division?
binary fission
what process does eukaryotic cells go through for cell division?
mitosis
what two processes keep the endomembrane system in equilibrium?
endocytosis
exocytosis
what is endocytosis?
cells membranes import material through a cavity into the cell
what is exocytosis?
waste is secreted out of the cell through the plasma membrane
why are model organisms used?
to gain knowledge from studying the model
what is the chemistry of life?
based on carbon compounds (study of carbon compounds: organic chemistry)
chemical reactions take place in a aqueous environment
the most complicated chemistry known to man
huge polymers
highly regulated
what are the three types of chemical bonds?
covalent: polar & non polar, e- shared, not transferred
ionic: cation (+) and anion (-), electrons. are gained or lost
hydrogen: weak interactions
what are the three types of interactions?
hydrophilic: water loving
hydrophobic: water hating/ fearing
Van der Waals: attractive force due to fluctuating electoral charges
what are the characteristics of a acid?
releases H+, has a pH between 0-6, moles/liter: 1 — 10-6
what are the characteristics of a bases?
accepts H+, removes H+ from solution, has a pH between 8 - 14, moles/liter: 10-8 __ 10-14
what are buffers?
weak acids and bases that readily take up or release protons to keep the environment of the cell relatively constant
what forms macromolecules?
subunits —-—→ macromolecules—-—→ macromolecular assembly
-covalent bonds used to turn subunits to macromolecules
-non-covalent bonds used to macromolecules to macromolecules assemble
(subunits: amino acids, nucleotides)(macromolecules: RNA molecule, protein) (macromolecular assembly: ribosome)
what is needed, not needed, and what kind of reaction is HYDROLYSIS?
water is needed, energy is not needed, energetically favorable reaction, monomer —→polymer
what is needed, not needed, and what kind of reaction is CONDENSATION?
energy is needed, energetically unfavorable, polymer —→ monomer
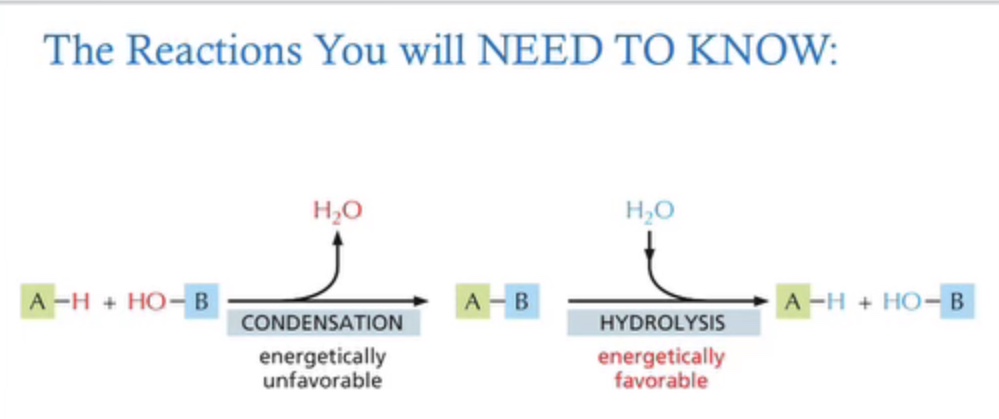
what is the reaction “equation” for condensation?
A-H +HO-B———condensation——→ A - B ———hydrolysis——> A-H + HO-B
condensation: releases water, energetically unfavorable
hydrolysis: takes in water, energetically favorable
what is the general formula for monosaccharides?
(CH2O)n ; n=3, 4, 5, 6
what are monosaccharides made?
two or more hydroxyl groups
how are monosaccharides created?
aldehydes and ketones react with the hydroxyl group closing the ring and creating a cyclic structure in aqueous solution.
what are isomers?
same formula, different atom arrangement
(arrangement matters to the cells)
what creates a disaccharide?
it is created when the carbon that carries the aldehyde or the ketone can react with any hydroxyl group on a second sugar
what are characteristics of oligosaccharides?
linear and branched molecules made from simple repeating sugar units, short chains less than 10 units (<10)
what are the characteristics of polysaccharides?
linear and branched molecules made from simple repeating sugar units, long chains greater or equal to 10 units (≥10)
what are fatty acids made of?
carboxyl group at one end and long hydrocarbon on other
if there is a double bond in hydrocarbon tail, it is unsaturated
no double bonds are saturated
what are triacylglycerols?
stored fatty acids, energy reserve, Esther linkage forms to glycerol
what are peptide bonds?
bonds that link amino acids together through amide linkage
proteins are longer polymers, peptides are shorter polymers
what are nucleotides?
subunits of nucleic acids
consists of :
nitrogen containing base, 5-carbon sugar, phosphate group
what are the nomenclatures for Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Uracil, Thymine?
