Psychopathology: Substance-Related and Sexual Disorders Overview
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
What is substance use disorder?
A condition where an individual uses more of a substance than intended and continues despite significant adverse consequences.
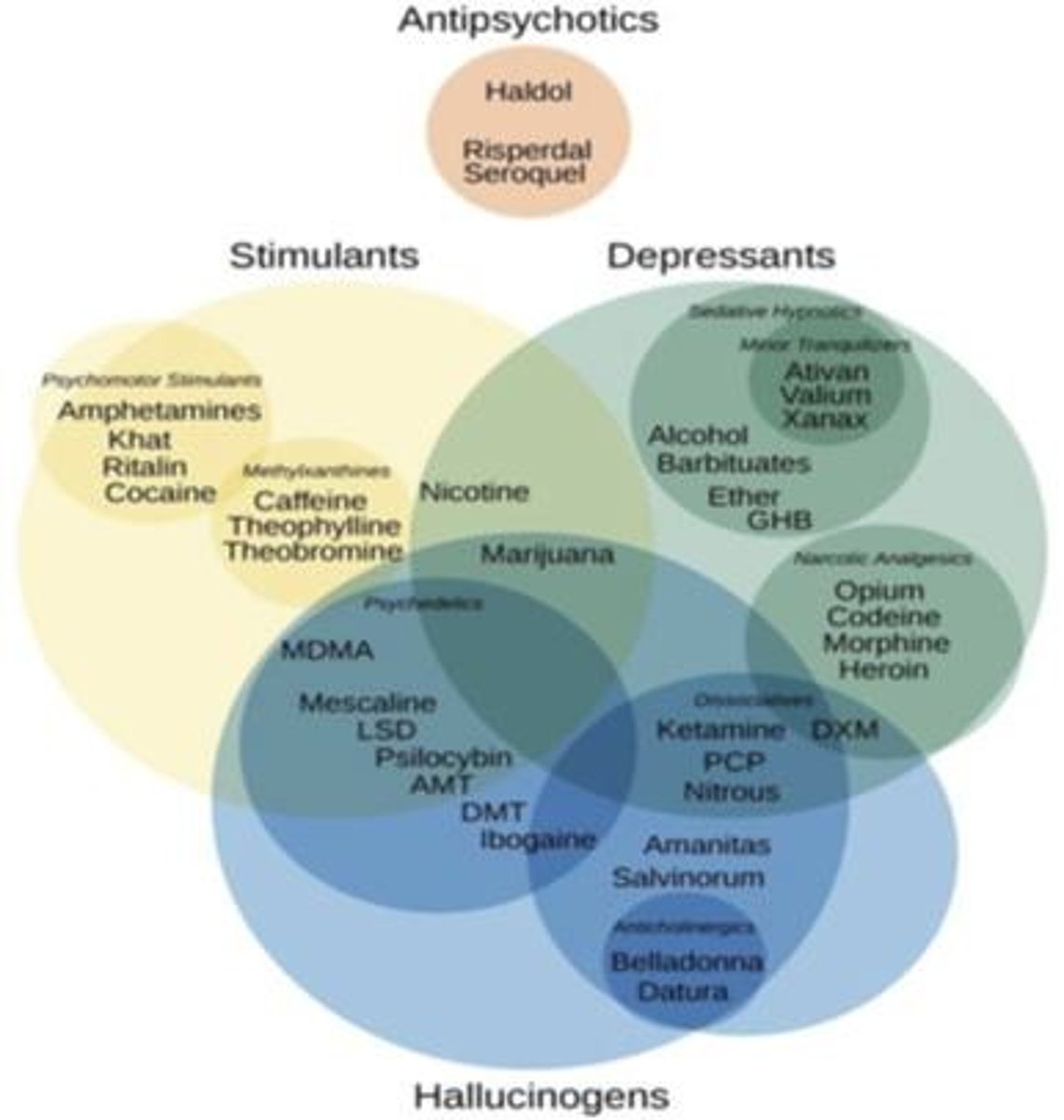
What are the two types of dependence associated with substance use disorders?
