Laboratory Techniques
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
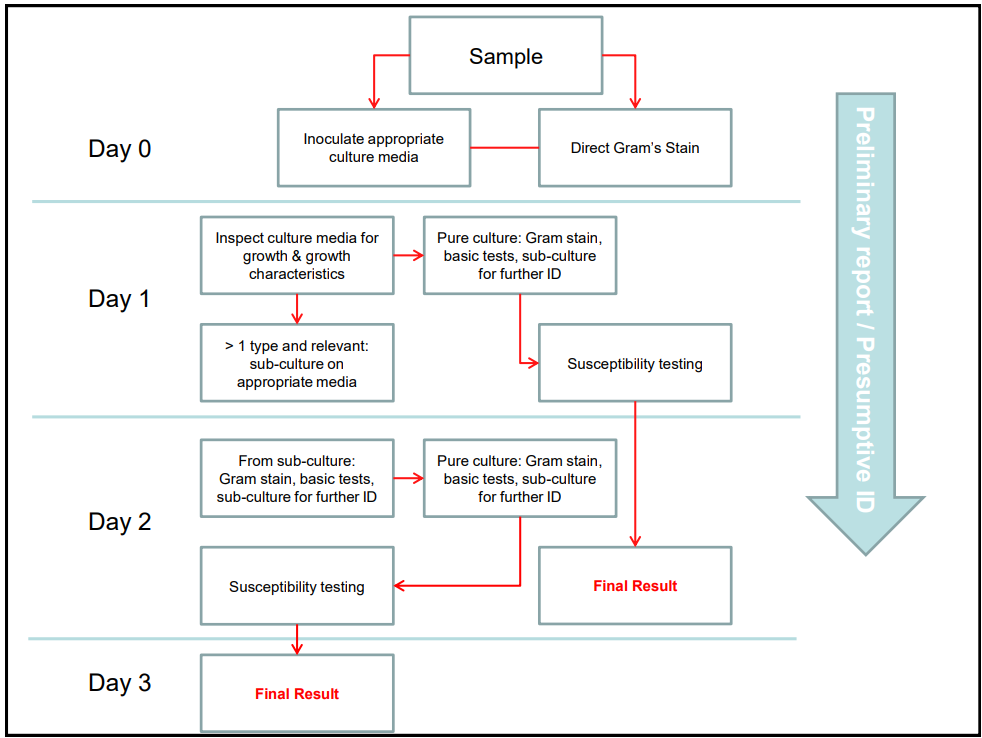
Preliminary report / Presumptive ID (photo)
Typical Samples
Pus swabs/fluid (Wounds)
Other swabs (Nasal, throat)
Sputum samples
Aspirates (Joint, BAL)
Urine samples
Stool samples
Medical devices (IUCD)
Fluids (CAPD)
Aseptic Techniques (10)
Keep caps and lids off the workbench - retain in hand
Replace caps and lids as soon as possible
Place agar media lids facing upwards
After the plates are inoculated, the lids should be replaced
Discard loops - open bench - dispose into sharps bin
Keep samples away from the face when opening culture containers
Wear appropriate PPE when handling cultures
Open caps slowly in a microbiological safety cabinet - minimize aerosol production
Autoclave and sterilize forceps or scissors before use
Use disposable forceps or scissors - dispose into a sharps bin
Subculture from Solid to Liquid (4)
Select a representative colony or colonies to sub-culture
Use aseptic technique to transfer to an appropriate broth* with a sterile disposable loop
Emulsify the organism using the inside surface of the container
Gently agitate before incubation to distribute organisms throughout the broth
Inoculation Techniques
Ensure that culture media are inoculated in a sequence that minimizes the risk of cross-contamination
Liquid media should be inoculated after solid media when swabs and stools are examined
to avoid diluting the organisms present in the sample
Liquid media should be inoculated first when processing fluid specimens
Smears for staining are usually made after all culture media have been inoculated
When the smear is required prior to culture, great care should be taken to avoid contamination
Do not place the loop back into the specimen after touching the slide
Inoculation Techniques Types (6)
Streak Plate Method
Used to isolate a pure colony of a microorganism from a mixed culture
Pour Plate Method
Used to estimate the number of viable microorganisms in a sample (TVC, TCC)
Spread Plate Method
Used for enumeration of microbial populations, especially when counting colonies on the surface of the plate
