MKT exam 2
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Steps in New Product Development Process
Idea Generation → Screening → Concept Development/Testing → Marketing Strategy → Business Analysis → Product Development → Market Testing → Commercialization.
Idea Generation
The initial stage where new product ideas are created through brainstorming, customer feedback, or market research.
Brainstorming, crowdsourcing, and identifying customer needs.
Idea Screening
The process of evaluating and filtering new product ideas to identify those that are feasible and align with business objectives.
Evaluating ideas systematically using criteria like feasibility and potential market impact.
Concept Development and Testing
The stage where selected product ideas are refined into detailed concepts and tested with potential customers to gather feedback and validate the concept's viability.
Marketing Strategy Development
The process of defining the marketing approach and tactics to promote a product, including target market identification, positioning, and the marketing mix elements.
Formulating a plan for market entry.
Business Analysis
Forecasting profitability and understanding risks.
Product Development
Creating prototypes and refining designs.
Market Testing
Small-scale product launches to gauge market response.
Role of Empathy in Ideation:
Using empathy maps to understand customer needs.
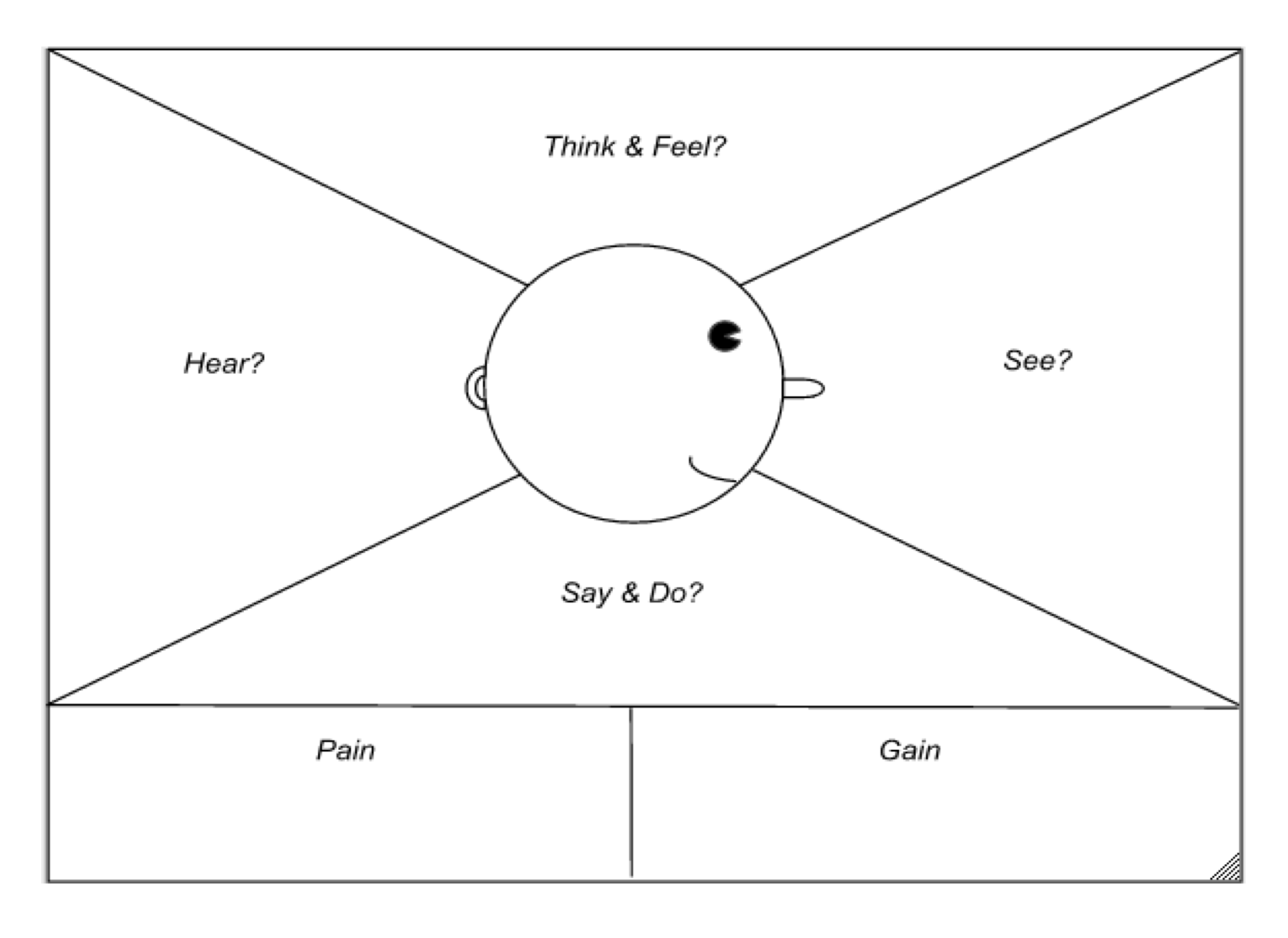
Commercialization
Full-scale product launch
R-W-W Screening
Is it Real? Can we Win? Is it Worth doing?
Forecasting
Q=M×A×P×F formula (market size, awareness, purchase probability, frequency).
Product Lifecycle: Stages
Introduction: The product is introduced to the market. Sales are low, and costs are high. Marketing efforts focus on awareness and creating demand.
Growth: Sales start increasing, profits begin to rise, competitors enter the market. Companies differentiate their product and expand distribution.
Maturity: Sales growth slows, competition intensifies, and products become more standardized. Companies focus on cost control and customer loyalty.
Decline: Sales decline due to new technologies or consumer preferences. Companies may discontinue the product or reduce marketing costs.
Product Lifecycle: consumers
Innovators