Physical dependence, which involves withdrawal symptoms upon cessation, and psychological dependence, which is an emotional need for the substance.
What is tolerance in the context of substance use?
The need for increasing amounts of a drug to achieve effects previously experienced at lower doses.
What are common symptoms of drug withdrawal?
Negative symptoms experienced when drug use is discontinued, which can vary based on the substance.
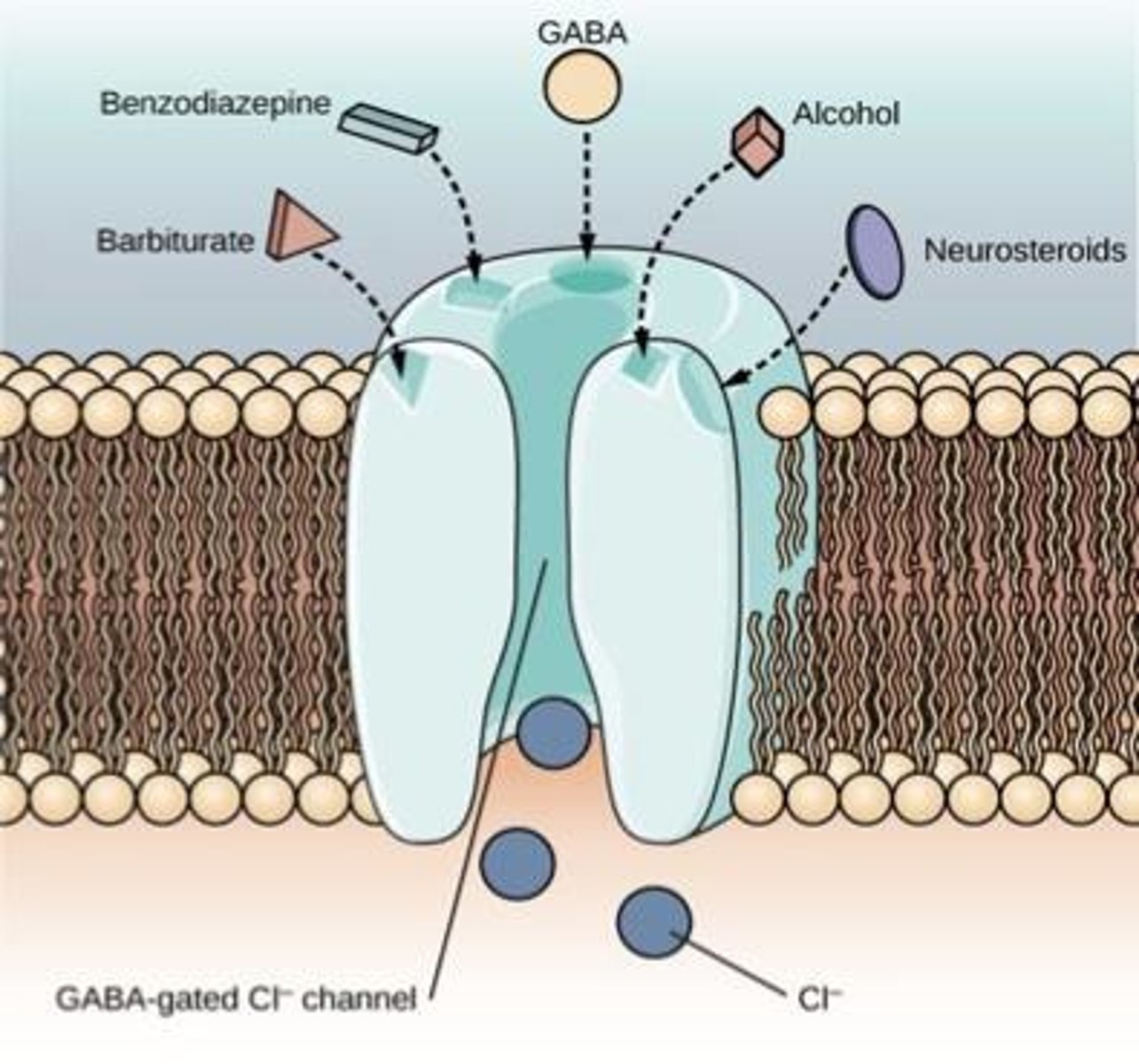
What is the impact of depressants on the nervous system?
