Utah CNA
1/387
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
388 Terms
Apical pulse
pulse taken with a stethoscope and near the apex of the heart
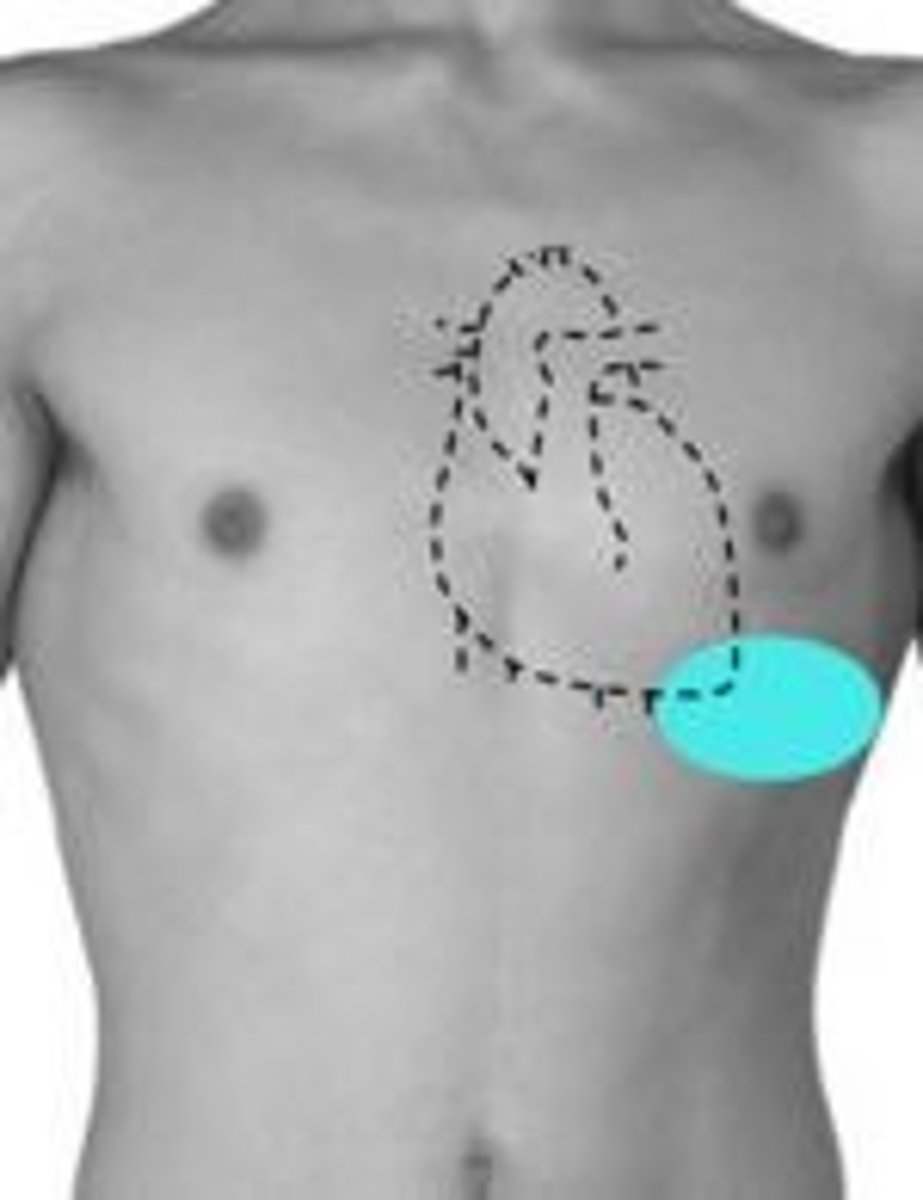
axillary
armpit area
blood pressure
pressure of blood in the circulatory system. closely related to force/rate of heartbeat and diameter/elasticity of arterial walls
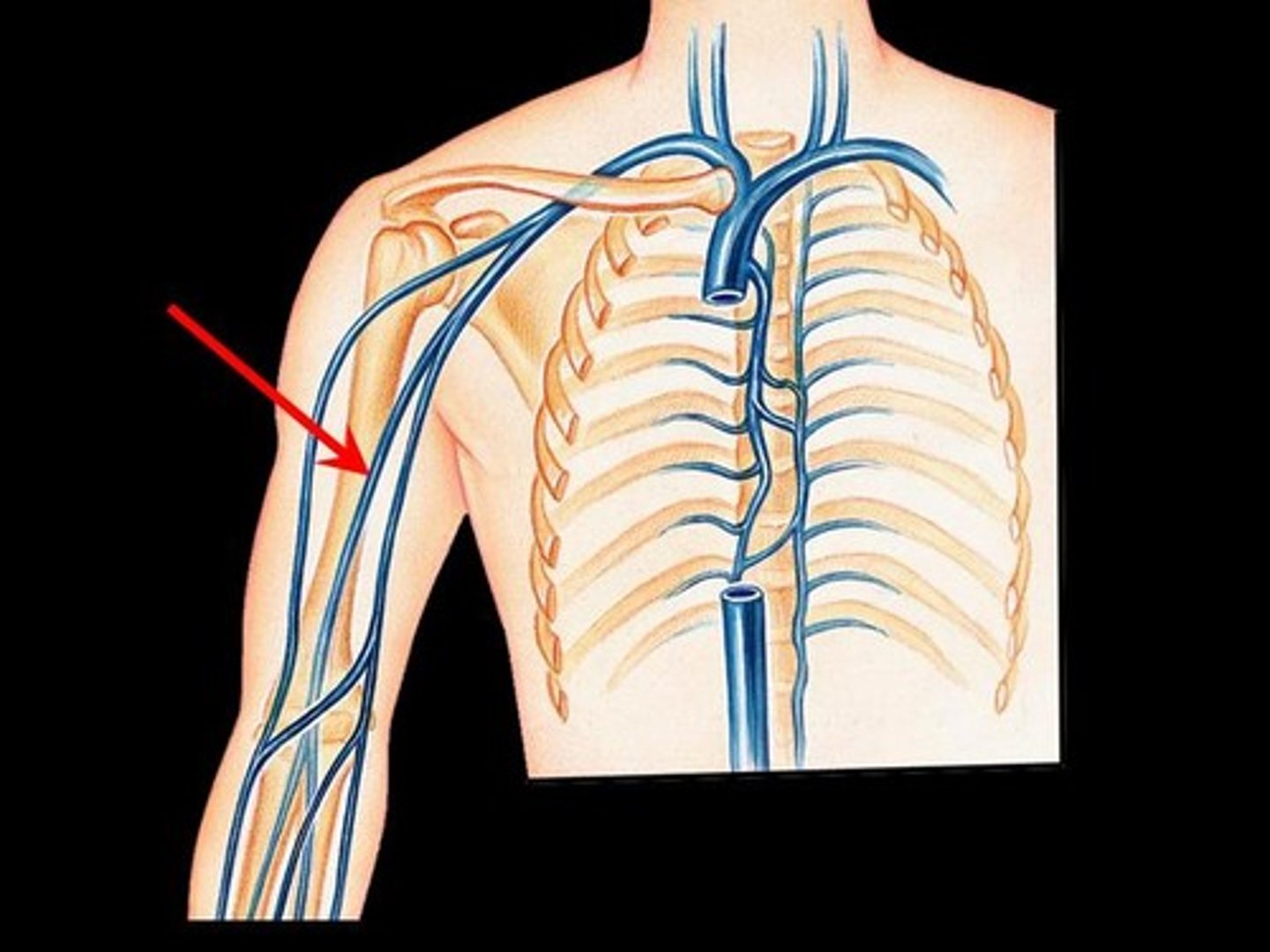
