AS 3.1.1.1-3.1.1.5 Economic methodology and the economic problem
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
what do consumers do?
Consumers are assumed to act rationally. They do this by maximising their utility
what do producers do?
Producers are assumed to act rationally. They do this by selling goods/services in a way that maximises their profits
what do the goverment do?
Governments are assumed to act rationally. They do this by placing the interests of the people they serve first in order to maximise their welfare
what do workers do?
Workers are assumed to act rationally. They do this by balancing welfare at work with consideration of both pay and benefits
what is a normative statement?
These judgements are built around opinions and beliefs as to what the best economic policies or solutions
Normative economic statements are often the basis for the manifestos of political parties and the different economic agendas they put forward
eg.
very economy should aim to provide free healthcare for its citizens
Corporation taxes in an economy should be higher than personal income taxes
The best way to deal with a rise in crime is to employ more police
what is a positive statement?
These positive economic statements are based on empirical evidence and tend to be statements of fact
They can be proven to be true or false
e.g
The unemployment rate in India has fallen from 8% to 7.3% in the past twelve months
Increasing the minimum wage last year in the UK resulted in improvements to wage inequality
Prices in the EU have risen dramatically, partly due to the 20% increase in the price of oil
what is refutation?
Refutation is the act of a statement or theory being proved to be wrong by the empirical evidence
Refutation helps to determine if an economic statement is positive
what is the principle of ceteris paribus?
It allows economists to simplify and explain causes and effects, even if the explanation is somewhat limited by the assumptions
E.g. There are many factors that affect the level of unemployment in an economy (interest rates, consumer confidence, firms' investment, government policies, etc.). Using ceteris paribus, economists can simplify the economic model to analyse just two variables (e.g. unemployment and interest rates)
what are value judgments?
Value judgments influence governments' choices with regard to the economic policies they choose to adopt and spend money on
what are needs?
Needs are essential for survival, eg. food and shelter
what are wants?
Wants are desires for goods and services that are not essential, eg. electronics
what is the purpose of economic activity?
The purpose of economic activity is to take inputs, add value to them, and create products which meet customer needs and wants
what are the three fundamental questions of economics?
What to produce? As resources are limited in supply, decisions carry an opportunity cost. Which goods/services should be produced, e.g. better rail services or more public hospitals?
How to produce it? Would it be better for the economy to have labour-intensive production so that more people are employed, or should goods/services be produced using machinery?
Who to produce it for? Should goods/services only be made available to those who can afford them, or should they be freely available to all?
factors of production
land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship
what is land?
Non man-made natural resources available for production
what is labour?
The human input into the production process
what is capital?
Capital is any man-made resource that is used to produce goods/services
E.g. Tools, buildings, machines and computers
what is enterprise?
Enterprise involves taking risks in setting up or running a firm
what is a free market ?
a market economy with no government intervention
what are factor markets?
a market where factors of production are bought and sold
what is opportunity cost?
Opportunity cost is the loss of the next best alternative when making a decision
Due to the problem of scarcity, choices have to be made about how to best allocate limited resources amongst competing wants and needs
what is the production possibility frontiers (PPF) curve ?
is an economic model that considers the maximum possible production (output) that a country can generate if it uses all of its factors of production to produce only two goods/services
draw a PPF curve
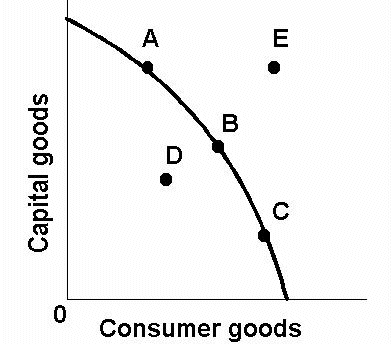
explain the PPF curve?
The use of PPC to depict the maximum productive potential of an economy
The curve demonstrates the possible combinations of the maximum output this economy can produce using all of its resources (factors of production)
At A, its resources are used to produce only consumer goods (300)
At B, its resources are used to produce only capital goods (200)
Points C and D both represent full (efficient) use of an economy's resources as these points fall on the curve. At C, 150 capital goods and 120 consumer goods are produced
the use of PPF curve to depict opportunity cost
To produce one more unit of capital goods, this economy must give up production of some units of consumer goods (limited resources)
If this economy moves from point C (120, 150) to D (225, 100), the opportunity cost of producing an additional 105 units of consumer goods is 50 capital goods
A movement in the PPC occurs when there is any change in the allocation of existing resources within an economy such as the movement from point C to D
what is productive efficiency?
it is the maximum output that can be produced from the available factors of production to produce goods and services
There is no wastage of scarce resources
what is allocative efficiency?
Makes the best possible use of scarce resources to produce the combinations of goods and services that are optimal for society, thus minimising resource waste
what does it mean if the PPF curve shifts inward?
inward shift means economic decline.
Economic decline occurs when there is any impact on an economy that reduces the quantity or quality of the available factors of production
what is economic decline?
Economic decline occurs when there is any impact on an economy that reduces the quantity or quality of the available factors of production
what does it mean when there is an outward shift on the PPF curve?
outward shift means economic growth
This shift is caused by an increase in the quality or quantity of the available factors of production
what is economic growth?
Economic growth occurs when there is an increase in the productive potential of an economy
This is demonstrated by an outward shift of the entire curve. More consumer goods and more capital goods can now be produced using all of the available resources
define resource
is an input used in production
define the term ‘scarce resources’
a ‘scarce resource’ refers to a factor of production or input that has associated opportunity costs, where the demand for it exceeds the available supply and it is utilised in the production process.
eg. due to a lack of medical engineers there have been many constraints in the advancements eg. cancer treatments.
define pure market economy
an economic system where the government has little to no involvement, and the prices and allocation of resources are determined by supply and demand.
In a pure market economy, private individuals and businesses own the resources, and they decide what to produce based on profit.
define mixed economy
an economic system that combines elements of a free market and a planned economy, with some government intervention and some private ownership.
Mixed economies typically accept private ownership of most means of production, with some government intervention, mainly through regulations.
define planned economy
an economic system in which industry is controlled by the government and the government makes all decisions about what to do with the money made.