UNIT 1 AP MACRO
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topic 1.1 Scarcity Topic 1.2 Opportunity Cost and the PPC Topic 1.3 Comparative Advantage and Trade Topic 1.4 Demand Topic 1.5 Supply Topic 1.6 Market Equilibrium
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
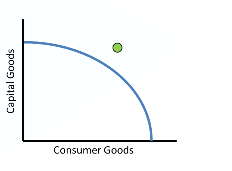
Where on the PPC do you find a productively efficient level of output?
Anywhere ON the curve.
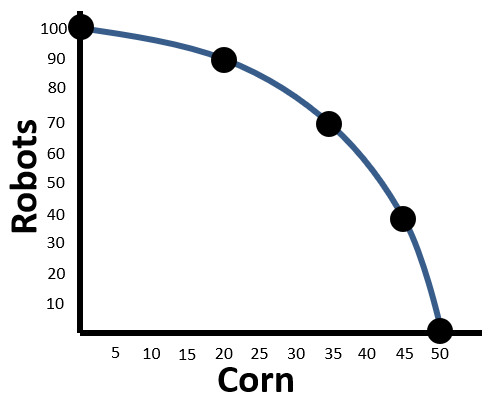
What is the law of supply?
Producers will offer higher quantities of a product for sale when prices are high and lower quantities of a product when prices are low.
What is the definition of Opportunity cost?
The value of the best alternative not chosen, it is the cost of a CHOICE.

What is the Income effect
When prices rise, the purchasing power of a consumer’s income decreases. This is one of the reasons for the downward sloping demand curve. As prices rise, consumers cannot afford as many units.
How do you find mutually beneficial Terms of Trade after calculating Comparative Advantage?
One unit of good A will be traded for an amount between the two countries’ opportunity costs for producing one unit of good A.
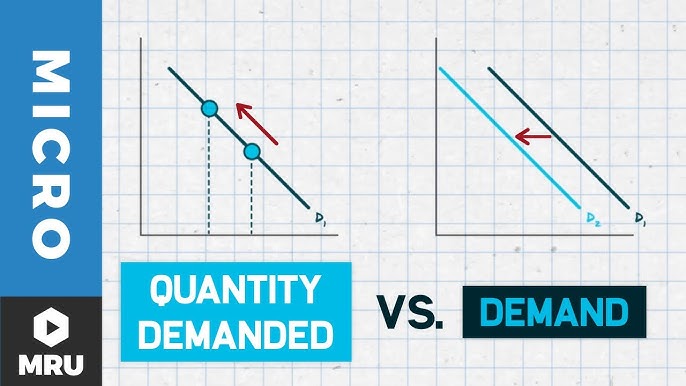
What changes quantity demanded?
Price changes quantity demanded but price does not change demand.
What are the 4 resources?
Land, Labor, Capital, and Entrepreneurship.

What changes demand?
Consumers tastes, market size, income (inferior and normal goods), Prices of related goods (complements and substitutes), and expectation of the future.
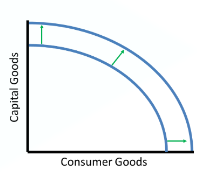
How will an increase in the quality or quantity of resources impact the PPC?
It will shift the curve outward. It will be possible to produce more capital goods and consumer goods.
What is the difference between quantity supplied and SUPPLY?
Quantity supplied is the amount of a good or service producers are willing to offer at a specific price( a POINT on the CURVE). Supply is the amount of a good or service producers are willing to offer at all possible prices (the ENTIRE CURVE.
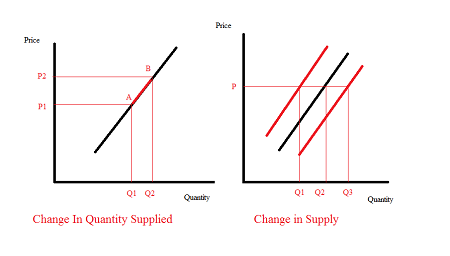
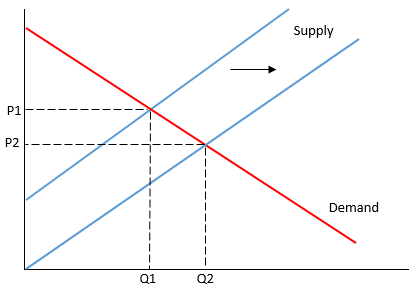
How does an increase in supply impact the equilibrium price and quantity?
Price level decreases and quantity increases.
What is the difference between quantity demanded and demand?
Quantity demanded is an amount of a good or service consumers are willing and able to purchase at a specific price (a point on the demand curve). Demand is the amount of a good or service consumers are willing and able to purchase at all possible prices (the ENTIRE curve).