Characteristics: Risk-takers, adventurous, and eager to try new ideas.
Role: First to adopt an innovation, driving initial exposure and acceptance.
Early Adopters
Characteristics: Visionary and influential, often opinion leaders in their communities.
Role: Bridge the gap between innovators and the broader population, promoting the innovation.
Majority
Divided into:
Early Majority: Adopt the innovation after seeing evidence of its effectiveness.
Late Majority: More skeptical and cautious, adopting only after most people have done so.
Role: Represent the bulk of users, leading to widespread adoption.
Laggards
Characteristics: Resistant to change, preferring traditional methods.
Role: Last to adopt, often after the innovation is well-established or replaced.
Brand Strategies
Adjust based on lifecycle stage, e.g., penetration pricing in growth or cost-cutting in declin
What is innovation built on?
The intersection of humans, technology, and business.
Why does successful innovation begin with empathy?
Empathy allows you to understand customers’ needs, ensuring products address real problems.
What are some techniques for idea generation?
Brainstorming, crowdsourcing, and design thinking sessions.
How do you screen for worthy ideas?
Using criteria like feasibility, alignment with business objectives, and market potential.
Customer Value-Based:
Based on perceived value.
Cost-Based
Adding a markup to costs.
Competition-Based:
Based on competitor pricing.
Breakeven Analysis:
Formula: Fixed Costs ÷ (Price - Variable Cost).
New Product Pricing:
Skim Pricing: High initial price for early adopters.
Penetration Pricing: Low price to capture market share.
What are the three parts of a marketing strategy statement?
target market description, value proposition, and sales/marketing objectives.
What are customer-centered, team-based, and systematic new product development approaches?
Customer-centered: Focus on customer needs.
Team-based: Collaborative work across departments.
Systematic: Structured and consistent innovation processes.
Channels of Distribution:
Paths products take from producer to consumer
Channel Structures
Vertical Marketing System (VMS): Unified approach with a central authority.
Horizontal Marketing System (HMS): Collaboration between companies at the same level.
