7. HYDRATION AND EXERCISE
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
what is the most abundant substance in the body
water
how much of the body is made up of water?
45-75%
distribution of water in the body depends on what 3 things?
age
sex
body composition
how does age impact water in the body
% of total body water decreases with age
how does sex impact water in the body
males typically have more body water than females (higher FFM)
how does body comp impact water in the body
muscle has more water than fat
muscle is ______% water
65%
fat is _% water
10-40%
what are the 4 functions of water in the body?
universal solvent
transport
lubricant
regulation of body temperature
water as universal solvent (what does it do, this mean?)
critical for majority of bodily processes including digestion, pH balance, and enzymatic reactions
water as transport for what (function)
water is the medium for the transport of oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to cells throughout the body.
water is also critical for what bodily function
removal of waste
water as a lubricant (what body parts)
joints, eyes, mouth, intestinal tract
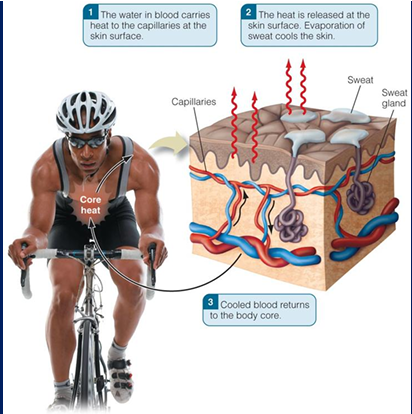
how does water function in body regulation (key word)
water is critical for regulating body temperature through sweating
how does water help regulate body temp? (3 steps)
Water in blood carries heat to the capillaries at skin surface
The heat is released at the skin surface. Evaporation of sweat cools the skin.
Cooled body returns to the body core
what 3 things contribute to water intake?
metabolism, food, fluid
how much does it contribute to water intake? (ml)
metabolism
food
Drinks
metabolism= 300 ml
food= 700 ml
beverages= 1,500 ml
total—> 2,550 ml
what organs contributes to water output (4)
intestines, lungs, kidneys, skin
amount of water released (ml)
intestines (stool)
lungs (breathing)
kidneys (urine)
skin (sweat)
intestines (stool): 100 ml
lungs (breathing): 350 ml
kidneys (urine): 1,500 ml
skin (sweat): 600 ml
what is the most variable output of water?
sweat
define hyperhydration
fluid intake > fluid loss
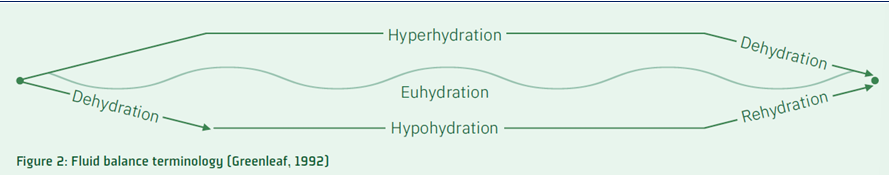
define euhydration
fluid intake = fluid loss
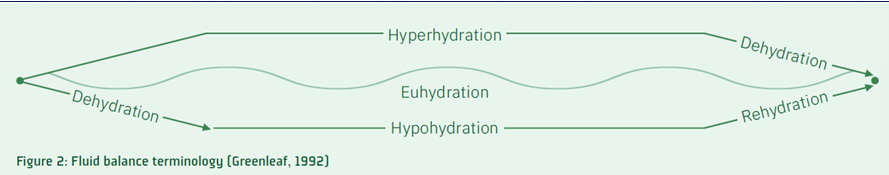
define hypohydration
fluid intake < fluid loss
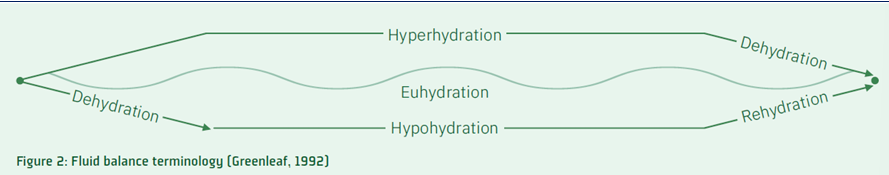
define dehydration
process of losing body water
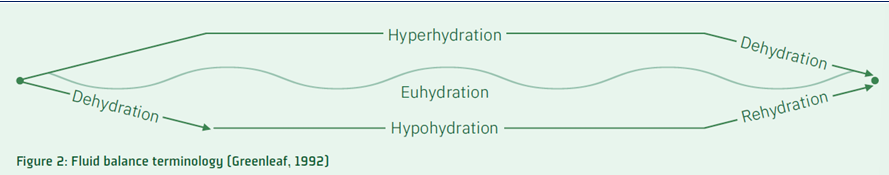
define rehydration
process of replacing or regaining body water
define hydration**
is process that starts with the ingestion of fluid, followed by emptying from stomach and absorption through intestines, then distribution of the fluid throughout body and finally retention or excretion by kidneys
4 steps of hydration:
fluid intake
fluid absorption
fluid distribution
fluid retention
fluid intake is __% from beverages?