When outputs are given, what is the formula for comparative advantage?
Other over: The Opportunity Cost of 1 unit of Good A is: B/A
The Opportunity Cost of 1 unit of Good B is: A/B
What is Marginal utility?
A change in total utility for the next unit consumed or the additional satisfaction gained from consuming one more unit of a good or service.
What is the Substitution effect?
When prices rise, consumers substitute similar but cheaper products. This is one of the reasons for the downward sloping demand curve.

How would you explain why a country has a comparative advantage in good A?
They can produce good A with a lower opportunity cost than the other country.
If price is below equilibrium, what economic problem is created? What will happen to price and quantity if there is no intervention?
There will be a shortage (Qs<Qd). Price will eventually rise. Qs will increase and Qd will decrease until equilibrium is reached.
What changes quantity supply
Price changes quantity supplied but does not change supply.
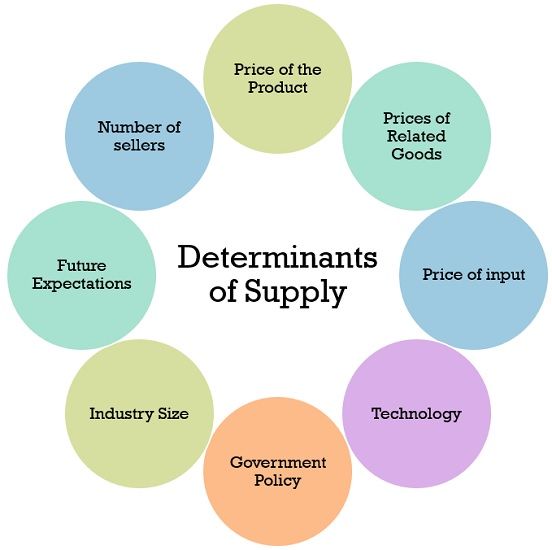
What changes supply?
Determinants of supply-
Price of inputs, market size/number of consumers, technology, government tools (taxes, subsidies and regulation), price of other goods, weather, producer expectations.
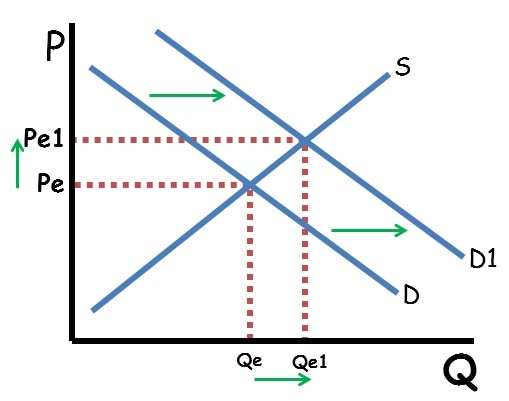
How would you explain why a change in consumers tastes increases price and quantity?
Demand curve shifted to the right.
How does an increase in demand impact equilibrium price and quantity?
Price and quantity both increase.
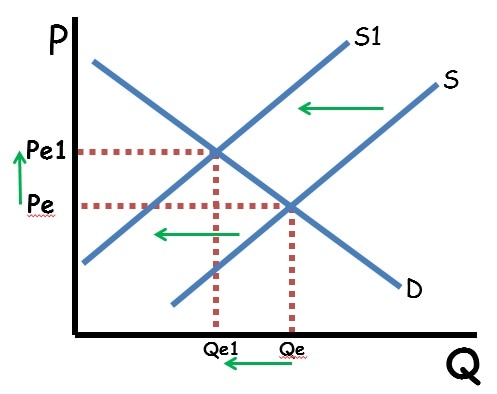
How does a decrease in supply impact equilibrium price and quantity?
Price increases and quantity decreases.
Explain why an increase in the price of one substitute would cause an increase in the price of the other?
As the price of Good A increases, demand for Good B will increase.
If a country develops technology to increase the ability to produce consumers goods while not changing the ability to produce capital goods, how will it be shown on the PPC?
The consumer goods side will shift outward while the capital goods side does not shift.
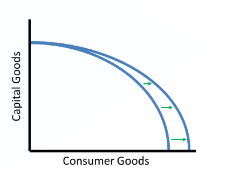
What level of output today will cause the PPC to shift outward more quickly?
Having level of production with more capital goods and fewer consumer goods.
If the price is above equilibrium, what economic problem is caused ? What will happen to price and quantity if there is not intervention?
There will be a surplus (Qs>Qd). Price will eventually go down. Qs will decrease and Qd will increase until equilibrium is reached.
What is the law of diminishing marginal utility?
The additional satisfaction gained from consuming more units of a good decreases with each additional unit consumed.
If an economy is experiencing a recession, how is that illustrated on the PPC.
