MODULE 7
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Temporary Storage (ephemeral storage)
Added to your Amazon EC2 instance
What is Amazon EBS?
Persistent, mountable storage that can be mounted as a device to an Amazon EC2 Instance.
What can EBS be mounted to?
Mounted as a device to an Amazon EC2 instance
Only within the same Availability Zone
Only ________ Amazon EC2 instance can mount an Amazon EBS volume at a time
One
Amazon EFS…
Shared File System that multiple instances can mount at the same time
Amazon S3…
Persistent storage where each file becomes an object and is available through a URL (accessed anywhere)
Amazon S3 Glacier…
For cold storage for data that is not accessed frequently (long term data storage)
Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store)
Persistent block storage volumes for use with Amazon EC2 Instances
Persistent storage…
Data storage that RETAINS data after power to that device is shut off
Also known as non-volatile storage
Each EBS volume is…
Automatically replicated within AZ
Designed for high availability and durability
Made to provide the consistent and low-latency performance NEEDED
Scale up or down (latency + low price)
Block Storage
Change one block (piece of the file) that contains the character
Faster and less bandwidth
Object Storage
Entire File must be updated
More cost effective
Amazon EBS
Enables you to create individual storage volumes and attach them to an EC2
Characteristics of Amazon EBS
Offers block-level storage (durable, detachable storage)
Automatically replicated within an AZ
Backed up automatically to Amazon S3 through snapshots
Offer low latency
Amazon EBS Uses include:
Boot volumes and storage for Amazon EC2 instances
Data storage with a file system
Database hosts
Enterprise applications
What is a snapshot?
A backup of an Amazon EBS volume
First snapshot is called the baseline snapshot
Any other snapshot after the baseline shows only what is different from the previous
What is an AMI?
EBS Volumes included as part of the “backup” of your instances into an AMI
Stored in Amazon S3 and can be reused to create new Amazon EC2 instances
Two types of EBS Volumes
Solid State Drives (SSDs)
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
What is the same and what is different in terms of
Maximum Volume Size
Maximum IOPs Volume
Maximum Throughput Volume
For your SSDs and HDDs?
Max Vol is same
Max Iops: SSD > HDD
Max Throughput: SSD > HDD
Solid State Drives have 2 specific types:
General Purpose
Provisioned IOPs
Hard Disk Drives have 2 specific types:
Throughput-Optimized
Cold
Review slide 12
(Amazon EBS volume types)
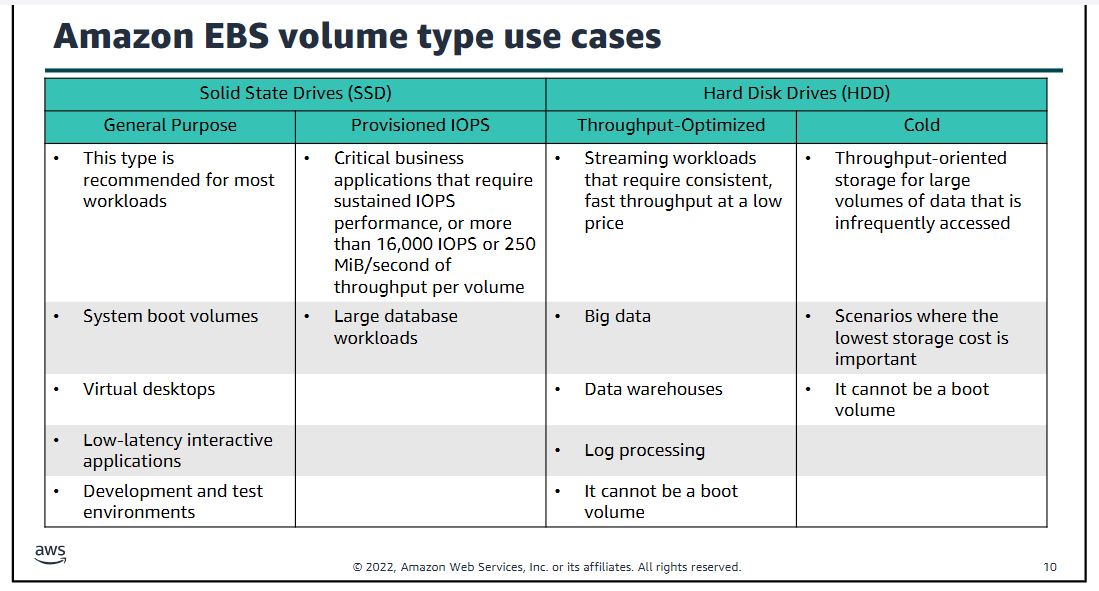
(Amazon EBS volume type use cases)
Amazon EBS Features (3 important features)
Snapshots
Encryption
Elasticity
Snapshots
Point-in-time snapshots
Recreate a new volume at any time
Sharing snapshots or even copying snapshots to different AWS Regions is known as what?