70-80%
fluid intake is __% from foods
20-30%
what types of foods contribute a lot of water?
fruits and vegetables
define hypovolemia
decrease in the amount of water in the blood
when is physiological thirst stimulated?
by decrease in the amount of water in the blood (hypovolemia) and increase in plasma osmolality
during exercise, what occurs (relating to water content)
both hypovolemia and increased plasma osmolality occur during dehydration due to sweating
it is very important to note that physiological thirst occurs once
body is already dehydrated
threshold for thirst and body hydration
Threshold for thirst lags behind body hydration changes
how does thirst occur? (5 steps)
sweat loss decreases plasma volume, increasing plasma osmolality (increase Na and Cl)
baroreceptors sense changes and stimulate ADH (vasopressin)
kidneys conserve water and sodium
thirst centers triggered
drinking helps restore levels
what does sweat loss do to blood?
↓ plasma volume, ↑ plasma osmolality (plasma Na+ and Cl- ↑↑)
what senses changes in plasma volume and osmolality?
baroreceptors
what do baroreceptors do?
release ADH (vasopressin)
as a result to ADH, what occurs
kidneys conserve water and sodium
conservation of water and sodium from the kidneys causes what
thirst centers to be triggered causing thirst
what helps restore plasma levels?
drinking fluids
what is mild dehydration (% weight loss)
< 2% weight loss
mild dehydration effects on performance
typically has no deleterious effects
what conditions may dehydrate athlete by >2-3% of body weight
prolonged vigorous intensity exercise ( > 2 hours) in warm temperatures (> 85 F)
prolonged vigorous exercise in warm temps (>85F) effect on performance?
can significantly impair performance
prolonged vigorous exercise in warm temps (>85F) impairs performance due to? (2)
increase H2O and electrolyte loss
what is considered significant dehydration (% weight loss)
>2%
Significant dehydration (> 2% body weight losses) has been found to impair
performance in the heat
in what conditions has significant dehydration (3-4% body weight loss) seen to impair aerobic performance, as well as cognitive performance and technical skill in certain team sports
cooler conditions…
at what temps is performance seen to be impaired?
>85F
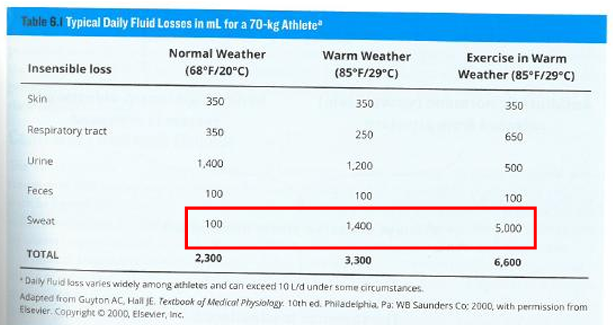
Exercise in warm weather ( > 85 F) impact on fluid?
increases fluid losses (x 50)
how should fluid goals for athletes be set
ALWAYS individualized (not one amount for everyone)
fluid needs differ based on (5)
genetics
body size
body composition
exercise habits
environmental conditions
DRI reccs for water in (AI)
men
woman
Adequate intake (AI) in men 3.7 L/day (16 cups per day)
Adequate intake (AI) in women 2.7 L/day (12 cups per day)
what is important to note regarding fluid intake
these values can be met from a variety of foods and fluids (not just fluid)
for athletes, guidelines for fluid before exercise?