brachial artery
major blood vessel of the upper arm
centigrade
relating to the temperature scale in which the boiling point of water is at 100 degrees and the freezing point of water is at 0 degrees
diastolic
second measurement of blood pressure; phase when the heart relaxes. normal range is 60-80
ear canal
a tube running from the outer ear to the middle ear
Fahrenheit
A temperature scale with the freezing point of water 32 degrees and the boiling point of 212 degrees
hypertension
high blood pressure
hypotension
low blood pressure
pulse
the rhythmical throbbing caused by the regular contraction and alternate expansion of an artery
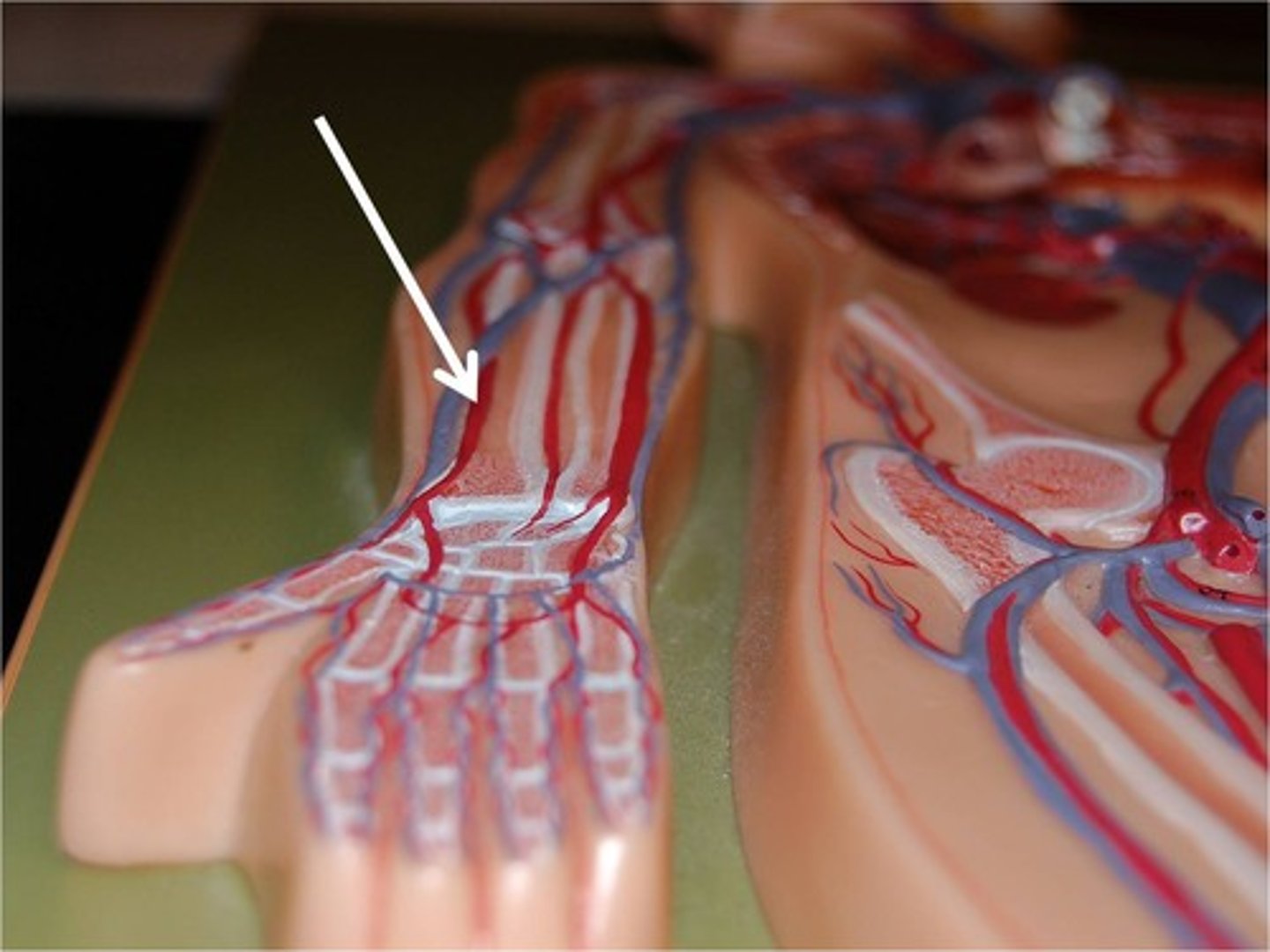
Radial artery
Artery of the lower arm. It is felt when taking the pulse at the wrist.