Base Nucleoside Abbrv
Adenine Adenosine A
Guanine Guanosine G
Cytosine Cytidine C
Uracil Uridine U
Thymine Thymidine T
what bonds are nucleic acids joined with?
phosphodiester bonds
what are catabolic reactions?
breaking down of LARGE molecules to SMALL to create energy. (polymer —→ monomers)
energetically favorable
what are anabolic/ Biosynthetic Reactions?
uses energy to build LARGE molecules from SMALL molecules. (monomer —→ polymer)
energetically unfavorable
what is metabolism?
the total sum of both the catabolic and anabolic reactions (m=c+a)
what is the 1st law of thermodynamics?
energy CANNOT be created or destroyed
energy can be converted to another form of energy and transferred to another location
heat is a form of energy
follows the principle of energy conservation
what is kinetic energy?
the energy of motion
what is potential energy?
energy because of position
what is the energy conversion principle?
potential energy —> kinetic —> heat energy
true or false: universe is a closed energy system-no exchange of energy with surroundings
true
what is the 2nd law of thermodynamics?
in any isolated system, the degree of disorder can only increase
spontaneous change towards arrangements with greatest probability
arrangements with greatest probability are more disordered
what is entropy?
measure of disorder of a system
disorder more likely than order
how are living cells related to the 2nd law of thermodynamics?
living cells must take in some types of energy, uses the energy to create order within itself with many chemical reactions specified to create order
some energy is converted to heat energy, following the 2nd law of thermodynamics
what is heat energy?
disordered form of energy, random movement of molecules.
heat is quickly dispersed into the cells surrounding causing more motion and chaos
what is photosynthetic process?
the energy of sunlight is absorbed by the plants, algae , and some bacteria
the plants, algae, or bacteria takes in H2O and CO2 that is expired by living organisms to create sugars, O2, and other organic molecules
O2 is respirated by most living organisms who expire CO2
respiration is useful energy for cells
cycle gets repeated
what is oxidation?
L: loss of
E: electrons
O: oxidations
O: oxidation
I: is
L: loss of electrons
what is reduction?
G: gain of
E: electrons
R: reduction
R: reduction
I: is
G: gaining of electrons
what are energetically favorable reactions?
downhill reactions, release of energy, hydrolysis
what are energetically unfavorable reactions?
uphill reactions, intake of energy, condensation
what is activation energy?
initial input of energy to give a boost over the energy barrier
what are enzymes?
biological catalyst
reduces the activation energy needed for reactions
enzymes are the most effective catalyst
speeds up reactions 1014 times faster than without a enzyme
the activation energy is aided by enzymes
chemical reactions would not occur without enzymes
highly selective with an active site
what is the relationship between enzymes and substrates?
substrate bonds to active site on enzyme
both must collide with each other for reaction to occur
1000 reactions per second
increased substrate concentration = increased rate of reaction until enzyme is saturated
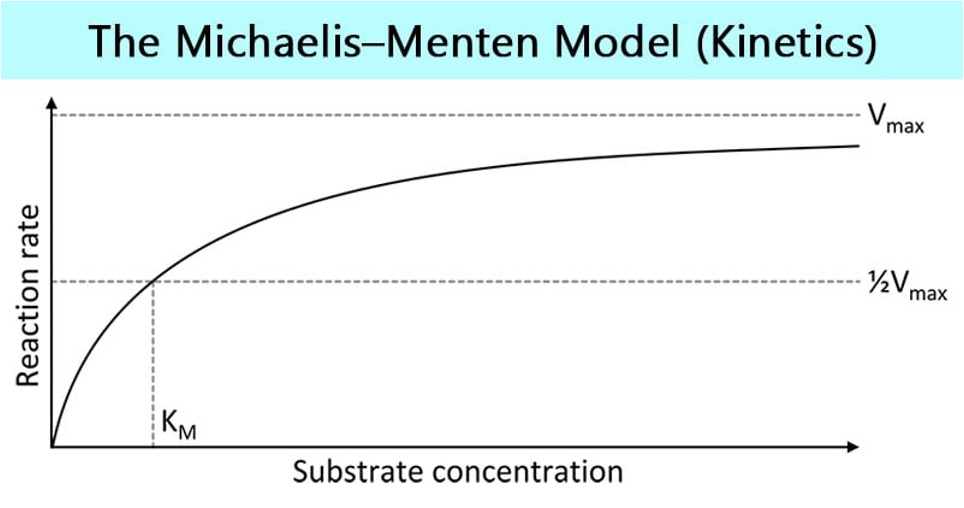
what is the Michaelis-Menton Model of Kinetics
Vmax= enzyme is saturated
KM= Michaelis’ constant, substrate value when enzyme is working at ½ Vmax
If lower KM- substrate binds tightly to enzyme
if higher KM- weak binding
what is the equilibrium constant?