5-7 ml/kg 2-4 hours before execise
how to calculate fluid needs before exercise
______kg x 5mL = _______ mL
_____kg x 7mL = ______ mL
needs= ___________ to ________ mL
fluid intake during exercise depends on
sweat rate
general guideline for fluids during exercise
0.4-0.8 L/h
guidelines recommend ingestion of what with water
sodium (to reduce sweat losses)
after exercise guidelines?
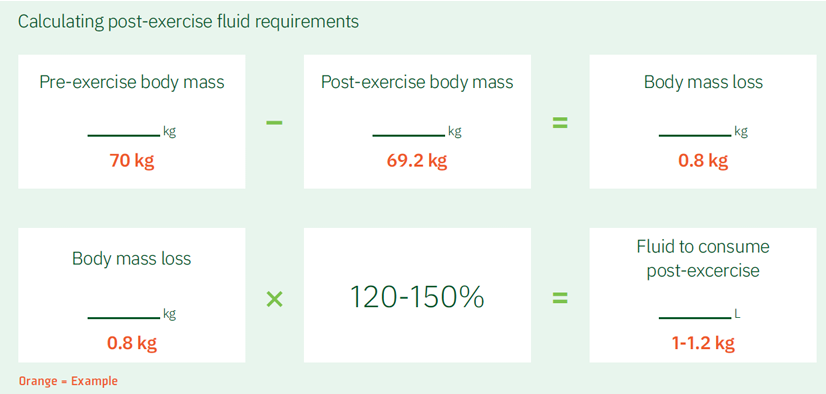
1.25-1.5 L fluid for every 1 kg lost during exercise
fluid intake during exercise has the goal to **
limit dehydration to 2% of body mass
after exercise, you want to replace fluid losses by (%) if dehydration is severe/rapid hydration needed
120-150% of body mass loss
beneficial response to adequate fluid intake durig intake (4)
↓ Heart rate
↑ stroke volume and cardiac output
↑ skin blood flow and ↓ core temperature
↑↑↑ performance
benefits for fluid intake during exercise are seen when
dehydration is minimized
minimal dehydration is defined as
<2% decrease in body weight
fluid intake choices 4 hours prior to exercise?
Gatorade, Powerade, water, fruit juice
when may coffee serve as good pre-exercise fluid
1 hr before (studies show a bit of caffeine can improve performance)
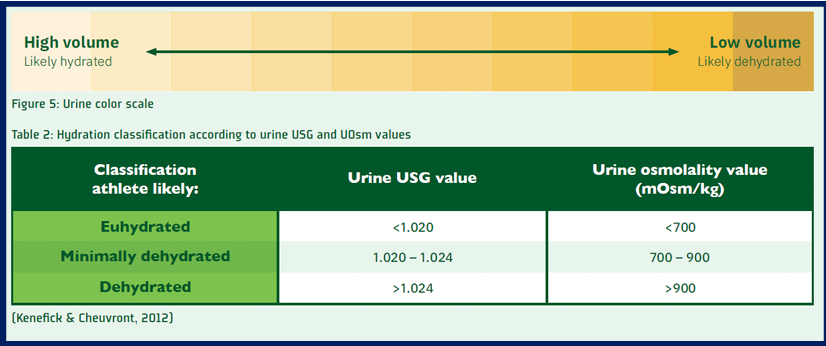
what can be used to determine hydration status prior to exercise/ start of exercise (2)
urine color OR urine specific gravity test
athletes should have _____________ fluid intake plans
customized
simple approach for fluid needs is to do what?
