Anemia
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Certified, card-carrying HATER - I'm making a separate deck for reference ranges because that's stupid
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Anemia
A reduction in RBC mass leading to decreased O2 delivery to tissues
Folate deficiency, anemia of chronic disease, thalassemia, pernicious anemia, iron deficiency, G6PD deficiency, sickle cell
Classic anemia causes
low Hgb, Low Hct, low RBC count
Labs for basic anemia - get a CBC
Anisocytosis
Variation in sizes of RBCs (wide RDW)
Poikilocytosis
Variation in the SHAPE of RBCs
MCHC (mean corpuscular Hgb Concentration)
Average Hgb concentration per RBC (basically how dark the cells are)
Mean cell volume (MCV - micro under 80, macro over 100)
A measure of the average RBC size
Mean Corpuscular Hgb (MCH)
Average amount of Hgb per RBC (a measure of weight)
Reticulocytes (0.5-1.5%)
A measure of immature RBCs which indicate that the bone marrow is working to put out RBCs
Serum Iron
A measurement of circulating iron (bound and unbound)
Serum Ferritin
A measurement of circulating iron storage (increase = increase in body iron stores)
Total Iron Binding Capacity (TIBC)
A measurement of circulation transport protein for iron (increases as stores are depleted, calculated from serum transferritin)
CBC w/ diff, Retic count, Blood smear, Iron studies, hemolysis labs, bone marrow biopsy
Labs to order for an anemia workup (in order of when to do them)
B12, folate
What are the macrocytic (100+ MCV) anemias?
Megaloblastic (AKA pernicious)
An anemia with large, structurally abnormal, immature RBCs - due to lack of B12 and folic acid
Intrinsic factor (IF - produced in the stomach, absorbed in the terminal illeum)
What is required for B12 to be absorbed?
Defective myelin in the CNS (neurologic dysfunction)
B12 is required for DNA synthesis, what might a deficiency lead to
Inability to absorb (loss of IF or the Ileum), inadequate intake (vegans), fish tapeworm, metformin, cholestyramine, neomycin, colchicine
Causes of B12 deficiency
Paresthesias, loss of vibratory sense, ataxia, weakness, AMS, glossitis, cheilosis, diarrhea, anorexia
Clinical findings of B12 deficiencies
Macrocytosis (MCV 100+ - maybe normal in Fe is low), decreased serum B12, hypersegmented neutrophils, Macroovalocytes (large, oval RBCs), Increased RDW, Elevated MMA and homocysteine
Lab findings in B12 defiencies
MMA, homocysteine (inversely proportional)
Okay team so the labs are giving B12 deficiency, but we want to be sure, what can we check?
IM/PO/patch B12 (1x weekly until corrected)
Management of B12 deficiencies - neurologic symptoms can be reversed if treated promptly
citrus fruits, leafy greens, meat, egg, liver
Sources of Folic Acid
DNA Synthesis (presents without neuro changes)
Folic acid is required for
Inadequate dietary intake (most common), EtOH intake, Dialysis, TMP-SMX, Sulfasalazine, methotrexate, phenytoin, Increased requirements (pregnancy, hemolytic anemia, malignancy), Celiac disease, IBD, small bowel lymphoma, small bowel resections, 5-methyltetrahydrofolate transferase deficiencies
Causes of Folate deficiencies
Anemia symptoms, glossitis, cheilosis, diarrhea, anorexia, NORMAL neuro exam, neural tube defects (if low during pregnancy)
Findings in folate deficiencies
Anemia stuff, MCV (100+), hyper-segmented neutrophils, decreased serum folate, normal B12, normal MMA, elevated homocysteine