A point inside the curve shows an inefficient level of output. A recession causes high unemployment so the economy’s labor is not being used efficiently.
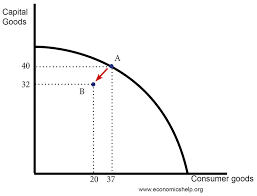
A straight line PPC shows what type of costs (increasing, decreasing, or constant and why?
Constant costs. It is caused by resources being perfectly adaptable to the production of both goods. In the illustration, you can see as more cookies are produced, the cost in terms of cakes is constant.
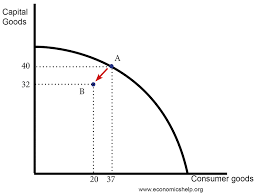
What is the law of demand?
Consumers will purchase higher quantities of goods and services at low prices and lower quantities at high prices.
If citizens want more consumer goods, how is that shown on the PPC?
Production moves along the curve showing more consumer goods but with a cost of some capital goods.
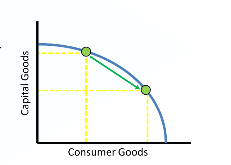
How does a decrease in demand impact equilibrium price and quanitiy?
Price and quantity both decrease.
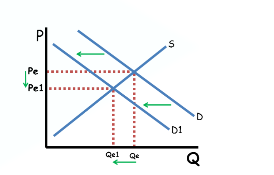
What is scarcity?
The inability of limited resources (or goods and services) to satisfy wants.
How will a decrease in the quality or quantity of resources impact the PPC?
It will shift the curve inward. It will no longer be possible to produce as many capital goods and consumer goods.
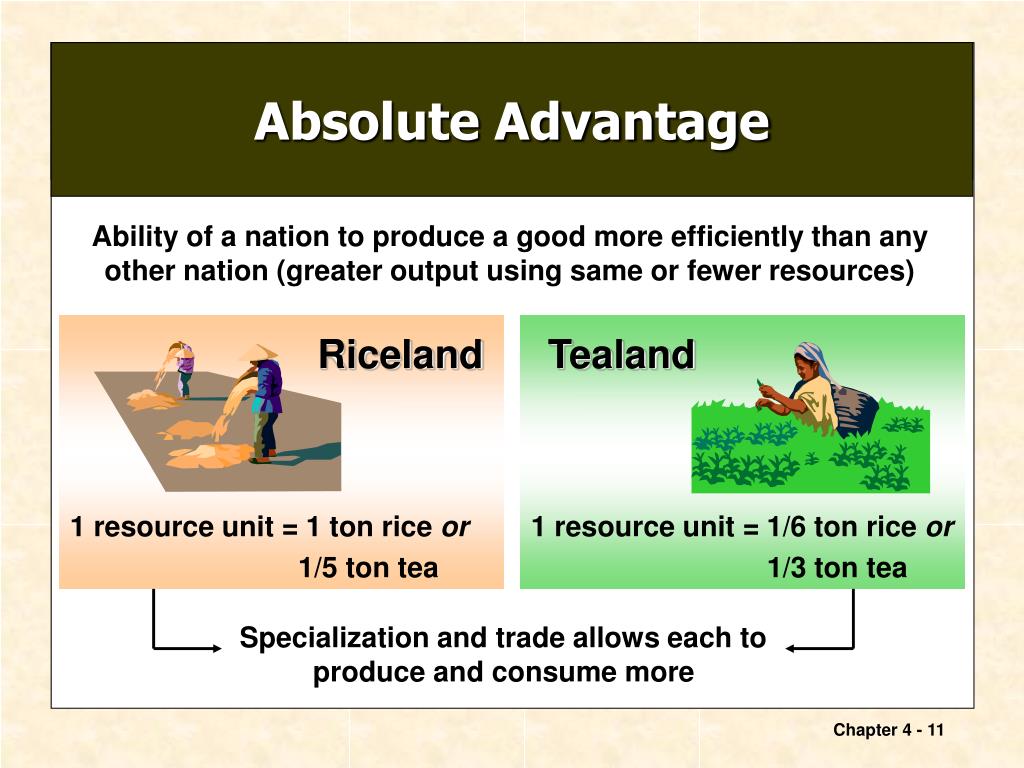
What is Absolute Advantage?
The ability to produce something in greater quantities or using fewer resources than another entity.
When inputs are given, what is the formula for comparative advantage?
It over:
The opportunity cost of 1 unit of Good A is: A/B
The opportunity cost of 1 unit of Good B is: B/A
What is Comparative Advantage?
The ability to produce something with a lower opportunity cost.
How would you illustrate a point of production that is not possible with fixed resources (although specialization and trade would allow a country to consume at that level)?
A point outside the curve is a point of production that is not possible.