record body weight before and after exercise
weight loss means (in terms of fluid needs)
inadequate drinking
weight gain means (in terms of fluid needs)
excessive drinking
advanced approach for fluid needs involved what 3 things
make calculations based on weight, fluid intake, urine output
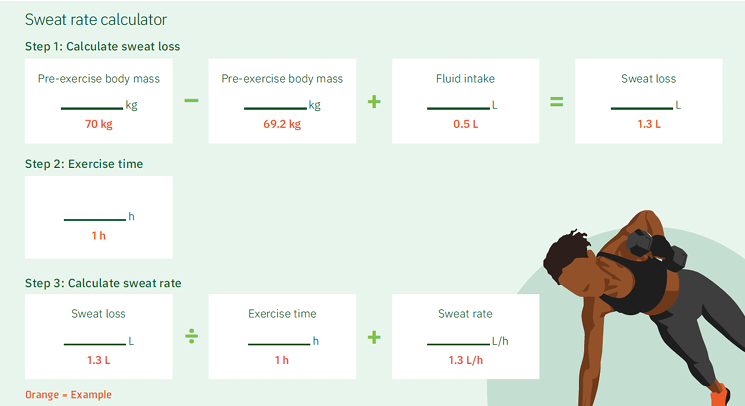
calculating sweat rate math
Charlotte cycles for 3 hours in Houston in summer. Her pre-exercise body weight is 65 kg and her post-exercise body weight is 63 kg. She drank 500 ml of fluids during her ride and did not go to the bathroom. What was her hourly sweat rate?
∆ body weight = 65 kg − 63 kg = 2 kg
2,000 g + 500 ml of fluids = 2,500 ml of sweat lost during the ride
2,500 ml / 3 hours = 833 ml per hour or 13.9 ml/min
during exercise drinks (for most athletes)
Powerade, Gatorade, water is just fine (90% of time)
when exercise is >2.5 hrs, what drinks can be useful
60-90g of multiple transporter carbs containing fluid
symptoms of dehydration?
Increased thirst and presence of dry mouth
Little or no urine output
Dark, concentrated urine
Fatigue, confusion, headaches
Muscle cramps
Chills → can be a sign of heat stroke
post exercise, we want to replenish fluid losses to how much
120-150%
post exercise fluid needs math
post exercise fluid choices
water, Gatorade, Powerade, milk
why is milk a good post exercise fluid?
contains protein, fat, and electrolytes
what are electrolytes ** (what minerals)
sodium, chloride, potassium, calcium and magnesium
functions of electrolytes (4)
regulating fluids in the blood plasma
blood pH
enabling muscle contractions
nerve conduction
sweating effects which electrolytes
sodium and chloride (rest is minimal loss)
electrolyte loss due to sweating can lead to what?
severe muscle cramping and hyponatremia
what is hyponatremia
Low sodium levels in the blood (< 135 mEg/L)
symptoms of hyponatremia
Fatigue, headache, confusion, nausea + vomiting, muscle cramps and spasms
hyponatremia has similar symtoms to what?
dehydration (which makes it hard to know / detect)
what causes hyponatremia in athletes?
Syndrome of inappropriate anti-diuretic hormone (SIADH) (high levels of ADH) combined with intake of too much water or fluids
what general things cause hyponatremia (not relating to exercise or sweat)
medications (diuretics), severe diarrhea or vomiting
athlete-related risk factors for hyponatremia include (6)
Excessive drinking
Weight gain during exercise
Low body weight
Female sex
Slow running pace
Inexperienced runners
event related risk factors for hyponatremia include (4)
High availability of drinking fluids
> 4 hour exercise duration
Unusually hot conditions
Extreme cold temperatures
what is recommended for athletes at risk for hyponatremia (before exercise)
do not overconsume fluids
what is recommended for athletes at risk for hyponatremia (during exercise)
Drink to thirst. Beverages containing sodium at aid stations
what is recommended for athletes at risk for hyponatremia (after exercise)
Hypertonic saline solutions to ↓ risk of symptomatic hyponatremia following exercise
what should be a focus post exercise to reduce risk of hyponatremia?
electrolyte replacement sources —> food and beverages containing sodium
for marathon races in hot climates, what is recommended pre (1)during the race race?
Pre-race nutrition and hydration should be optimal
Probably need 0.8 – 1.0 L/hour of fluids during the race with additional sodium
60 – 90 g of CHO per hour in the form of single and multiple transportable CHOs
what is key when exercise will take place in a hot climate that athlete is not used to?
heat acclimation