UV Light and DNA Protection in Life Science Lab
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
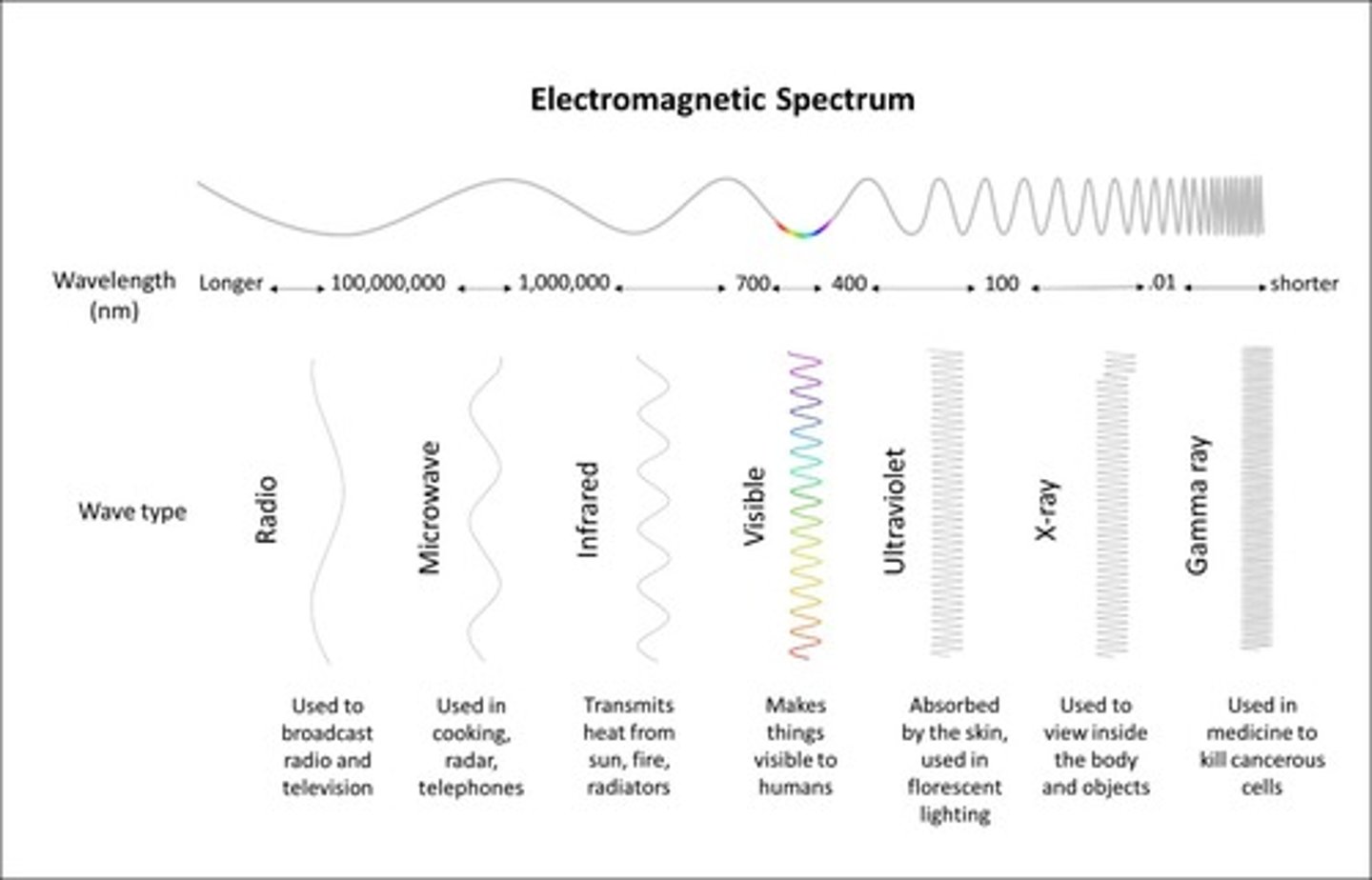
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The range of all types of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, ultraviolet light, and others, characterized by their wavelengths.