Depressants suppress central nervous system activity, leading to effects such as slowed brain function and decreased heart rate.
How is alcohol intoxication measured?
In terms of Blood Alcohol Content (BAC), with a BAC of 0.10 indicating 0.10 g of alcohol per 100 ml of blood.
What BAC level is considered potentially fatal?
BAC levels above 0.40.
What defines alcohol use disorder (AUD)?
Any drinking that results in mental and/or physical health problems, ranging from mild to severe.
What are some signs of alcohol intoxication?
Signs include slurred speech, incoordination, unsteady gait, nystagmus, and impairment in attention or memory.
What is stimulant use disorder?
A type of substance use disorder involving the abuse of stimulants, marked by problematic behavioral or psychological changes.
What are the effects of stimulants on the brain?
Stimulants increase overall levels of neural activity, leading to effects like increased heart rate and heightened alertness.
What are some dangerous side effects of cocaine?
Increased body temperature, irregular heart rate, high blood pressure, and increased risk of heart attack.
What are common opioids?
Heroin, morphine, methadone, and codeine.
What is opioid use disorder (OUD)?
A substance use disorder related to opioid use that causes significant impairment or distress.
What are some withdrawal symptoms associated with opioids?
Nausea, muscle aches, diarrhea, trouble sleeping, agitation, and low mood.
What are sedative, hypnotic, or anxiolytic drugs used for?
They are used to induce sleep, relieve anxiety, and treat insomnia.
What is the role of methadone clinics?
They help individuals manage withdrawal symptoms from opioid addiction through the use of methadone.
What are common misconceptions about addiction?
Stereotypes include the belief that addiction is a choice or that individuals with substance use disorders lack willpower.
What is the significance of cultural factors in anorexia nervosa?
Cultural factors can influence the development and manifestation of anorexia nervosa, affecting perceptions of body image and eating behaviors.
Can you name five sleep-wake disorders?
Insomnia, narcolepsy, sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome, and circadian rhythm sleep disorder.
What are some common treatments for sleep-wake disorders?
Cognitive behavioral therapy, medication, lifestyle changes, and sleep hygiene education.
What is the difference between alcohol intoxication and alcohol withdrawal?
Intoxication involves behavioral or psychological changes after alcohol ingestion, while withdrawal includes symptoms following reduced alcohol use.
What is the purpose of affirmations in recovery?
Affirmations help reinforce self-worth and encourage positive thinking during the recovery process.
What are some potential challenges of cutting off contact with someone struggling with addiction?
It may lead to feelings of abandonment, increased isolation, and could hinder the recovery process.
What are hallucinogens?
A class of drugs that cause profound alterations in sensory and perceptual experiences.
What criteria did Leo Hollister propose for hallucinogens?
Changes in thought, perception, and mood should predominate; minimal intellectual impairment; no stupor or excessive stimulation; minimal autonomic side effects; and absence of addictive craving.
What are the effects of mescaline and LSD on the brain?
They act as serotonin agonists.
How do PCP and ketamine affect the NMDA glutamate receptor?
They act as antagonists.
What is hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD)?
A chronic disorder characterized by non-psychotic flashbacks of visual hallucinations from previous hallucinogenic experiences.
What is inhalant use disorder?
A problematic pattern of inhalant use leading to clinically significant impairment or distress.
What is cannabis, and what is its primary psychoactive component?
Cannabis, also known as marijuana, is a psychoactive drug, with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) as its main psychoactive component.

What is cannabis withdrawal?
Cessation of heavy and prolonged cannabis use leading to withdrawal symptoms.
What is cannabis use disorder?
A behavioral disorder resulting from chronic cannabis use, combining abuse and dependence.
What are the biological explanations for addiction?