Disaster Recovery (DR) protection
Encryption
Encrypted Amazon EBS Volumes
No Additional Cost
Elasticity
Increase Capacity
Change to Different types (from Hard Drives to SSDs… from a 50 GB volume to a 16 TB volume)
4 things considered for Amazon EBS Cost Estimation
Volumes
IOPs
Snapshots
Data transfer
Pricing: Volumes →
Amazon EBS volumes persist independently from the instance
All volume types are charged by the amount that is provisioned per month
Pricing: IOPs →
General Purpose SSD
Magnetic
Provisioned IOPS SSD
General Purpose SSD
Charged by the amount that you provision in GB per month until storage is released
Magnetic
Charged by the number of requests to the volume
Provisioned IOPS SSD
Charged by the amount that you provision in IOPS (multiplied by the percentage of days that you provision for the month)
Pricing: Snapshot →
Added cost of Amazon EBS Snapshots to Amazon S3 is per GB-month of data stored
Pricing: Data Transfer →
Inbound data transfer is FREE
Outbound data transfer across Regions incurs charges
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3)
Object-level storage
Data is stored as objects in buckets
Virtually unlimited storage
Single object is limited to 5 TB
Designed for 11 9s of durability
Granular Access to bucket and objects using IAM
Data stored in Amazon S3 is ________ with any particular server, and you __________ manage any infrastructure yourself.
NOT associated
DO NOT need to
What else can Amazon S3 do?
Store almost any data file (images videos, even database snapshots) as objects
Provides low-latency (HTTP or HTTPS)
Retrieve data anytime from anywhere
Access S3 through a VPC
Event notifications
Analyze storage access patterns
Amazon S3 storage classes:
S3 Standard
S3 Intelligent Tiering
S3 Standard-Infrequent Access
S3 One-Zone-Infrequent Access
S3 Glacier
S3 Glacier Deep Archive
Amazon S3 Standard
Designed for high durability, availability, and performance object storage
Frequently Accessed Data
Low latency and high throughput
Use Cases:
Cloud applications, dynamic websites, content distribution, mobile and gaming applications and big data analytics
Amazon S3 Intelligent-Tiering
Designed to optimize costs by automatically moving data to the most cost-effective access tier
Moves object objects back and forth based on the access patterns of the user
No retrieval fees and no additional fees
Long-lived data with access patterns that are unknown or unpredictable
Amazon S3 Standard Infrequent Access (Amazon S3 Standard-IA)
Used for data that is accessed less frequently, but requires rapid access when needed
High durability, low latency
Low cost and high performance makes IA good for long-term storage and backups
Amazon S3 One Zone Infrequent Access (Amazon S3 One Zone-IA)
Used for data that is accessed less frequently, but requires rapid access when needed
Unliked other storage classes, which store data in a minimum of 3 AZs, it stores data in a single AZ
Costs less than Standard-IA
Amazon S3 Glacier
Secure, durable, low-cost storage class
Reliably store ANY amount of data at costs
Keep costs low using three retrieval options:
Upload objects directly to S3 Glacier
Use S3 lifecycle policies to transfer data between classes for active data and Amazon S3 Glacier
Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive
Lowest-cost Storage Class for Amazon S3
Supports long-term retention and digital preservation for data that might be accessed once or twice in a year
Used specifically for retention of datasets for 7-10 years
Cost-effective and easy-to-manage alternative
Provides 11 9s durability
Replicated and stored across at least 3 AZs and can be restored within 12 hours
What are buckets?
Amazon S3 stores data inside buckets
Must be uniquely named across all of Amazon S3 globally
Buckets are logical containers for objects, where you can have one or more in your account
Can create, delete, and list objects in the bucket
Can also view access logs for the bucket and its objects
Choose the geo region where Amazon S3 stores the bucket and its contents
Steps to upload your data:
Create a bucket in an AWS Region
Upload almost any number of objects to the bucket
Two styles of URL
Region Code → Amazon AWS → Bucket Name
Bucket Name → Region Cde → Amazon AWS
What happens to data that is stored in a bucket?
Buckets are associated with a specific AWS Region.
When you store data in the bucket, it is redundantly stored across multiple AWS facilities
S3 durably stores your data, and so even if there is concurrent data loss in two facilities, the data will still be stored.
How does Amazon S3 manage your storage?
Amazon S3 is designed for seamless scaling
Automatically manages the storage behind your bucket while your data grows
Scales to handle a high volume of reqests
Do not need to provisionthe storage
How can you access Amazon S3?
Console
CLI
SDK
You can also access data in your bucket through endpoints
Use Cases for Amazon S3:
Storing application assets
Static web hosting
Backup and disaster recovery (DR)
Staging area for big data
Etc.
Amazon S3 common scenarios:
Backup and storage
Provide data backup and storage services
Application Hosting
Provide services that deploy, install, and manage web applications
Media hosting
Hosts video, photo, music uploads
Software delivery
Host software applications that customers can download
Amazon S3 pricing
Pay only for what you use, including —
GBs per month
Transfer OUT to other regions
PUT, COPY, POST, LIST, and GET requests
What do you NOT pay for?