Lab findings in Folate deficiencies
PO/IV Folic acid (1-5 mg), prenatal vitamins for pregnant patients
Management of Folate deficiencies
Iron deficiencies, thalassemia, sideroblastic
Types of Microcytic Anemia
Iron deficiency anemia
What is the most common cause of anemia worldwide and can occur at any age, usually if scarce or if there is a supply-demand mismatch

Blood loss (most common - menstruation, GI/GU ulcers/cancer, blood donation), Poor intake, Pregnancy/lactation (increased need), malabsorption (celiac disease, crohn’s, surgical resection)
Causes of Iron deficiency anemia
meat, poultry, fish, iron fortified breads/cereals, dried fruits, tofu, dark leafy green veggies
Sources of iron (1-1.5 mg/day)
Fatigue, pallor, tachycardia, exertional dyspnea, glossitis, cheilosis, koilonychia (spoon-shaped nails), pica, dry/rough skin (late stage), FOBT + (if GI loss), restless leg syndrome, esophageal webs, ecchymosis
Findings in iron deficiency
Anemia, Low MCV (under 80), hypochromic (low MCHC/MCH), Increase RDW, decrease reticulocytes (bone marrow ain’t got the goods), Decreased serum Fe, decreased ferritin, increased TIBC, decreased transferrin
Labs for Iron deficiency anemia
Treat the underlying, PO Fe therapy (30-60 mg elemental Fe OR 325 mg Fe sulfate, continue 4-6 months after Hgb normalizes), Monitor retic count (1 week later), monitor ferritin/Hgb, IV iron and heme referral if refractory
Treatment plan for Iron deficiency anemia
qod dosing improves absorption and reduces constipation, avoid enteric coated forms, take on an empty stomach
Patient education measures for Fe supplementation
Thalassemia
An autosomal recessive disorder that causes gene deletion/point mutations more common in Southeast Asian, Mediterranean, and African American populations
Alpha Thalassemia
Deficiency/Absence of the alpha-globin chains
Beta Thalassemia
Deficiency/Absence of the beta-globin chains
imbalance of globin chains (2 alpha, 2 beta normally - point mutation) → effective erythropoiesis and hemolysis
What is the pathophys for Thalassemia
2 genes chromosome 16 (for a total of 4 since its recessive)
What chromosome is affected in alpha Thalassemia - severity depends on the amount of deletion
hydrops fetalis/hemoglobin barts
If there is NO normal alpha chains →
Hemoglobin H disease
If there is 1 normal alpha chain →
Alpha thalassemia minor (clinically normal, microcytic mild anemia)
If there is 2 normal alpha chains →
Alpha thalassemia minima/silent carrier (clinically and hematologically normal)
If there is 3 normal alpha chains →
Chromo 11 (2 genes exist)
What chromosome is affected in beta Thalassemia - production can range from near normal to completely absent
Transfusion dependent (major/intermedia), Non-transfusion dependent, Minor, trait
Categories of Beta Thalassemia
Severe microcytic anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, bony deformities, osteopenia, fractures
Findings in Transfusion Dependent Beta Thalassemia
Microcytic, hemolytic anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, bony deformities, osteopenia, fractures
Findings in Non-Transfusion Dependent Beta Thalassemia
Anemia, decreased MCV/MCHC, target cells, acanthocytes, poikilocytosis, basophilic stippling, nucleated RBCs, normal Fe studies, elevated levels of HbA2 and HbF in beta
Labs for Thalassemia
the vibes of beta thalassemia, but the exclusion of beta
How do you diagnose alpha Thalassemia?