Wavelength
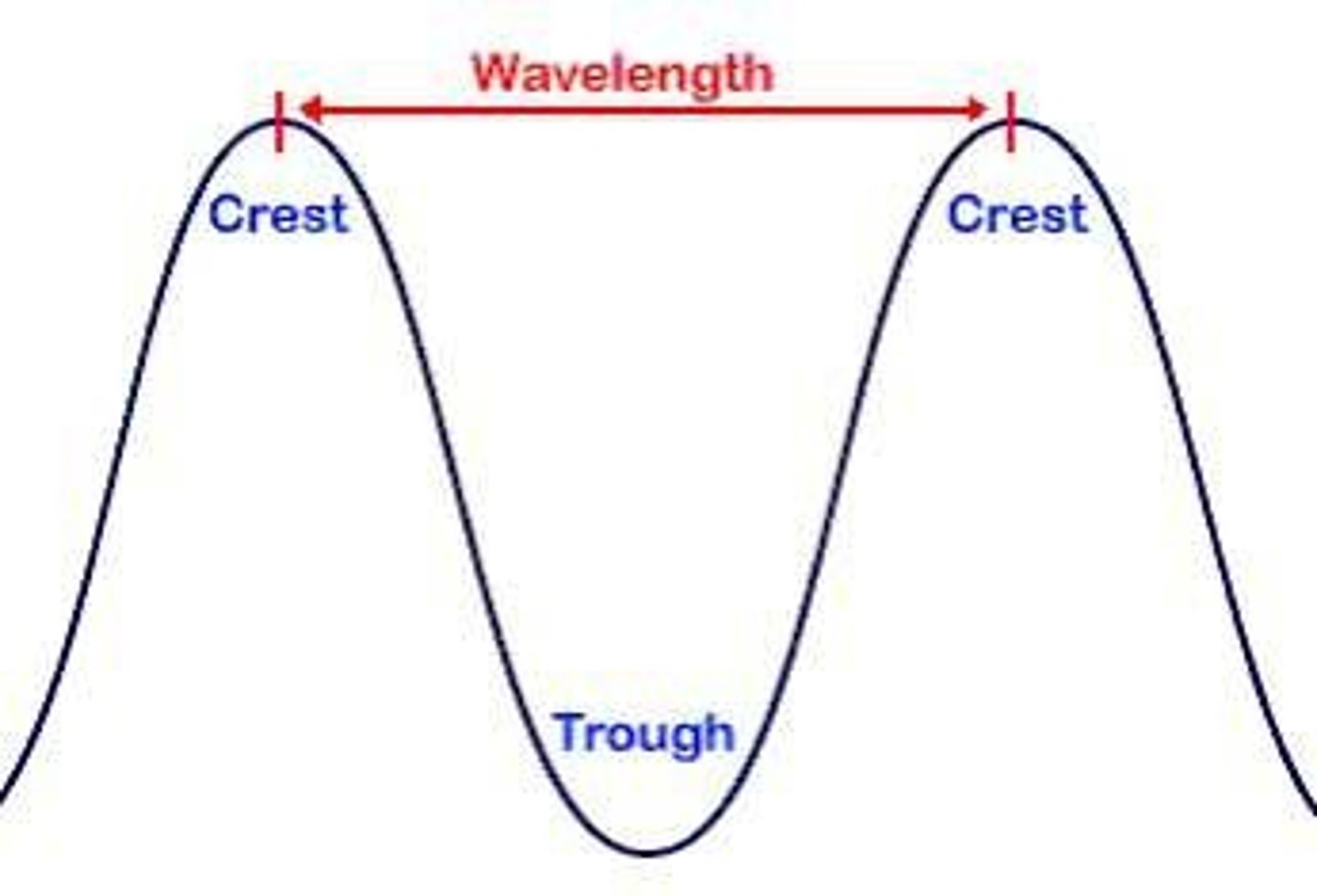
The distance between identical points in adjacent waves, typically measured in nanometers (nm).