Stab Inoculation (Deep Inoculation)
Used to inoculate a solid medium to assess microbial growth under anaerobic or aerobic conditions - up&down
Slant Inoculation
Used to grow a culture on a slanted agar surface for long-term storage of microbial cultures
+ for growing microorganisms in a solid medium with a large surface area
solid media is in tube (glass container)
controlled environment + protected to not dry out
Swab Inoculation
Used to obtain confluent growth on a surface medium
for susceptibility testing
for environmental / clinical sampling from surfaces
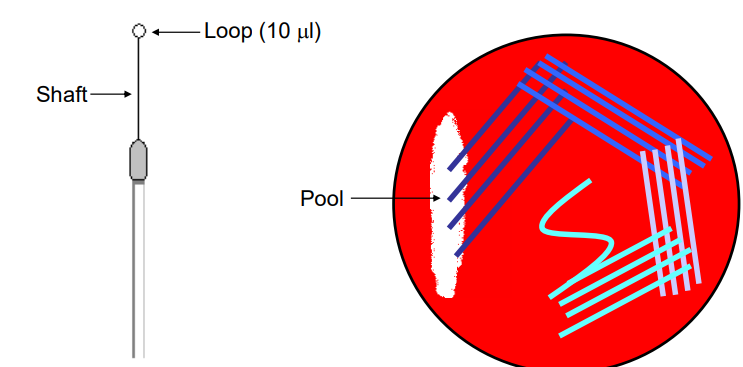
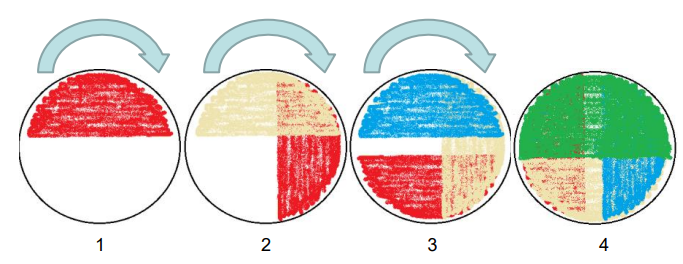
Streaking Agar Plates (3)
swap - create a pool
from pool outwards - pool up back down then up…
from those lines of streak outwards again and again
Uses:
Growth on Culture Media
The streaking technique is used to grow and isolate microorganisms from a mixed culture on solid agar media, enabling colony isolation
Automated Streaking
Use of automated equipment to perform streaking, which ensures consistent and reproducible isolation of colonies
improving laboratory efficiency and reducing human error
Streaking Agar Plates for urine sample steps
carry out count
check growth - if >100 (colony count) + <2 colonies → further testing

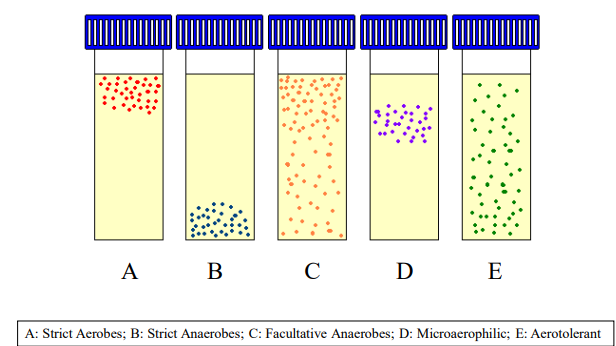
Optimal Atmospheric Conditions (photo)
Strict Aerobes bacterial species
Require oxygen for growth - Aerobic
Haemophilus influenzae
Strict Anaerobes
Cannot tolerate oxygen - anerobic
Bacteroides fragilis
Facultative Anaerobes
Can grow in both aerobic and anaerobic environments - Aerobic & Anaerobic
Staphylococcus aureus
Microaerophilic
Prefer low oxygen levels for optimal growth - Aerobic
Campylobacter jejuni
Aerotolerant Anaerobes
Can survive in oxygen but do not use it for growth - Anaerobic
Clostridium perfringens
Inoculating from Broth Cultures
Transfer the broth culture to the solid medium
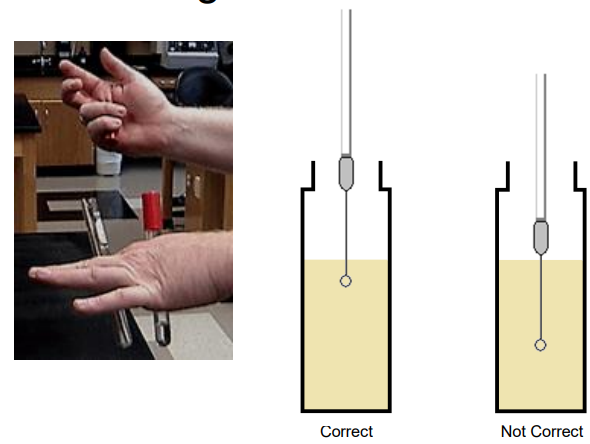
Swabbing Technique
Rotating of the technique results in confluent growth
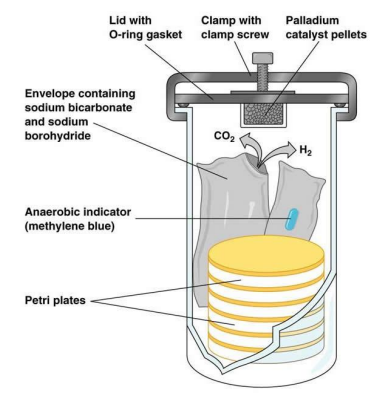
Anaerobic Jar (photo!)
