Understanding Inflation: Causes and Effects
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Inflation
Increase in overall price levels of goods.
Deflation
Decrease in overall price levels of goods.
Inflation Rate
Average 3-5% over the past 80 years.
Money Supply (MS)
Controlled by the Fed; fixed quantity in circulation.
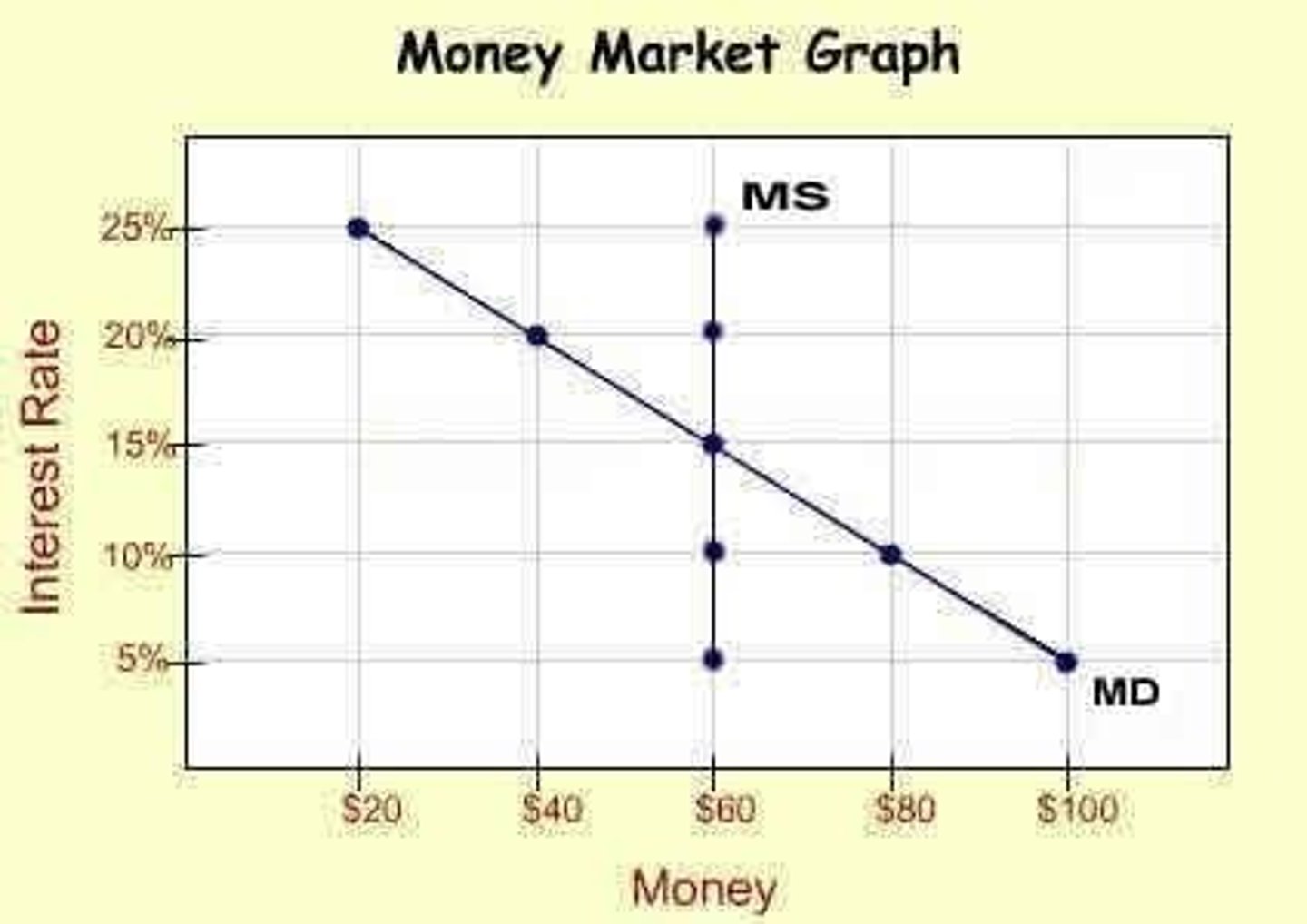
Demand for Money (MD)
Depends on personal preference and interest rates.
Monetary Equilibrium
Balance between money supply and demand.
Short-Run Effects
Interest rates influence money supply and demand.
Long-Run Effects
Prices adjust to equilibrium over several years.
Debtors
Borrowers who benefit from inflation.
Creditors
Lenders who lose value during inflation.
Real Interest Rate
Nominal interest rate adjusted for inflation.
Home Equity Loan
Loan based on the home's increased value.
Nominal Variables
Money and price levels without real impact.
Shoeleather Costs
Costs from frequent bank trips due to inflation.
Menu Costs
Costs of changing prices for businesses.
Relative Price Changes
Misinterpretation of price increases affects spending.
Demand-Pull Inflation
Caused by excessive demand for goods/services.
Cost-Push Inflation
Caused by rising production costs from suppliers.

Built-In Inflation
Inflation from wage demands to match rising prices.
Price Per Unit Cost (PUPC)
Total input cost divided by units of output.
Supply Shocks
Unexpected increases in production costs.
Home Value Appreciation
Increase in home value exceeding inflation rates.
Equilibrium Level
Point where money supplied equals money demanded.
Inflation's Costs
Negative impacts include confusion and resource misallocation.
Confusion and Inconvenience
Inflation distorts perceptions of value and earnings.
Economic Health Indicator
1-2% inflation signals a healthy economy.
Real Value
Actual purchasing power of money after inflation.
Homeowner Delight
Homeowners benefit from increased home equity.
Nominal Interest Rates
Interest rates not adjusted for inflation.