Epigenetic genes and their products are key components through which environmental influences affect an individual's genes.
What psychodynamic factors may contribute to addiction?
Unconscious factors from the past that create a trauma response leading to negative coping through substances.
What is expectancy theory in the context of addiction?
A cognitive explanation suggesting that the anticipation of euphoric effects motivates substance use.
How does social learning theory relate to substance use?
It posits that modeling behaviors of substance users can initiate and promote addiction.
What are common treatment options for drug addiction?
Behavioral counseling, medication, medical devices for withdrawal symptoms, and long-term follow-up.
What is cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) used for in addiction treatment?
To help patients understand how their thought processes influence their behavior.
What is covert conditioning in addiction treatment?
An approach using principles of applied behavioral analysis or cognitive-behavior therapy to improve behavior.
What is the significance of self-help support groups in addiction recovery?
They are organized and managed by members with personal experience, providing mutual support.
What are the diagnostic features of alcohol use disorder?
Includes loss of control over drinking, tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms.
What are the effects of opioids on brain function?
They impact brain function by binding to opioid receptors, leading to pain relief and euphoria.
How do hallucinogens affect the brain?
They alter sensory perception and can lead to visual and auditory hallucinations.

What is the role of pharmacological approaches in treating substance use disorders?
To help manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings.
What are the risks associated with inhalant use?
Can lead to significant health issues including brain damage and sudden death.
What are the psychological theories explaining addiction?
Include biological, psychodynamic, cognitive, behavioral, and social learning theories.
What is the primary goal of addiction treatment?
To help individuals stop using drugs, stay drug-free, and become productive in society.
What is the impact of long-term alcohol use on the nervous system?
Can lead to neurological damage and contribute to the development of alcohol use disorder.
What are the common misconceptions about substance-related disorders?
They often differ from the realities presented in clinical research regarding causes and treatments.
What is the significance of long-term follow-up in addiction treatment?
To prevent relapse and support sustained recovery.
What are affirmations in the context of personal development?