Transfers IN to Amazon S3
Transfer OUT from Amazon S3 to Cloudfront or Amazon EC2 in the same region (within region transfers)
(S3) Storage pricing requires you to consider the following:
Storage Class Type
Amount of Storage
Requests
Data Transfer
Storage Class Type
Standard Storage is designed for
11 9s of Durability
4 9s of Availability
S3 Standard-Infrequent Access (S-IA) is designed for
11 9s of Durability
3 9s of availability
Amount of Storage
Number and size of objects stored in your Amazon S3 Buckets
Requests
Number and type of requests (GET, PUT, COPY)
Type of requests:
Different rates for GET requests than other reqests
GET, PUT and COPY Requests
GET–Retrieves an object from Amazon S3. You must have READ access to use this operation.
PUT–Adds an object to a bucket. You must have WRITE permissions on a bucket to add an object to it.
COPY–Creates a copy of an object that is already stored in Amazon S3. A COPY operation is the same as performing a GET and then a PUT.
Data Transfer
Pricing is based on the amount of data that is transferred out of the Amazon S3 Region
Transfer in → Free
Transfer out → Incurred charges for data out
Amazon EFS (Elastic-File System)
Provides simple, scalable, elastic file storage for use with AWS services and on-premises resources
Simple interface to create and configure systems quickly and easily
Fully managed service that eliminates storage tasks
What is EFS built to do?
Dynamically scale on demand
Grow and shrink as you add and remove files
Designed to make sure you optimize storage
Amazon EFS Features
File storage in the AWS Cloud
Use Cases:
Big data and analytics, media processing workflows, content management, web serving, and home directories
Petabyte-scale, low-latency file system
Shared storage
Elastic capacity
NFS versions 4.0 and 4.1
Compatible with Linux AMIs for EC2
Amazon EFS Architecture
Provides file storage in the cloud (over a network)
Create file system, mount the file system on an EC2 instance
Read and write data from and to your file system
Access your EFS system from EC2 instances in your VPC
How and from where should Amazon EC2 instances access the file system?
Instances that run in multiple AZs within the same region can access the file system, so many users can access and share a common data source
Steps for Amazon EFS Implementation
Create your Amazon EC2 resources and launch your Amazon EC2 instance.
Create your Amazon EFS file system.
Create your mount targets in the appropriate subnets.
Connect your Amazon EC2 instances to the mount targets.
Verify/clean up the resources and protection of your AWS account.
The file system is considered the primary resource. Each file system has properties such as:
ID
Creation token
Creation time
File system size in bytes
Mount targets that are created
File system state
To configure the primary resource (file system), the resources can be used:
Mount Target - Access file system, created in VPC
Tags - Organize file system, assign metadata
Tags are a key-value pair
Properties of mount targets:
Subnet ID
Security groups
One or more per file system
Must be kept in the same VPC
Created in a VPC subnet
One per AZ
IP Address
Mount target state
Do mount targets and tags (subresources) exist unless they are associated with a file system?
No, they do NOT exist
Amazon S3 Glacier
Data archiving service that is designed for security, durability, and an extremely low cost
Characteristics of S3 Glacier
Designed to provide 11 9s of durability for objects
Supports encryption of data in transit and at rest (uses SSL or TLS)
Vault Lock Feature
Low-cost design works well for long-term archiving
Archive
Any object (photo, video, file) that you store in Amazon S3 Glacier
Base unit of storage in Glacier
Has its own unique ID and it could also have a description
Vault
Container for storing the archives
When you create a vault, you specify the vault name and the Region where you want to locate the vault
Vault Lock Feature + Vault Access Policy + Vault Lock Policy
Lock Feature enforces compliance through a policy →
Vault Access Policy
Determine who CAN and who CANNOT access the data that is stored in the vault (What operations users can and cannot perform)
Vault lock policy
To make sure a vault CANNOT be altered
Three options for access to archives:
Expedited (1-5 minutes → Highest Cost)
Standard (3-4 hours → In between option)
Bulk (5-12 hours → Lowest Cost)
Amazon S3 Glacier Use Cases
Media asset Archiving
Healthcare information archiving
Regulatory and compliance archiving
Scientific data archiving
Digital preservation
Magnetic Tape Replacement
How can you store and access data in Amazon S3 Glacier (what do you use)?
AWS Management Console (only a few operations — creating and managing vaults and policies — are available)
Everything else requires:
Amazon S3 Glacier REST APIs
AWS Java or .NET SDKs
AWS CLI
Lifecycle policies
Lifecycle policies
Enable you to delete or move objects based on AGE
Can cycle data at regular intervals between different Amazon S3 storage types
Reduces costs
Storage comparison → Slide 56
(understand the chart)
Amazon S3 Glacier is encrypted by default.
However, Amazon S3 must initiate _____ in order to encrypt.
Server-side encryption
What can server-side encryption do?
Employs strong multi-factor encryption
Enables you to set your own encryption keys
Combines secure, highly available hardware and software
Security with Amazon S3 Glacier:
Control access with IAM
Encrypts your data with AES-256
Manages your keys for you