Nanometer
A unit of measurement equal to 10^-9 meters, used to measure wavelengths of light.
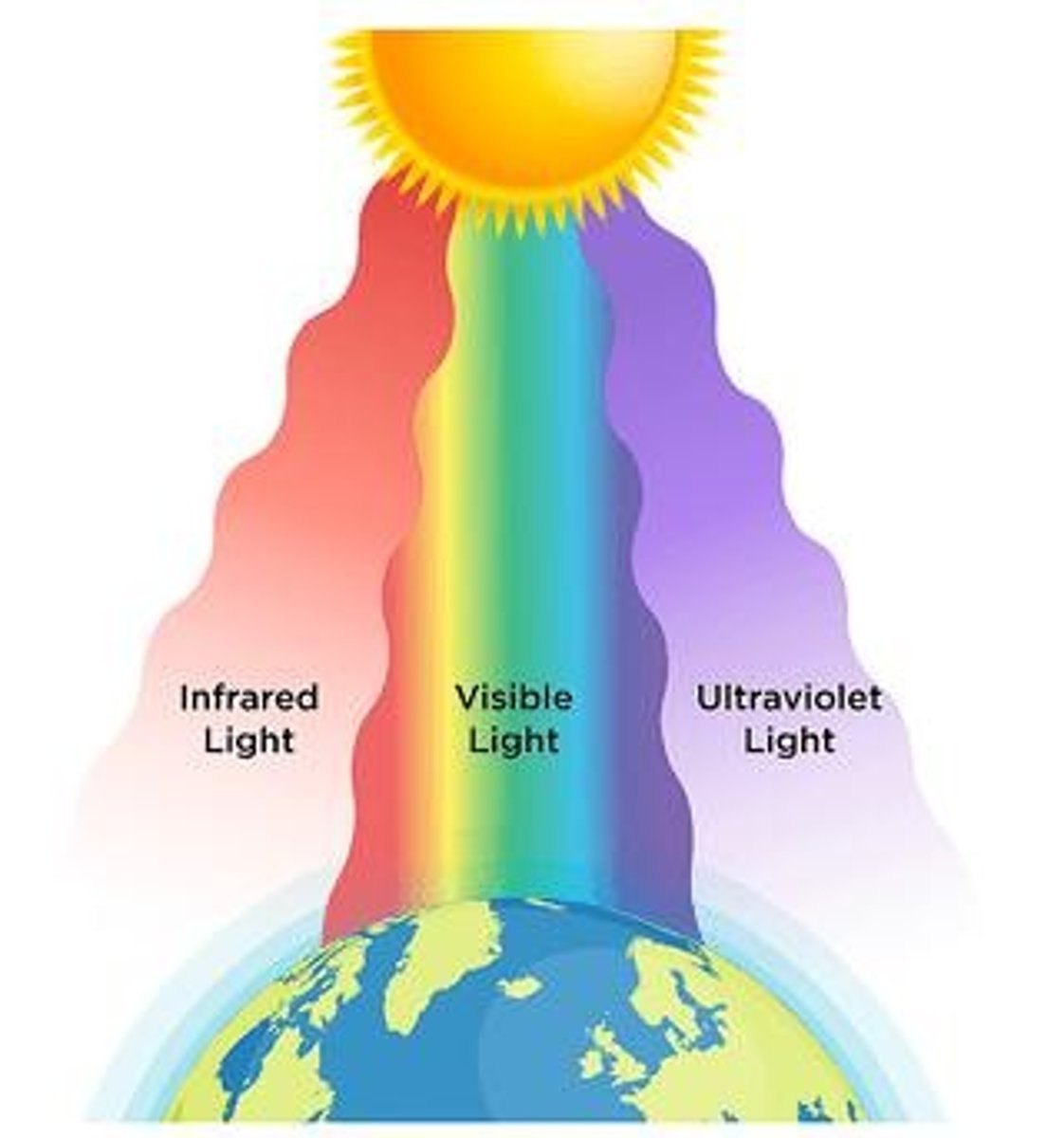
Visible Light
The portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye, with wavelengths ranging from 380-750nm.