Positive statements that reinforce self-belief and motivation, such as 'I do not give up, I find solutions.'
How do environmental and cultural factors influence substance use and addiction?
They shape individual behaviors and perceptions regarding substance use, impacting addiction rates.
What parallels exist between biopsychosocial factors contributing to substance-related disorders and sexual dysfunctions?
Both involve biological, psychological, and social influences that can affect behavior and health.
What is the difference between stimulants and opioids?
Stimulants increase alertness and energy, while opioids are primarily used for pain relief and can cause sedation.
Which statement is false regarding Sexual Deviations and Dysfunctions?
C. Sexual aversion disorder is classified as a type of sexual dysfunction characterized by recurrent, intense sexual urges, fantasies, or behaviors with non-human objects.
What is gender dysphoria?
A condition where individuals experience significant distress due to a marked incongruence between their expressed gender and assigned gender.
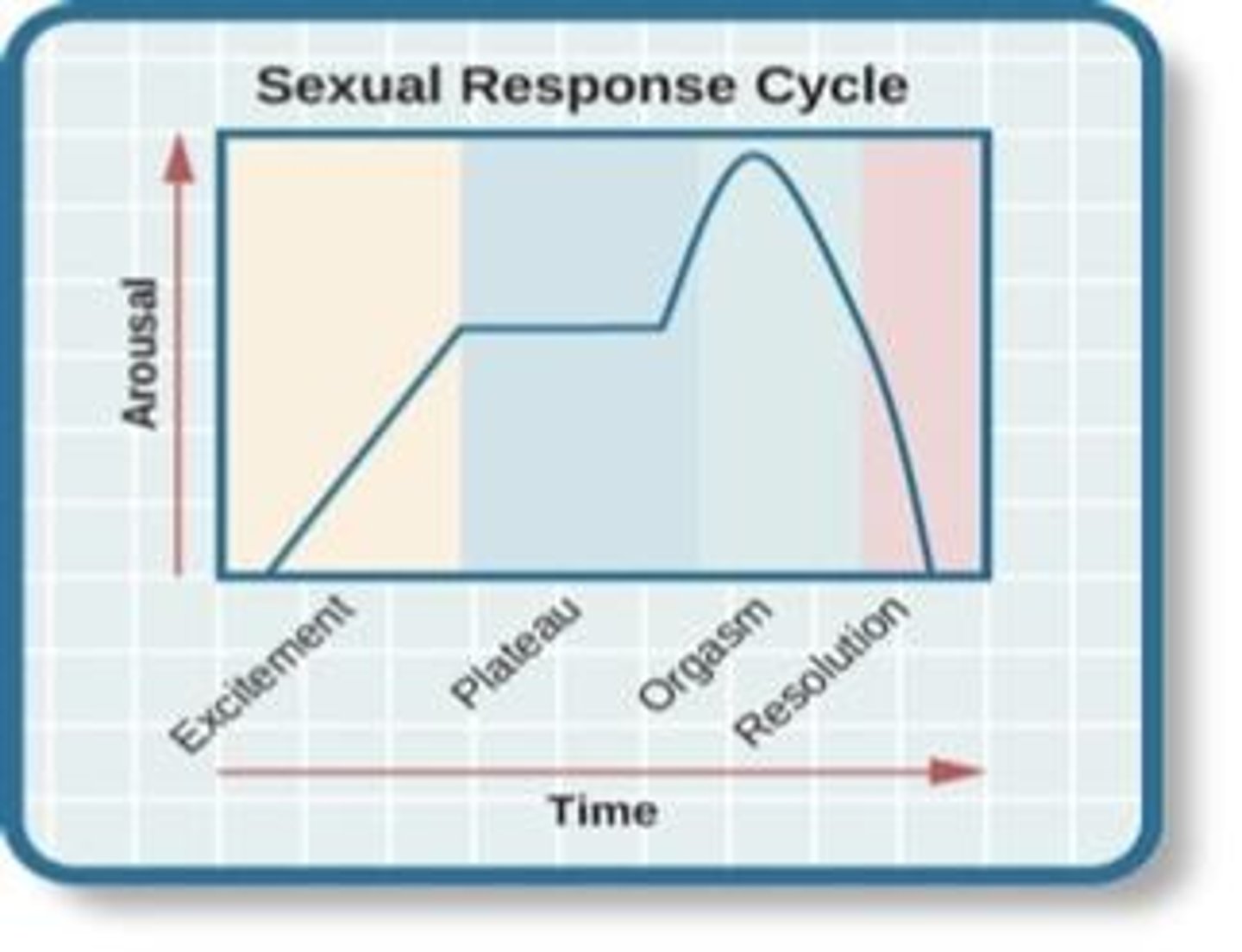
What are the phases of the human sexual response cycle according to Masters and Johnson?
Excitement, Plateau, Orgasm, Resolution, and Refractory period.
What occurs during the excitement phase of the sexual response cycle?
Arousal is marked by erection of the penis or clitoris and lubrication of the vaginal canal.
What happens during the orgasm phase of the sexual response cycle?
Marked by rhythmic contractions of the pelvis and uterus in women, along with increased muscle tension.
What is sexual orientation?
An enduring pattern of romantic or sexual attraction to persons of another sex or gender, the same sex or gender, or to both.
What does the term 'cisgender' refer to?
People whose sense of personal identity and gender corresponds with their sex assigned at birth.
What is the definition of genderfluid?
A gender identity that varies over time.
What is the difference between early-onset and late-onset gender dysphoria?
Early-onset is behaviorally visible in childhood, while late-onset does not show visible signs until later in life.
What does the term 'non-binary' mean?
A spectrum of gender identities that are not exclusively masculine or feminine.
What is the Oedipus complex?
A psychoanalytic theory suggesting sexual fantasies for the parent of the opposite gender and hatred for the parent of the same gender.
What is gender-affirming surgery?
Surgical procedures performed on a transgender person to change their sex characteristics to better reflect their gender identity.
What is bottom surgery?
Surgery to alter the genitalia of a transgender person.
What is top surgery?
Surgery to alter the chest and breast tissue of a transgender person.