rectal
pertaining to the rectum (bum)
sphygmomanometer
instrument to measure blood pressure
systolic
first measurement of b/p. pressure in the arteries during contraction of the ventricles. normal range is 100-130
temporal
thermometer placed on temple or forehead
tympanic
Temperature taken in the ear
normal range b/p
130/80
normal range pulse
60-100 bpm
normal range respirations
12-20 breaths per minute
normal range temp oral/tympanic
97.6-99.6
normal range temp rectal
98.6-100.6
normal range temp axillary
96.6-98.6
the 5 vital signs
pulse, respiration, temperature, b/p, pain
oral digital thermometer
blue/green tip; contraindications-tooth damage, <5 y/o; @least 15 min after hot/cold food or beverage
rectal thermometer
red tip; patient should be in left sims or left lateral; most accurate; insert 1/2-1 inch
tempanic thermometer
1/4 to 1/2 inch inside ear; position ear up and back; wait 15-30 min after shower, hearing aid, etc.
temporal thermometer
electronic thermometer measures temperature on forehead
pulse oximeter
top number is oxygen saturation; bottom number is pulse; normal oxygen saturation is 90-100
Febrial
have fever
Afebrial
not have fever
braidy
slow
tacky
fast
dys
difficulty
hyper
high
hypo
low
cardio
heart
tension
blood pressure
pnea
lungs/breathing
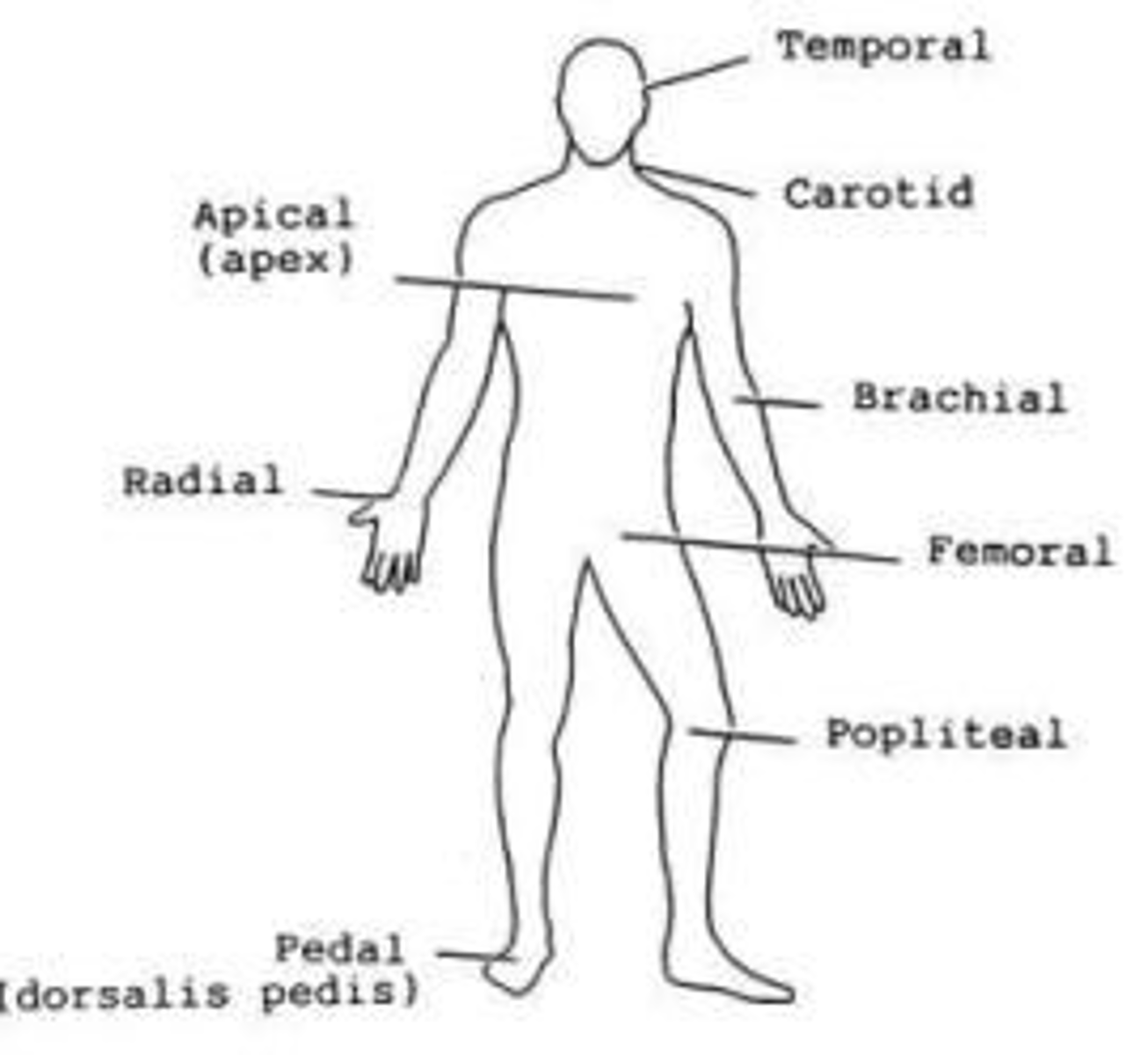
pulse sights
coratid, apical, brachial, radial
pain
the body stress signal or warning sign
LTC
long-term care facility, nursing home; residents usually have chronic condition; have rehab & restorative
hospitals
acute care; patients; specific
home health/hospice
hospice patients expected to die within 6 months; hospice not done in hospitals but are done in LTC, rehab, etc.
Medicare part C requires
treatment, equipment, etc. needs to be deemed medically necessary
Medicare qualifications
65+ y/o
Medicaid qualifications
low income (decided state by state)
health care team
interdisciplinary team
Resident (health care team)
focus of team but also member
doctor (MD or medical doctor)
doctor's orders, prescribe and diagnose
CNA
ADL, vitals, lift/position
PT (Physical Therapist)
mobility/movement
ST (Speech Therapist)
speech, swallowing
nurse in LTC
organizing of care, nurse's care plan
DON
director of nursing
OT (Occupational Therapist)
adaptations, improve functionality, help work w/disability