Nothing
Management plan for alpha-thalassemia trait or beta minor

genetic counseling for prospective parents
Management plan for carriers of the alpha/beta thalassemia
Refer to Hematologist (especially NTDT, TDT, HbH), splenectomy, transfusion with chelation, folic acid, vitamin C, bone marrow transplant (curative for beta - especially if done early)
Management plan for severe thalassemia cases
Fe overload → cardiomegaly (restrictive), CHF, hepatosplenomegaly, death ☠
Consequences of frequent transfusions in thalassemia
Sideroblastic anemia
An anemia due to the inability to incorporate iron into heme, leading to the accumulation of iron in the mitochondria - either congenital or acquired
subtype of myelodysplasia, excessive EtOH, isoniazid, linezolid, Cu deficiency, lead poisoing
Acquired causes of Sideroblastic anemia
Lead impairs enzymes (cell death), abnormal heme synthesis
Pathophys for lead poisoning induced Sideroblastic anemia
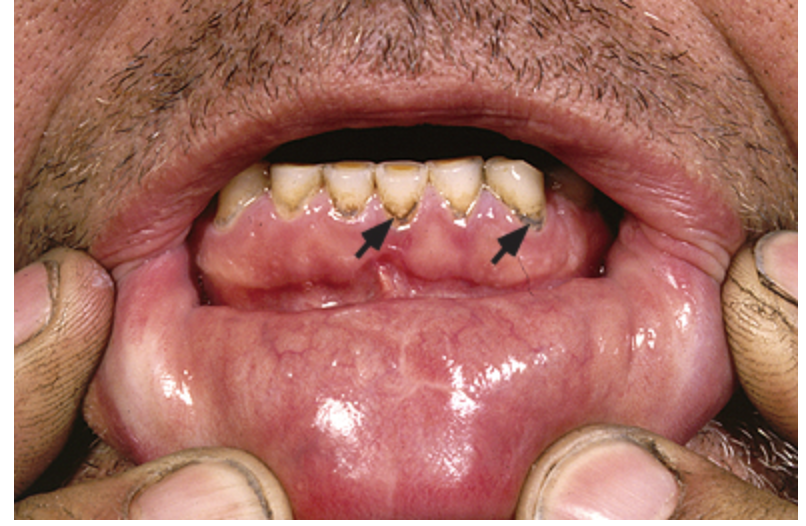
pale, abdominal pain, fatigue, learning disabilities, neurologic/behavioral issues (ataxic, slurred speech, seizures, comatose, foot/wrist drop), lead line along the gum line
Features of Lead poisoning
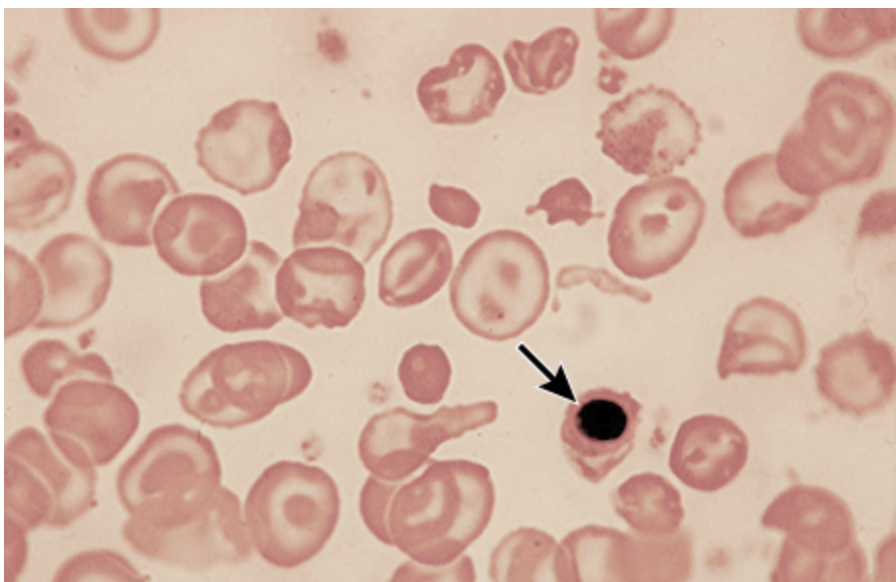
Microcytic, hypochromic anemia, basophilic stippling, increased serum lead, increased serum Fe, normal/decreased TIBC, increased transferrin/ferritin, Lead lines on X-rays of the long bones
Diagnostic findings in Lead poisonings
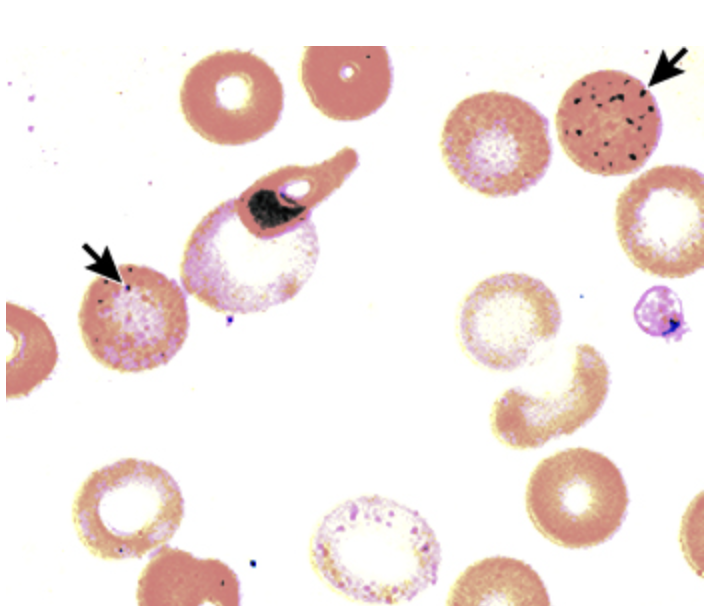
Bone marrow examination - a prussian blue iron stain showing ring sideroblast (due to iron load)
Definitive diagnosis of lead poisoning
remove lead source, transfusion MAYBE, chelation therapy, consult heme and toxicology
Management of lead poisoning
Anemia of chronic disease
Which types of anemia can be Micro or Normocytic?
Chronic infection/inflammation, liver disease, chronic kidney disease, RA, malignancy