What is the role of societal stigma in gender dysphoria?
People with gender dysphoria often suffer due to being stigmatized and victimized by society.
What is the significance of genetic variation in gender dysphoria?
It suggests evidence for the biological etiology of the symptoms associated with gender dysphoria.
What is the purpose of a transition for transgender individuals?
To take actions that help the external world recognize and reflect their internal gender.
What does the term 'gender non-conforming' mean?
Anyone whose appearance and behavior do not reflect the gender roles expected of them.
What is the importance of understanding variations in sexual orientation?
It helps in recognizing the diverse patterns of attraction and identity among individuals.
What is the refractory period in the sexual response cycle?
A period following orgasm during which an individual is incapable of experiencing another orgasm.
What are sexual desire disorders?
Characterized by a lack or absence of sexual desire or libido for sexual activity, including conditions like hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD).
What is erectile dysfunction?
A sexual dysfunction characterized by the inability to develop or maintain an erection of the penis.
What are orgasm disorders?
Include conditions such as delayed ejaculation, premature ejaculation (PE), anejaculation, retrograde ejaculation, and anorgasmia.
What defines premature ejaculation (PE)?
A prevalent sexual dysfunction in men characterized by ejaculation occurring around 1 minute or less of vaginal penetration, experienced in almost all occasions during partnered sexual activity.
What is female orgasm disorder?
A type of sexual dysfunction where a person cannot achieve orgasm despite adequate stimulation.
What are sexual pain disorders?
Affect women almost exclusively and include dyspareunia (painful intercourse) and vaginismus (involuntary muscle spasms that interfere with intercourse).
What is genito-pelvic pain/penetration disorder (GPPPD)?
A condition that encompasses both dyspareunia and vaginismus as female sexual dysfunctions.
What biological factors can lead to sexual dysfunctions?
Physical factors such as the use of drugs like alcohol, nicotine, narcotics, stimulants, antihypertensives, antihistamines, and some psychotherapeutic drugs.
What are the three categories of psychological factors associated with sexual dysfunction?
Predisposing factors, precipitating factors, and maintaining factors.
How do sociocultural factors affect sexual dysfunction?
Cultural and societal myths surrounding sex may contribute to the development of sexual dysfunctions.
What is cognitive sexual therapy (CST)?
A cognitive-behavioral integrative psychotherapy aimed specifically at addressing and treating sexual dysfunctions.
What are sexual scripts?
Ideas about how males and females are supposed to interact, including expected behaviors in sexual or romantic situations.
What is sensate focus in sex therapy?
A technique that refocuses participants on their own sensory perceptions and sensuality rather than goal-oriented behavior focused on penetrative sex.
What sexual dysfunction does Lisa's scenario represent?
Sexual desire disorder, characterized by a noticeable decrease in sexual interest and arousal.
What sexual dysfunction does Carlos's scenario represent?
Orgasm disorder, specifically difficulty in reaching orgasm despite adequate sexual stimulation.
What sexual dysfunction does Emma's scenario represent?
Sexual pain disorder, characterized by severe pain during intercourse and involuntary pelvic floor muscle spasms.
What is fetishism?
A paraphilia involving sexual attraction to non-living objects or specific body parts.
What is transvestic fetishism?
A paraphilia involving sexual arousal from cross-dressing.
What is exhibitionism?
A paraphilia characterized by the exposure of one's genitals to an unsuspecting person.
What is voyeurism?
A paraphilia involving sexual arousal from watching others engage in sexual activities without their knowledge.
What is frotteurism?
A paraphilia involving sexual arousal from touching or rubbing against a non-consenting person.
What is sexual sadism?
A paraphilia characterized by deriving pleasure from inflicting pain or humiliation on another person.
What is sexual masochism?
A paraphilia involving sexual arousal from being humiliated or made to suffer.
What is pedophilia?
A paraphilia characterized by sexual attraction to prepubescent children.
What are paraphilias?
Persistent and recurrent sexual interests, urges, fantasies, or behaviors involving atypical objects, activities, or situations.