sealed container
Oxygen is eliminated through chemical reactions or gas-generation methods
Palladium catalyst promotes the reaction of hydrogen with oxygen to form water, visible as droplets at the bottom of jar
Indicators (chemical or biological) verify anaerobic conditions
Chemical indicator:
White: Reached anaerobic conditions
Blue: Anaerobic conditions not reached
Biological:
Strict Aerobe:
No growth
anaerobic conditions have been reached
Weak Aerobe
Growth
not reached
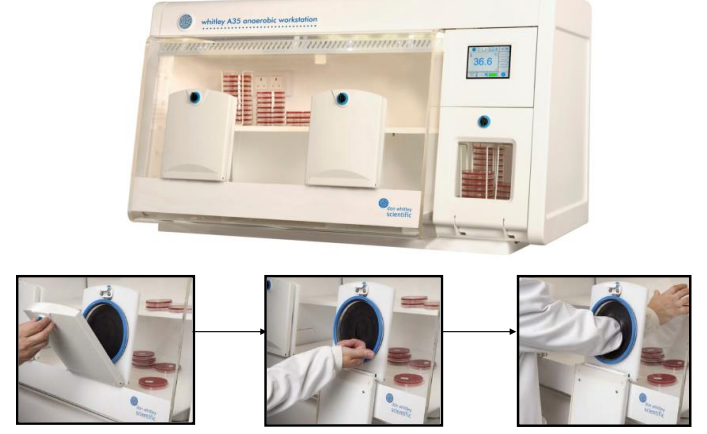
Anaerobic Incubator (4)
Provides an oxygen-free environment for cultivating anaerobic bacteria
Equipped with gas controls for nitrogen, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide levels
Includes temperature regulation to optimize bacterial growth conditions
Prevents oxygen exposure during incubation to maintain anaerobic conditions
CO₂ Generating Incubator (4)
Provides a controlled environment with adjustable CO₂ levels to support the growth of microorganisms and cell cultures
Maintains stable temperature, humidity, and CO₂ concentrations to mimic physiological conditions
Used primarily for growing fastidious organisms requiring specific CO₂ levels
Equipped with CO₂ sensors for precise monitoring and adjustments

Identification of Bacteria (9+6)
Microscopy
Morphology - arrangement, cocci, bacilli
Staining reactions - positive/negative
Cultural Characteristics
Colonial growth
Morphology
Size, shape of colony, edge, elevation
Changes brought to the culture medium
Haemolysis, pigmentation
Ability to grow on certain/specific media
Presence of bile, antibiotics
Growth on special media
Selective (e.g., DCLS)
Differentiating (e.g., MSA)
Biochemical characteristics
Carbohydrate fermentation
Serological tests
Analysis of metabolic end products
Identification of anaerobes
Molecular biology techniques
Growth characteristics*
Growth characteristics - Identification of Bacteria
Rapidity (18 to 24 hours, 72 hours)
Optimal atmospheric conditions
Anaerobes
Strict anaerobes (Bacteroides fragilis)
Aerotolerant (Clostridium perfringens)
Facultative anaerobes (Staphylococcus aureus)
Strict Aerobes (Haemophilus influenzae)
Microaerophilic (Campylobacter jejuni)
Optimal temperature
Psychrophiles
Mesophiles
Thermophiles
Microscopy Morphology
Determines bacterial shape and arrangement
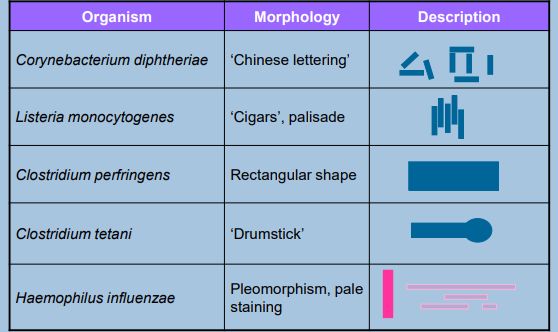
Microscopical Morphology (G+C) (photo!)
