neuro physiology
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
anatomical divisions of nervous system
central nervous system, peripheral nervous system
physiological divisions of nervous system
autonomic nervous system (sympathetic and parasympathetic), somatic nervous system
what types of functions is the autonomic nervous system responsible for
involuntary
what types of functions is the somatic nervous system responsible for
voluntary → motor control of muscles, sensory information from muscles
two parts of the CNS
brain, spinal cord
parts of the PNS
nerves, sensory receptors
functional components of sympathetic nervous system
“fight or flight” reactions, mobilizes energy for emergencies (reaction to dangerous situations, prepares for protection)
functional components of parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest functions; conserves energy and restores balance of visceral function
soma
cell body of neurons
dendrites
part of neurons that collect information from environment
axon
part of neuron that sends information from one soma to the next cell
sensory (afferent) neurons
sends information from PNS to CNS
motor (efferent) neurons
sends information from CNS to PNS
synapse
connection/space between two neurons
neurotransmitters
chemicals released by one neuron and picked up by the other
excitation
increased activity
inhibition
decreased activity
glial cells
cells that support neurons and facilitate communication
myelin sheath
type of glial cell that speeds conduction of nerve impulse
nodes of ranvier
space between myelin sheath
cerebral cortex (gray matter)
on outside of cerebrum; made of somas and glial cells
white matter
on inside of cerebrum; made up of myelin sheaths
two divisions of cerebrum
right and left hemispheres
gyri
mountains/hills on brain surface
fissures/sulci
valleys on brain surface
central longitudinal fissure
gap between hemispheres of cerebrum
central fissure
gap between frontal and parietal lobes
lateral fissure
gap between frontal and temporal lobes
role of frontal lobe
primary motor cortex and cognitive function
role of parietal lobe
primary sensory cortex
role of temporal lobe
language and speech
role of occipital lobe
primary visual cortex
role of insular lobe
autonomic functions and some emotion
brodmann areas
“map” of brain showing what part is responsible for what function
role of precentral gyrus
primary motor cortex
role of postcentral gyrus
primary sensory cortex
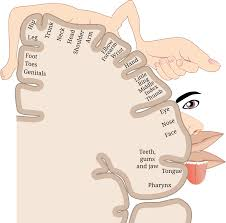
cortical homunculus
representation of motor/sensory cortex
three major layers of protection for the brain
bone, meninges, cerebrospinal fluid
dura mater
most superficial layer of meninges; thick, fibrous, dense tissue; most “tough mother”
arachnoid mater
second-most superficial layer of meninges; white and clear web-like structure with fluid
pia mater
deepest layer of meninges; thinnest layer; contours to all valleys of brain
protective function of cerebrospinal fluid
cushioning
nutritive function of cerebrospinal fluid
provides nutrients and removes waste
spinal tap
a way of sampling the cerebrospinal fluid
where is cerebrospinal fluid produced
ventricles (inside cerebrum)
fasciculi
connection fibers in the brain
association fibers
fasciculi within a hemisphere
commissural fibers
fasciculi that cross hemispheres
corpus callosum
biggest set of commissural fibers
projection fibers
fasciculi that connect the cerebral cortex to lower areas of the CNS
function of basal ganglia
background movement, initiation of movement
function of hippocampus
memory
function of thalamus
sensory information
functions of cerebellum
communicates with sensory aspects of CNS for execution of motor movements
maintains equilibrium + balance
coordinates muscle action in:
stereotyped (automoatic) movements like speech
nonstereotyped (unique) movement like reaching for something
does not initiate muscle movement, but helps coordinate it
function of brainstem
controls essential life functions (keeps blood flowing, respiration going, heart beating)
function of cerebrum
complex cognitive functions
function of spinal cord
reflexes, communication to cerebrum
trigeminal nerve (CN V)
somatosensory information (touch, pain) from the face and head; muscles for chewing
facial nerve (CN VII)
taste (anterior 2/3 of tongue); somatosensory information from ear; controls muscles used in facial expression
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
hearing; balance
glossopheryngeal nerve (CN IX)
taste (posterior 1/3 of tongue); somatosensory information from tongue, tonsil, pharynx; controls some muscles used in swallowing
vagus nerve (CN X)
sensory, motor, and automatic functions of viscera (glands, digestion, heart rate), swallowing and taste sensation
spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
controls muscles used in head movement
hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
controls muscles of tongue
function of muscle spindles
sense muscle length; neurons fire when shape changes
function of golgi tendon organs
sense muscle tension
motor function of posterior parietal lobe
spatial orientation via visual cortex and proprioception
motor function of premotor area
action planning: integrates posterior parietal info to create motor plan
motor function of supplementary motor area
action initiation
motor system function of motor strip
execution of voluntary movement
characteristics of left hemisphere
speech and language; discrete, sequential, rapidly changing information
characteristics of right hemisphere
holistic information; spatial orientation, facial recognition, shapes, artistic abilities, intonation, prosody, tones, music
aphasia
damage to a region of the brain controlling aspects of speech and/or langage