Infrared Light
Electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths that transmit heat, ranging from 780nm to 1mm.
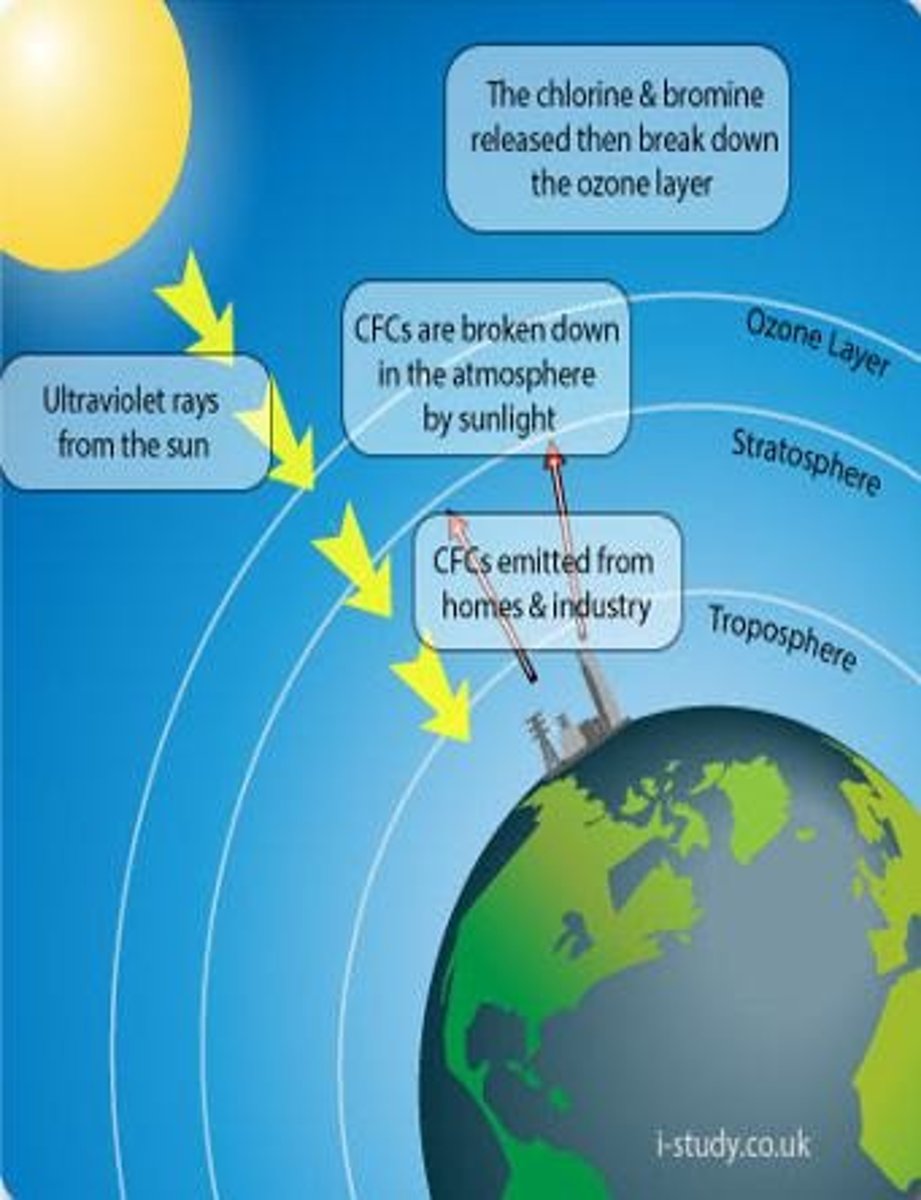
Ultraviolet Light
Invisible electromagnetic radiation with shorter wavelengths than visible light, ranging from 100nm to 400nm, which can cause harm.