RT (respiratory therapist)
breathing/lungs
Social worker
social services, psycho-social needs and conflicts
Q
every
QD
every day
QOD
every other day
BID
twice a day
TID
three times a day
QID
four times a day
AC
before meals
OC
after meals
HS
hours of sleep
5 rights of delegation
right task
right circumstance
right person
right direction/communication
right supervision
(meet all requirements!)
HIPAA
A law which includes guidelines for maintaining patient confidentiality/privacy
Focus of OBRA
autonomy
policy
required guideline/rule
procedure
how you are going to do something
misappropriation of property
illegal or improper use of resident's money, property, assets; by another, without consent, for personal gain
legal v ethical
lawful; right vs. wrong
abuse
purposeful and intentional mistreatment
neglect
failure to provide care
assault
unlawful threat
battery
unlawful contact
main types of abuse
physical, emotional, sexual
APS
Adult Protective Services
Incident report
documentation of incident; for the staff's or CNA's legal protection
When does charting need to be done?
right after care is completed. use black ink. cross out error and put correction.
gait belt
transfer belt; safety belt
Ombudsman
resident advocate
MDS
minimum data set; must be completed within 14 days of admittance; keep up to date
most common reason need to fill out incident report
falls
infection control parts
medical asepsis
surgical asepsis
barrier methods
standard precautions
transmission based precautions
medical asepsis
clean; free of pathogens/infection
surgical asepsis
sterile; free of microorganisms
standard precautions
universal precautions; thorough hand wash, PPE, disposal of biohazard waste.
microbe
microorganism found everywhere
pathogen
A microbe that is harmful and can cause an infection
autoclaving
Method of sterilization using steam under pressure
transmission-based precautions
used in addition to standard precautions for patients with suspected infection with pathogens that can be transmitted by
airborne
droplet
contact
CNA also called
nurse aide, patient care tech
liability
someone can be held responsible for harming someone else
All facilities have manuals outlining their policies and procedures. T/F
true
RACE
rescue, alarm, contain, extinguish
PASS
Pull, Aim, Squeeze, Sweep
cyanotic
pale or bluish skin