[AB]/ [A][B] = Kon/Koff = K + equilibrium constant
what are inhibitors?
they stop or block substrates from binding with a enzyme
what are competitive inhibitors?
inhibitors that block the active site so a substrate can’t bind (compete with substrate for bonding to the enzyme)
what are noncompetitive inhibitors?
inhibitors do not bind directly to the active site, but instead bind to another area on the enzyme causing the enzyme to change shape and the substrate cannot bind
what are cofactors?
nonprotein partners that are essential for function, bind to enzymes and change shape of active site
what are coenzymes?
they are organic cofactors made from water-soluble vitamins and it transfers electrons between enzymes
what is a allosteric enzyme?
enzymes that change shape with binding of an effector
what is a allosteric site?
the site where the inhibitor or activator binds
what is a allosteric inhibitor?
a substrate that binds to the allosteric site to inhibit enzyme activity
what is a allosteric activator?
a substrate that binds to the allosteric site to activate enzyme activity
what is energy coupling? (hardest part of test apparently)
enzymes cannot force unfavorable reactions
cells need energetically reactions to occur to grow, divide, and live
occurs when the energy produced by one reaction or system is used to drive another reaction or system
what is a exergonic reaction?
has less free energy, favorable, is spontaneous
what is a endergonic reaction?
has more free energy, unfavorable, less spontaneous
what goes first, exergonic or endergonic?
exergonic goes first
what is the equation for free energy?
(ΔG) = (+ΔG) + (-ΔG)
(ΔG)= free energy
what are activated carrier molecules and some examples?
energy that is stored as a chemical bond energy in a carrier molecule
molecules readily diffuse through the cell and carry their bond energy with them to release at another faction of the cell
ex: NADH, NADPH, ATP
what are the characteristics of Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP)?
technically a nucleotide
very abundant
does cellular work
10,000,000 ATP molecules are used and generated per sec in each cell
ATP transfers terminal phosphate to another molecule in phosphorylation reaction
ATP used to power the pumps in membrane transport
30% of ATP is used by the sodium pump
breaks down food in the body
why is ATP so important?
ATP takes metabolized food molecules and delivers the energy that is needed to power cell reactions throughout the cell
what is NADH?
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
catabolic, energy favorable
intermediate in catabolic system of reactions that generate ATP through oxidation
what is NADPH?
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
anabolic/biosynthetic, energy unfavorable
works with enzymes to catalyze anabolic reactions
what are NADH and NADPH?
cofactors that carry high energy electrons and hydrogen atoms.
exam questions: what is the hypothesis of the article?
UCYN-A is becoming a nitrogen fixing organelle in marine alga
exam questions: what were the findings from the article?
UCYN-A lost its genome size causing shrinking
a criteria of organelle is to be in sync with the rest of the cell. UCYN-A has synchronized with its “host” cell, B. bigelowii making it one step closer to being a organelle
proteins cannot be made in genome
UCYN-A can be taken encoded by the marine alga
exam questions: what were the weaknesses from the article?
really strong language for results but not strong enough for the information
redox reaction has indications but doesn’t know the mechanism. didn’t word it with the “standards”
a lot of unknown
title is off
abstract is off from the actual paper
vagueness on data but over done conclusion
exam questions: what was the conclusion of the article?
suggests UCYN-A is going through evolution to become a nitrogen fixing organelle, nitroplast