Underlying causes of Anemia of chronic disease
Decreased RBC life, block in the release of iron from macrophage, cytokine inhibition of EPO
Patho for Anemia of chronic disease
Anemia (Hbg is typically higher than 9), normocytic normochromic (most common - but can be hypochromic, microcytic), normal/low retics, decreased serum Fe, Decreased TIBC, Normal/elevated ferritin
Lab findings for Anemia of chronic disease
Treat the underlying cause, EPO (30,000 units SQ/week), Darbepoetin (300 mcg/2-3 weeks), in severe cases consider multiple anemia types (poor diet or GI bleeding)
Management of Anemia of chronic disease
MI, CVA
Excessive EPO (stimulation of RBC creation) increases the risk of
Aplastic, hemolytic anemia, hereditary spherocytosis, sickle cell anemia
Types of Normocytic anemia
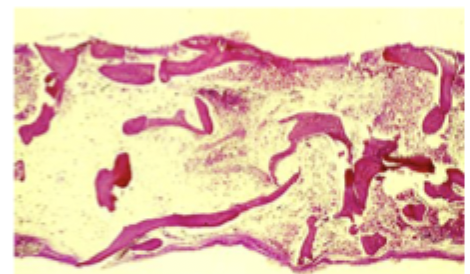
Aplastic anemia
A failure of the bone marrow which if left untreated can lead to death ☠
Pancytopenia with bone marrow hypoplasia/aplasia, loss of hematopoietic stem cells (defining factor)
Characteristics of aplastic anemia
Cancer treatments, Anti-eplileptics, NSAIDs, sulfonamides, chloramphenicol, PTU, methimazole, gold, arsenicals, benzene, solvents, glue vapors, EBV, Seronegative hepatitis, HIV, other herpes viruses, eosinophilic fasciitis, SLE, GVHD, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, thymoma, pregnancy, anorexia
Causes of aplastic anemia
ANEMIA SYMPTOMS (SHOCKER), neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, purpura, petechiae
Findings in aplastic anemia
Pancytopenia (RBC down, retic down), normocytic anemia (mild macrocytosis), Bone Marrow biopsy 🏆 (hypocellular marrow, few residual hematopoietic stem cells are normal, NO megaloblastic maligannt cells/fibrosis is absent)
Diagnostics for aplastic anemia
Hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT), intensive immunosuppressive therapy (IST)
Management for aplastic anemia