Multichannel Distribution: Using multiple channels to reach consumers
Channel Conflicts:
Vertical Conflict: Between different levels of the channel (e.g., supplier vs. retailer).
Horizontal Conflict: Between members at the same level (e.g., two retailers)
Distribution Strategies:
Intensive: Widely available products (e.g., soda).
Selective: Limited availability (e.g., electronics)Exclusive: Highly controlled availability (e.g., luxury items)(Lecture 17 Managing Mar…)
Logistics Functions:
Warehousing: Storage.
Inventory Management: Tracking stock levels.
Transportation: Moving goods efficiently.
Logistics Information Management: Using data to optimize the supply chain
What is the difference between vertical and horizontal channel conflict?
Vertical: Disputes between different levels, like a manufacturer and retailer.
Horizontal: Disputes among same-level members, like two competing retailers.
What is disintermediation?
Removing intermediaries, often due to digital disruption.
For what types of products are intensive, selective, or exclusive distribution most appropriate?
Intensive: Everyday items (e.g., snacks).
Selective: High-involvement products (e.g., laptops).
Exclusive: Luxury goods (e.g., designer bags).
Major Store Retailer Types
Specialty Store: Focuses on a specific product category.
Department Store: Wide variety of product lines.
Supermarket: Grocery and household items.
Convenience Store: Limited variety; fast and convenient.
Discount Store: Offers lower prices with fewer services.
Off-Price Retailer: Buys goods at below wholesale price.
Superstore: Large store with extensive assortment.
Retail Organizations
Corporate Chain: Owned by a single organization.
Voluntary Chain: Independent retailers banding together.
Retail Cooperative: Retailers collaborate for bulk purchasing.
Franchise Organization: License to operate under a brand.
Retail Strategy (STDP)
Segmenting, targeting, differentiating, and positioning to create value.
Retail Marketing Mix (4Ps)
Product/Service: Variety and quality.
Price: Competitive pricing strategies.
Promotion: Advertising and communication strategies.
Place: Location and accessibility.
Promotion Mix Elements
Advertising, Sales Promotion, PR, Personal Selling, Direct Marketing.
Push vs. Pull Strategy:
Push: Through intermediaries.
Pull: Direct to consumers.
Trends in Retailing
Omnichannel retailing.
Retail life cycle and wheel of retailing.
Wholesaling
Merchant Wholesaler: Buys and resells goods.
Broker: Facilitates transactions without owning goods.
Agent: Represents buyers or sellers in transactions.
Advertising: steps
Steps: Objective → Budget → Creative → Media Selection.
Execution: Storytelling, humor, testimonial.
Metrics: Impressions, CPM.
Tools include press releases, events.
Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC)
Coordinates various promotional tools for consistent messaging.
Different from promotional mix, which includes advertising, sales promotion, public relations, personal selling, and direct marketing.
Advertising Program Developmen
Setting Objectives: Inform, persuade, remind.
Budget Decisions: Methods include affordable, percent-of-sales, competitive-parity, and objective-and-task.
competitive-parity, and objective-and-task.
Creative Concept: Central theme of the advertisement.
Execution Style: Includes storytelling, humor, or testimonials.
Media Metrics
Impressions = Reach × Frequency.
Cost per Thousand (CPM) = Cost / Impressions in thousands.
what are the stages of the retail life cycle?
In the Introduction Stage: Focus on brand awareness and building demand.
In the Growth Stage: Focus on differentiating the product from competitors.
In the Maturity Stage: Focus on reinforcing brand loyalty and possibly rebranding.
In the Decline Stage: Consider discontinuing or repurposing the brand
Personal Selling Process:
Prospecting: Identify potential customers.
Preapproach: Research customer needs.
Approach: First contact, build rapport.
Presentation: Communicate the value proposition.
Handling Objections: Address customer concerns.
Closing: Finalize the sale.
Follow-Up: Ensure satisfaction, build loyalty.