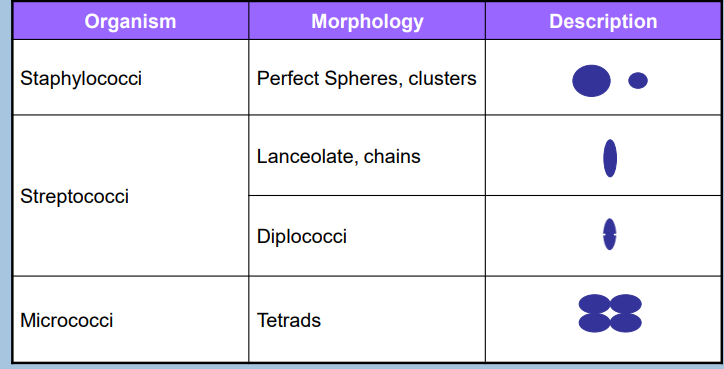
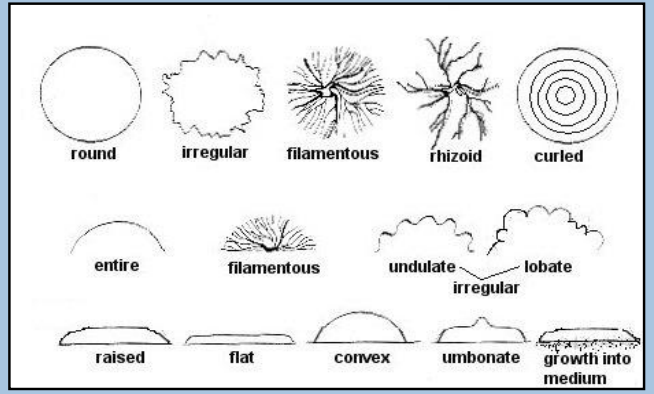
Description of Colonies (photo!)
Pleomorphism definition
Bacteria of the same species show different shapes and sizes
Bacterial Colony Characteristics (3)
Umbonate
raised, convex center that looks like a dome
fx.: Staphylococcus aureus
Filamentous
Thread-like, branching
fx.: Nocardia species*
Draughtsman
Irregular, lobate edges resembling a draughtsman's pattern
Lobe-like morphology
fx.: Streptomyces species
Mucoid Colonies (3)
Shiny, sticky, due to polysaccharide capsule
Helps in virulence and immune evasion
fx.: Klebsiella species

Swarming Colonies (4)
Concentric rings formed by flagellar motility
Enhanced black edges for contrast
Associated with rapid movement across agar
fx.: Proteus species
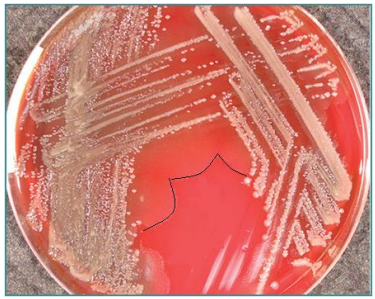
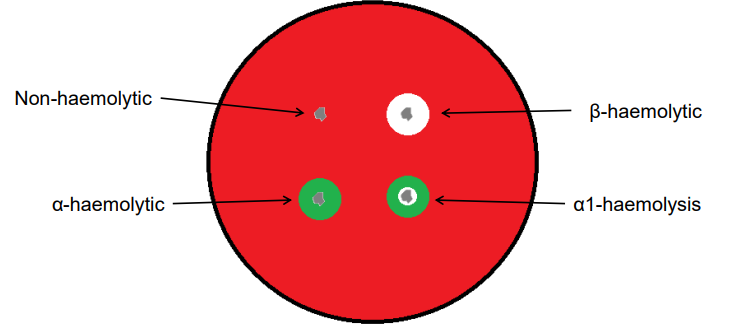
Haemolysis definition
The breakdown of red blood cells, which can be observed when bacteria produce enzymes that lyse red blood cells in agar media
Alpha-haemolysis (α-haemolysis)
Partial breakdown of red blood cells, creating a green or brown discoloration around the colony
Fx.: Streptococcus pneumoniae
Beta-haemolysis (β-haemolysis)
Complete breakdown of red blood cells, leading to a clear zone around the colony due to the full lysis of the cells
Fx.: Streptococcus pyogenes
green - partial distraction
Beta - complete distraction