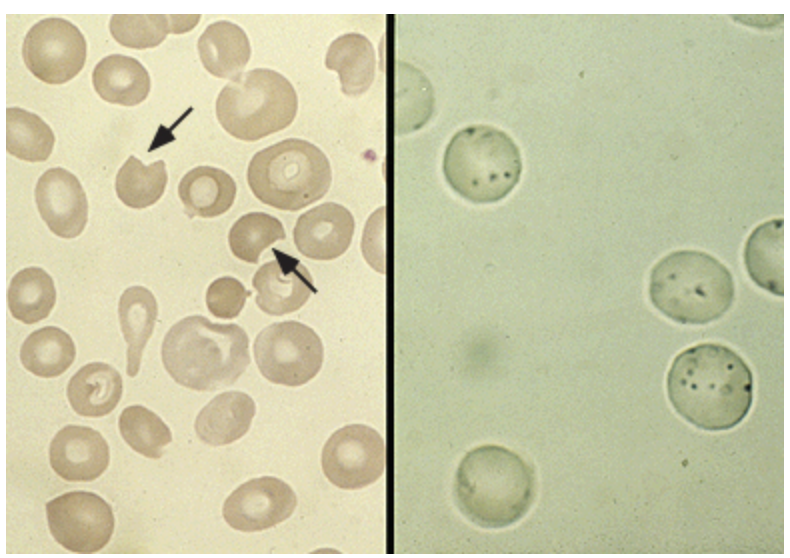
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency (G6PD)
A X-linked recessive disorder that leads to the loss of the HMP shunt that protects RBC from oxidative injury leading to hemolysis
Class I (severe enzyme deficiency, chronic anemia), Class II (severe enzyme deficiency with intermittent hemolysis), Class III, Class IV, Class V (no clinical significance - found on genetic testing)
Variant Classification of G6PD
infection, FQs, dapsone, nitrofurantoin, phenazopyridine, primaquine, sulfonylureas, methylene blue, fava beans, henna, naphthalene
Oxidative stressors of G6PD
jaundice, dark urine abd/low back pain
Findings of G6PD - depends on the severity and presence of hemolysis
Increased LDH, Normocytic Anemia, elevated retics, bite/blister cells, Heinz bodies, elevated indirect bili, hemoglobinuria; NADP assay (screening and confirmation), G6PD enzyme direct assay (will be a false neg during episodes)
Diagnostics for G6PD - can be normal between episodes
avoid triggers, transfuse in severe cases
Management of G6PD
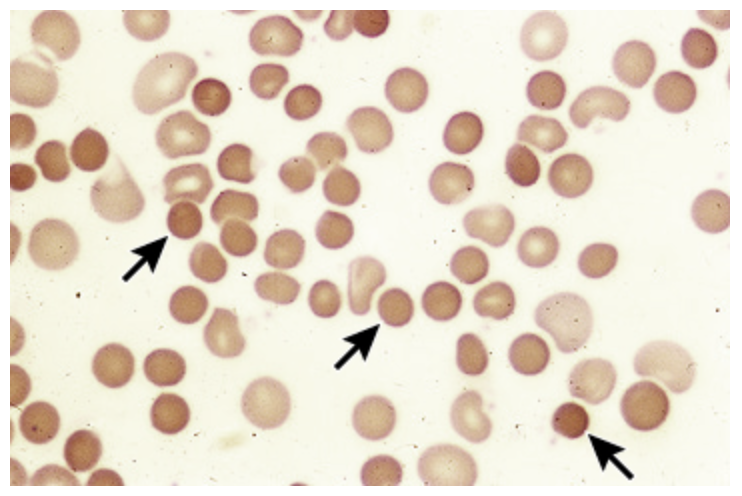
Hereditary Spherocytosis
An autosomal dominant disorder that results as a defect in the RBC membrane (a scaffolding protein in the RBC cytoskeleton) and a decreased surface-to-volume ratio leading to a spherical shape
ANEMIA, jaundice, splenomegaly (hypertrophy due to RBC destruction), pigmented gallstones, neonatal hyperbilirubinemia
Clinical findings in Hereditary Spherocytosis
Normocytic/microcytic, hyperchromic Anemia, increase retics, spherocytes, increased indirect bili, increased LDH
Diagnostics for Hereditary Spherocytosis
Refer to hematologist, folic acid 1 mg/day (must haves), splenectomy (moderate to severe), vaccines prior to splenectomy, monitor for hemolytic and aplastic crises
Management of Hereditary Spherocytosis
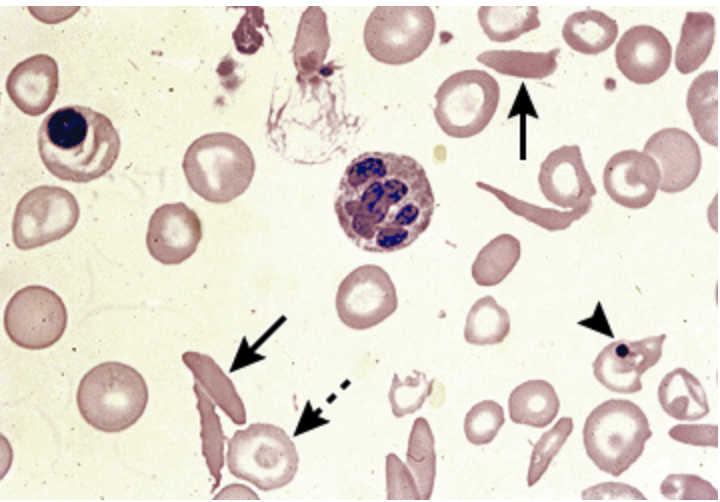
Sickle Cell anemia