Ozone Depletion
The reduction of the ozone layer due to pollutants like chlorofluorocarbons, increasing exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Non-ionizing Radiation
A type of radiation that does not carry enough energy to ionize atoms or molecules, including ultraviolet radiation.
Harmful Effects of UV Radiation
Increased risk of skin cancer and cataracts due to higher exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Earth's Atmosphere
The layer of gases surrounding Earth that allows certain electromagnetic radiation to reach the surface while blocking harmful radiation.
Photosynthesis
The process by which visible light is converted into chemical energy by plants.
Solar Radiation
Energy emitted by the sun in the form of waves that carry energy through space.
Types of Electromagnetic Waves
Includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
High-energy Radiation
Radiation that has enough energy to cause damage to living tissue, including X-rays and gamma rays.
Chlorofluorocarbons
Chemical compounds that deplete the ozone layer and increase exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Cataracts
A medical condition where the lens of the eye becomes cloudy, often linked to exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Radiation
Energy that is emitted in the form of waves or particles.
Wave Cycle
The complete sequence of a wave from one crest to the next.
Tanning Beds
Artificial sources of ultraviolet radiation used for cosmetic tanning.
Energy Carrying Capacity
The amount of energy carried by a wave, which increases with shorter wavelengths and higher frequency.
Chemical Energy
Energy stored in the bonds of chemical compounds, released during photosynthesis.
Ozone layer
Most of the Sun's UV radiation is absorbed by the Ozone layer, 10-20 miles above the Earth's surface.
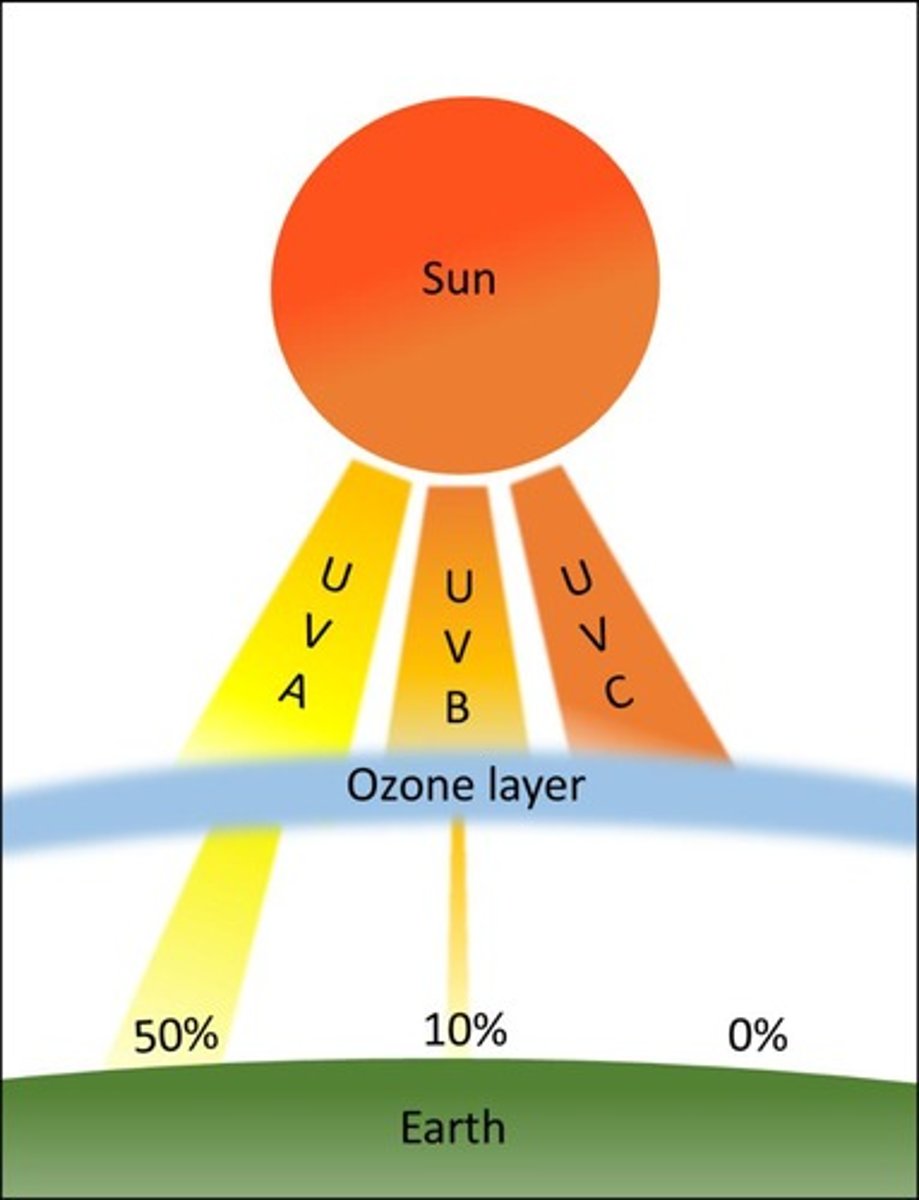
UVA
Longest UV wavelength/Least energetic; reaches the Earth's surface and can penetrate your skin more deeply than UVB.
UVB
Plays an important role in the formation of Vitamin D and makes up only 5% of the UV rays from the sun.