An autosomal recessive disorder of the hemoglobin S gene (mixed genotype is thought to be protective against malaria)
HbS is deoxygenated → sickle shape → leads to micro/macro vessel occlusion and hemolysis
Patho for Sickle Cell Anemia
vaso-occlusion, sequestration, aplastic
Components of a hemolytic crises of sickle cell anemia
Skin ulcerations, painful crises, retinopathy, ischemic necrosis of bones, renal dysfunction, hyposplenism, hepatic dysfunction, priapism, jaundice, gallstones, Pulmonary HTN, HF
Clinical findings in sickle cell anemia - starts at around 6 months (fetal hgb is replaced by S)
Acute vaso-occlusive crisis
What is the primary cause of hospitalization in sickle cell anemia
fever, dyspnea, hypoxia, chest pain, abdominal pain/swelling, HA, seizure, vision changes, priapism, pain refractory to home meds, AMI, stroke, organ failure
Signs and Symptoms of an Acute vaso-occlusive crisis - best indicator is hx
Acute chest syndrome
What clinical finding in Sickle Cell anemia presents with fever, cough, and infiltrate on a CXR
Universal newborn screening, Normochromic Normocytic anemia, sickled cells, Howell-jolly bodies, target cells, absent HbA and HbS on electrophoresis, increase indirect bili, hemoglobinuria, high performance liquid chromatography (preferred)
Diagnostics for Sickle cell anemia
folic acid (1mg day), daily vitamins, Pen VK until age 5, Vaccines, Hydroxyurea (increases NO, increased fetal Hgb, reduces leukocyte count)
Prevention of complications of sickle cell anemia
Pain control (NSAIDs to opioids), O2 (hypoxia/acute chest), blood transfusions for stroke prevention/treatment, acute chest, symptomatic anemia, Abx for infection, IV fluids, supportive care
Treatment of acute complications of sickle cell anemias
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), gene therapy (autologous transplant + editing of HbS gene)
Curative treatments of Sickle cell anemia