UVC
Highest energy portion of the UV radiation spectrum; entirely blocked by the Ozone Layer in the atmosphere.
Pyrimidine dimer
Molecular lesion produced upon exposure of DNA to UVB light, occurring when broken bonds allow cytosine (C) and thymine (T) bases to reconnect to a C or T on an adjacent nucleotide.
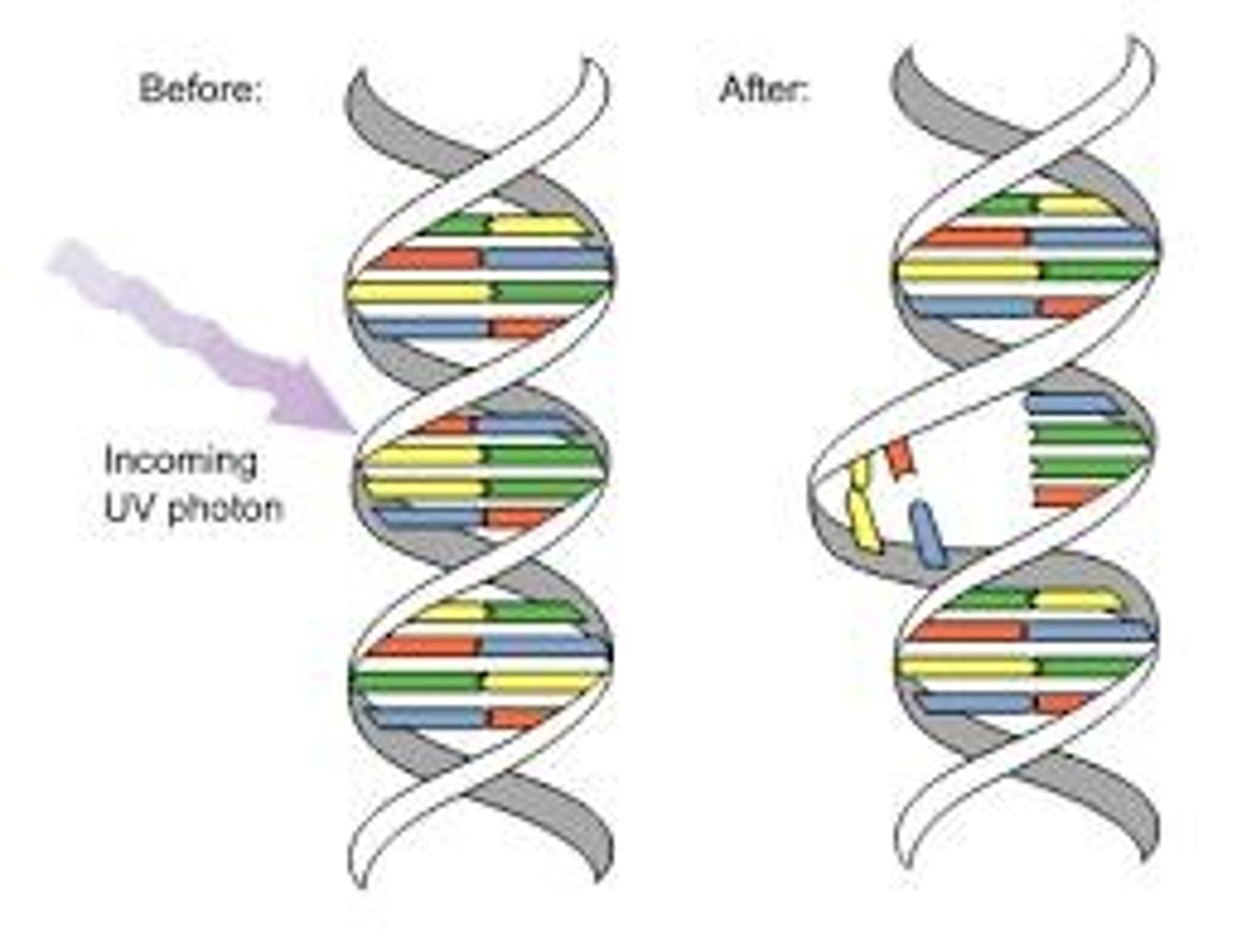
Nucleotide excision repair (NER)
A DNA repair mechanism in the cell that generally repairs mutations caused by UV radiation.
Xeroderma Pigmentosum (XP)
A genetic disease where some people are born with defects in their nucleotide excision repair (NER).
Skin Cancer
An increase of UV exposure can lead to non-melanoma skin cancer, which can often be cured by surgical removal of the affected skin.
Melanomas
A type of skin cancer that is more difficult to treat due to its tendency to spread or metastasize to other organs in the body.
Cumulative damage from UV radiation
Repeated exposure increases the risk of developing skin cancer over time.
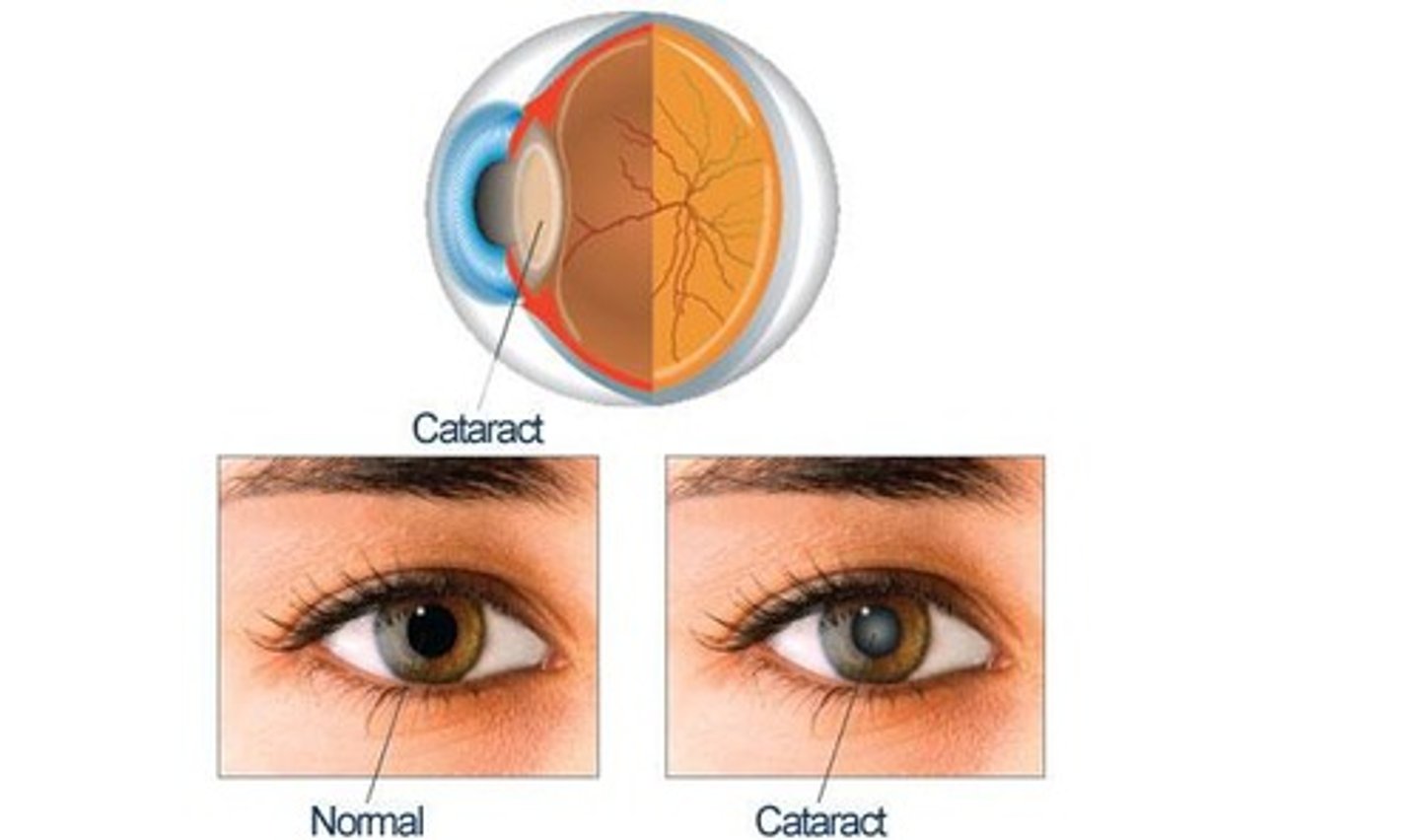
Cataracts
A form of eye damage that deforms the protein in the eye lens, increased likelihood due to UV radiation.
Sun Protection Factor (SPF)
Tells you the amount of time it would take for the sun to start burning your skin using that particular sunscreen compared to how long it would take you to burn without sunscreen.
Broad Spectrum sunscreen
Provides protection against both UVA and UVB radiation.
Physical barriers for UV protection
Includes clothing, wide-brim hats, and sunglasses to protect from UV radiation.
Artificial tanning beds
Should be avoided as they expose the skin to harmful UV radiation.
Activity A
Construct a Wave.
Activity B
Summarizing the steps involving the development of skin cancers.
Activity C
Testing the UV protection in various barriers using UV sensitive beads.
Activity D
Testing the effects of UV exposure and sunscreen on living cells using yeast strains as model organisms.
Baker's yeast
Contains genes for DNA repair.
Mutant Strain
Contains mutation of the DNA repair genes.
Fun Fact about Melanin
Melanin is responsible for tanning skin exposed to sunlight, which provides protection to the cells.
Premature aging
Sun exposure causes the skin to become thick, wrinkled, and leathery.